Publicaciones
Esta sección incluye una lista de los últimos artículos científicos del IPNA publicados en revistas incluidas en el Science Citation Index (SCI).
En DIGITAL.CSIC, repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos desde 1962, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc. del centro. El objetivo de DIGITAL.CSIC es organizar, preservar y difundir en acceso abierto los resultados de nuestra investigación.
En el repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc.
Análisis de la Producción Científica del IPNA 2014-2019: análisis bibliométrico realizado a partir de datos recogidos en Scopus y Web of Science.

Facilitated Adaptation as A Conservation Tool in the Present Climate Change Context: A Methodological Guide
Climate change poses a novel threat to biodiversity that urgently requires the development of adequate conservation strategies. Living organisms respond to environmental change by migrating to locations where their ecological niche is preserved or by adapting to the new environment. While the first response has been used to develop, discuss and implement the strategy of assisted migration, facilitated adaptation is only beginning to be considered as a potential approach. Here, we present a review of the conceptual framework for facilitated adaptation, integrating advances and methodologies from different disciplines. Briefly, facilitated adaptation involves a population reinforcement that introduces beneficial alleles to enable the evolutionary adaptation of a focal population to pressing environmental conditions. To this purpose, we propose two methodological approaches. The first one (called pre-existing adaptation approach) is based on using pre-adapted genotypes existing in the focal population, in other populations, or even in closely related species. The second approach (called de novo adaptation approach) aims to generate new pre-adapted genotypes from the diversity present in the species through artificial selection. For each approach, we present a stage-by-stage procedure, with some techniques that can be used for its implementation. The associated risks and difficulties of each approach are also discussed.
Torres, Elena; García-Fernández, Alfredo; Iñigo, Diana; Lara-Romero, Carlos; Morente-López, Javier; Prieto-Benítez, Samuel; Rubio Teso, María Luisa; Iriondo, José M.
Introduced rabbits as seed‑dispersing frugivores: a study case on a environmentally diverse oceanic island (Tenerife, Canaries)
Rabbits have travelled with humