Publicaciones
Esta sección incluye una lista de los últimos artículos científicos del IPNA publicados en revistas incluidas en el Science Citation Index (SCI).
En DIGITAL.CSIC, repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos desde 1962, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc. del centro. El objetivo de DIGITAL.CSIC es organizar, preservar y difundir en acceso abierto los resultados de nuestra investigación.
En el repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc.
Análisis de la Producción Científica del IPNA 2014-2019: análisis bibliométrico realizado a partir de datos recogidos en Scopus y Web of Science.

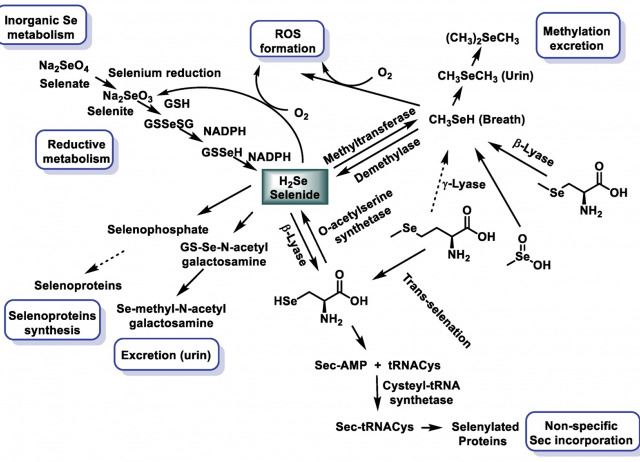
Selenium Nanoparticles in Critical Illness—Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Selenium (Se) has important anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, plays an important role in the immune system through redox balance, and is part of selenoproteins. In patients who are critically ill, Se supplementation causes alterations in inflammatory markers such as procalcitonin, leukocyte count, albumin, prealbumin, C-reactive protein (CRP), inflammatory cytokines, and cholesterol. The decrease in Se levels leads to a reduction in the levels of various selenoenzymes, in particular glutathione peroxidase and selenoprotein P. These antioxidant selenoproteins play a protective role against the lipoperoxidation of cell membranes and also participate in the process of regulating the inflammatory response. Currently, there are no conclusive data that allow us to affirm the existence of a significant reduction in mortality with the use of Se in intensive care. Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) can be used as dietary supplements or therapeutic agents due to their low toxicity and better bioavailability compared to traditional Se supplementation. In this review, we focus on the current state of research on SeNPs and their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties as a therapy for patients who are seriously ill, without the toxic effects of other Se species.
Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Bustamante Munguira, Elena; Andrés Juan, Celia; Pérez Lebeña, Eduardo.
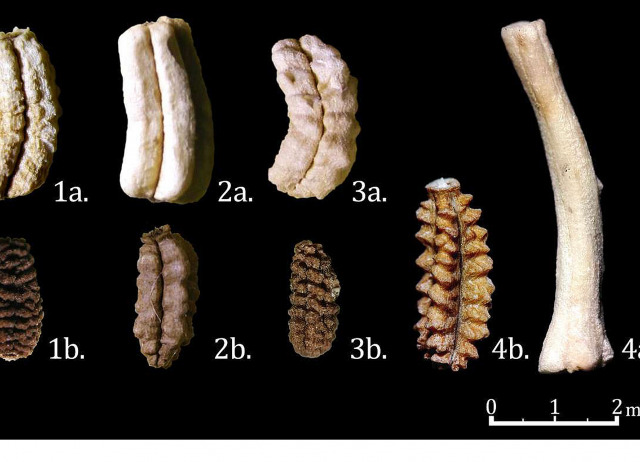
A new species of woodlouse (Isopoda, Oniscidea) from the Canarian laurel forest
A new species of terrestrial isopod, Porcellio aguerensis Orihuela-Rivero, sp. nov. of the family Porcellionidae (Oniscidea), is described from the laurel forest of Tenerife, Canary Islands. This new species belongs to the Atlantic group (“scaber”) as defined by Vandel due to the structure of the male pleopod 1 and its “primitive” glandular system. Some diagnostic characters that allow it to be differentiated from other species are revealed, such as (i) the smooth dorsal surface, (ii) the sinuosity of the posterior margin of the first pereonites, (iii) the configuration of the glandular system, and (iv) the structure of the male pleopod 1 exopod. The affinity of Porcellio aguerensis Orihuela-Rivero, sp. nov. with the morphologically closest members of the genus is discussed, both with continental and insular species, hypothesizing a relationship between the Canarian species of Porcellio and the “primitive” continental lineages of the genus. A key of the Porcellio species occurring in Tenerife is included. The conservation of Porcellio aguerensis Orihuela-Rivero, sp. nov. within a scenario of increasing dominance of invasive species is discussed.
Orihuela-Rivero, Raúl; Balibrea, Carmen; Noguerales, Víctor; López, Heriberto; Oromí, Pedro.
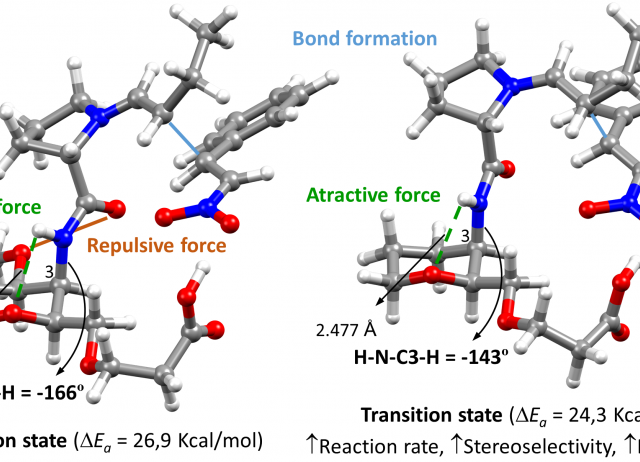
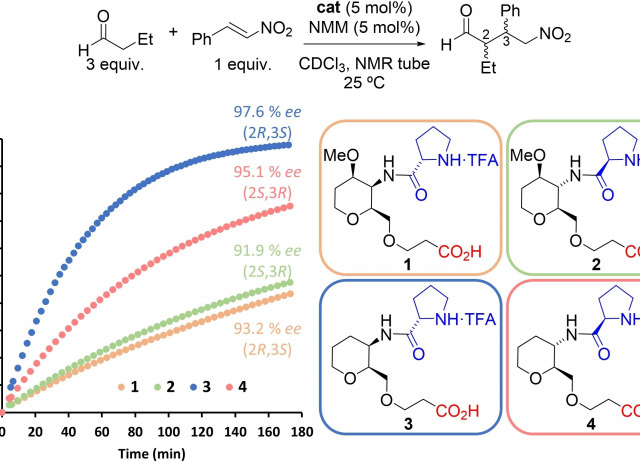
Disclosing the Intra-Catalyst Non-Covalent Interactions in Tetrahydropyran-Based Dipeptidic Catalysts
Herein, we describe how minor structural modifications to our bifunctional organocatalysts based on sugar amino acids (SAAs) can alter the network of non-covalent interactions (NCIs) within the catalyst, leading to significant changes in their catalytic activity. This is attributed to the intra-catalyst NCIs, which induce conformational changes that are reflected in the transition state of the rate-determining step of the Michael addition of aldehydes to trans-β-nitrostyrenes. Through kinetic experiments, conformational analysis, and DFT calculations, we found that the presence of a methoxy group at the C4 position of the tetrahydropyran ring reduces the catalytic activity by a factor of five compared to the catalyst without the methoxy group. Additionally, we have identified the different intra-catalyst NCIs, both attractive and repulsive, that drive the conformational changes, ultimately modifying the energy levels of the transition states of the rate- and enantioselectivity-determining step of the reaction.
Irma García-Monzón, Jorge Borges-González, Ezequiel Q. Morales, Israel Fernández, Tomás Martín.
Disclosing the Intra-Catalyst Non-Covalent Interactions in Tetrahydropyran-Based Dipeptidic Catalysts
Herein, we describe how minor structural modifications to our bifunctional organocatalysts based on sugar amino acids (SAAs) can alter the network of non-covalent interactions (NCIs) within the catalyst, leading to significant changes in their catalytic activity. This is attributed to the intra-catalyst NCIs, which induce conformational changes that are reflected in the transition state of the rate-determining step of the Michael addition of aldehydes to trans-β-nitrostyrenes. Through kinetic experiments, conformational analysis, and DFT calculations, we found that the presence of a methoxy group at the C4 position of the tetrahydropyran ring reduces the catalytic activity by a factor of five compared to the catalyst without the methoxy group. Additionally, we have identified the different intra-catalyst NCIs, both attractive and repulsive, that drive the conformational changes, ultimately modifying the energy levels of the transition states of the rate- and enantioselectivity-determining step of the reaction.
García-Monzón, Irma; Borges-González, Jorge; Quintana Morales, Ezequiel; Fernández, Israel; Martín, Tomás.
Dehydrothyrsiferol Against Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Treatment Outcome in a Murine Model
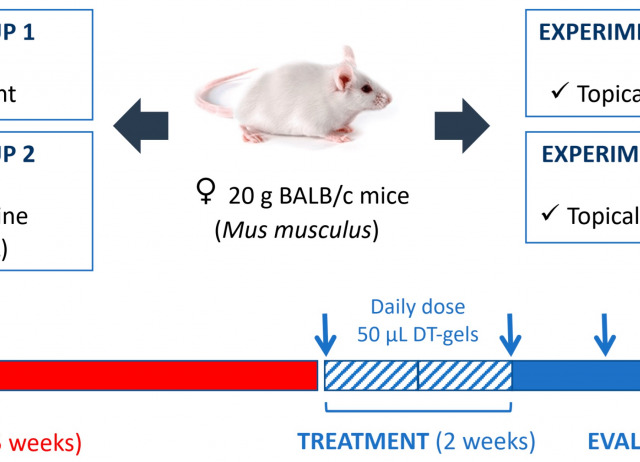
One of the most important steps in preclinical drug discovery is to demonstrate the in vivo efficacy of potential leishmanicidal compounds and good characteristics at the level of parasite killing prior to initiating human clinical trials. This paper describes the use of dehydrothyrsiferol (DT), isolated from the red alga Laurencia viridis, in a pharmaceutical form supported on Sepigel, and the in vivo efficacy against a mouse model of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Studying the ultrastructural effect of DT was also carried out to verify the suspected damage at the cellular level and determine the severity of damages produced in the homeostasis of promastigotes. BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania amazonensis were divided into four groups: untreated mice, mice treated with miltefosine orally and mice treated topically with 1% and 0.5% DT-Sepigel; treatment was carried out for two weeks. Treatment with DT significantly reduced the parasite load in skin, liver and spleen compared with the untreated group. In addition, DT-Sepigel at the lowest concentration (0.5%) showed the best results, reducing lesion size by 87% at 3 weeks post-treatment. DT-Sepigel has demonstrated to be a potent topical treatment that, in combined drug trials, may aim at combating cutaneous leishmaniasis.
López-Arencibia, Atteneri; Bethencourt-Estrella, Carlos J.; San Nicolás-Hernández, Desirée; Rodríguez-Expósito, Rubén L.; Domínguez-de-Barros, Angélica; Salazar-Villatoro, Lizbeth; Omaña-Molina, Maritza; Cen-Pacheco, Francisco; Díaz-Marrero, Ana Raquel; Fernández, José J.; Córdoba-Lanús, Elizabeth; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob; Piñero, José E.
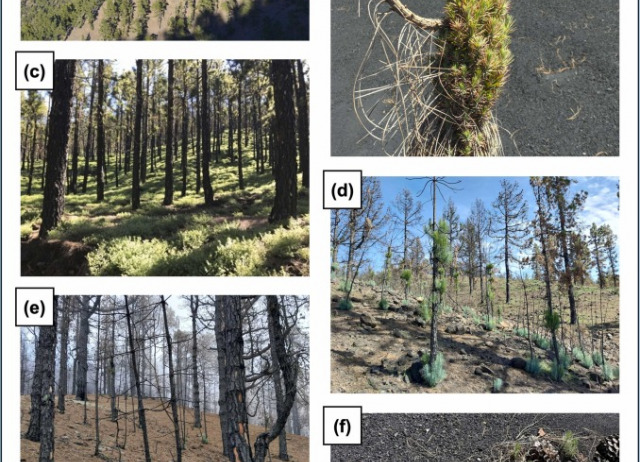
Volcanic eruption and wildfires as compounding drivers of first-year seedling establishment in Canary pine
On the island of La Palma, located in the Canary Islands, Spain, the Canary pine forest is largely unmanaged and depends on natural regeneration for sustainable population dynamics. Canary pine (Pinus canariensis C.Sm. ex DC.) has been continuously exposed to volcanic eruptions over evolutionary time scales. The species exhibits many adaptations to wildfires, but the current fire regime is likely not natural. While both volcanic eruptions and wildfires can devastate existing vegetation and unbalance ecosystems, they can also facilitate plant growth through mechanisms like nutrient release and increased light availability. Occasional successful regeneration events, driven by high first-year seedling establishment following a disturbance, could be essential to maintaining population structures. We investigated the interactions of volcanic eruption and past wildfires on first-year seedling establishment in the Canary pine forest after the 2021 Cumbre Vieja volcanic eruption. We combined in-situ seedling abundance data from 117 plots (5 m radius) with remote sensing to test the hypotheses that (1) the favorable conditions created by the eruption triggered a localized pulse in first-year seedling establishment of Canary pine and (2) seedling establishment was diminished in areas affected previously by wildfires (2012 and 2016). Using a two-part approach, consisting of univariate analysis of individual factors and multivariate analysis with generalized additive models, we find evidence consistent with our hypotheses. Plots located closer to the volcano and more heavily impacted by the eruption were significantly associated with higher seedling abundance (> 50 per plot). Furthermore, plots that had experienced prior burning in addition to volcanic impact showed lower seedling densities compared to plots impacted solely by the volcano. This suggests that fire history negatively influenced first-year seedling establishment following the eruption. We discuss the role of both wildfires and volcanic eruptions in the evolutionary history of Canary pine and highlight the task of disentangling the legacies of these two disturbances. Serotiny, traditionally considered to be a fire-specific adaptation, appears to also function after and increase the resilience of Canary pine to volcanic eruptions at the stand-level. Lastly, we raise the question of whether recurrent disturbances exceeding natural system dynamics could endanger the future demography of Canary pine by limiting infrequent but necessary forest regeneration events.
Wilkens, Vincent; Shatto, Christopher; Walentowitz, Anna; Weiser, Frank; Otto, Rüdiger; Guerrero-Campos, María; Jentsch, Anke; Medina, Félix M.; Marrero, Patricia; Nogales, Manuel; Vetaas, Ole R.; Beierkuhnlein, Carl.
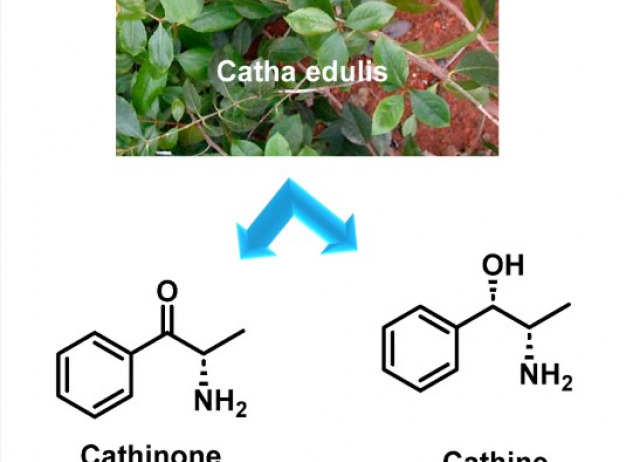
From Psychoactivity to Antimicrobial Agents: Multifaceted Applications of Synthetic Cathinones and Catha edulis Extracts
The emergence of new psychoactive substances (NPS) in the global drug market since the 2000s has posed major challenges for regulators and law enforcement agencies. Among these, synthetic cathinones have gained prominence due to their stimulant effects on the central nervous system, leading to widespread recreational use. These compounds, often marketed as alternatives to illicit stimulants such as amphetamines and cocaine, have been linked to numerous cases of intoxication, addiction and death. The structural diversity and enantiomeric forms of synthetic cathinones further complicate their detection and regulation and pose challenges to forensic toxicology. In addition to their psychoactive and toxicological effects, new research suggests that cathinones may have antimicrobial properties. Compounds derived from Catha edulis (khat), including cathinone, have shown antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, highlighting their potential role in the fight against antibiotic resistance. This article provides an overview of the chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicological effects and potential antimicrobial applications of synthetic cathinones. The potential therapeutic use of cathinone-derived compounds to combat antimicrobial resistance represents an exciting new frontier in drug development, although further research is needed to balance these benefits with the psychoactive risks.
Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Bustamante Munguira, Elena; Andrés Juan, Celia; Pérez-Lebeña, Eduardo.
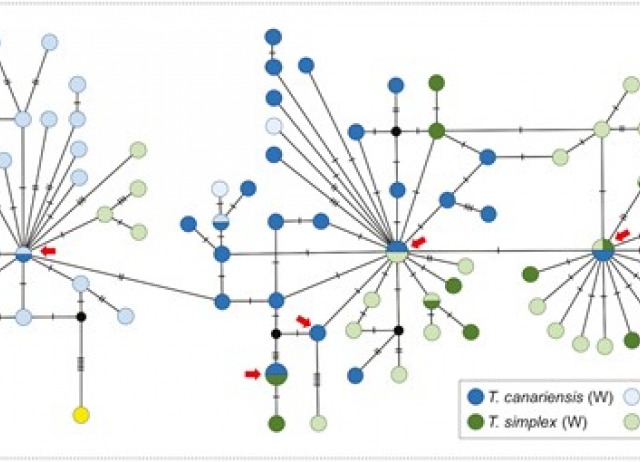
Arthropod mtDNA paraphyly: a case study of introgressive origin
Mitochondrial paraphyly between arthropod species is not uncommon and has been speculated to largely be the result of incomplete lineage sorting (ILS) of ancestral variation within the common ancestor of both species, with hybridization playing only a minor role. However, in the absence of comparable nuclear genetic data, the relative roles of ILS and hybridization in explaining mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) paraphyly remain unclear. Hybridization itself is a multifaceted gateway to mtDNA paraphyly, which may lead to paraphyly across both the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes, or paraphyly that is largely restricted to the mitochondrial genome. These different outcomes will depend upon the frequency of hybridization, its demographic context, and the extent to which mtDNA is subject to direct selection, indirect selection, or neutral processes. Here, we describe extensive mtDNA paraphyly between two species of iron-clad beetle (Zopheridae) and evaluate competing explanations for its origin. We first test between hypotheses of ILS and hybridization, revealing strong nuclear genetic differentiation between species, but with the complete replacement of Tarphius simplex mtDNA through the introgression of at least 5 mtDNA haplotypes from T. canariensis. We then contrast explanations of direct selection, indirect selection, or genetic drift for observed patterns of mtDNA introgression. Our results highlight how introgression can lead to complex patterns of mtDNA paraphyly across arthropod species, while simultaneously revealing the challenges for understanding the selective or neutral drivers that underpin such patterns.
Noguerales, Víctor; Emerson, Brent C.
Taxonomic assessment and historical context of Reichardia intermedia (Asteraceae) in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands harbor four species of the genus Reichardia according to the current knowledge. Three of them are endemic to the archipelago, one is widespread but probably also native. The discovery of a putative population of R. intermedia on La Gomera as a fifth Reichardia species triggered the revisiting of neglected historical occurrence reports of Reichardia for the Canarian archipelago. We combined phylogenetic and morphological evidence to confirm the identity of the newly discovered population and assessed the previous reports for the archipelago. Based on these findings, we confirm the presence of R. intermedia in the Canary Islands.
Sicilia-Pasos, Guillermo; Arjona, Yuren; Padrón-Mederos, Miguel A.; Reyes-Betancort, J. Alfredo; García, Ángel; Jay-García, Louis S.; Tuero-Septién, Javier; Patiño, Jairo.
Climb forest, climb: diverse disperser communities are key to assist plants tracking climate change on altitudinal gradients
- Climate change is forcing species to shift their distribution ranges. Animal seed dispersers might be particularly important in assisting plants tracking suitable climates to higher elevations. However, this role is still poorly understood due to a lack of comprehensive multi-guild datasets along elevational gradients.
- We compiled seed dispersal networks for the five altitudinal vegetation belts of the Tenerife Island (0–3718 m above sea level) to explore how plant and animal species might facilitate the mutual colonisation of uphill habitats under climate change.
- The overall network comprised 283 distinct interactions between 73 plant and 27 animal species, with seed dispersers offering viable pathways for plants to colonise upper vegetation belts. A pivotal role is played by a lizard as island-level hub, while four birds and one introduced mammal (rabbit) are also important connectors between belts. Eleven plant species were empirically found to be actively dispersed to elevations beyond their current known range, with observed vertical dispersal distances largely surpassing those required to escape climate change. Furthermore, over half of the plants arriving at higher elevations were exotic.
- Functionally diverse disperser communities are crucial for enabling plants tracking climate change on mountains, but exotic plants might particularly benefit from this upward lift.
Mendes, Sara Beatriz; Nogales, Manuel; Vargas, Pablo; Olesen, Jens M.; Marrero, Patricia; Romero, Javier; Rumeu, Beatriz; González-Castro, Aarón; Heleno, Ruben.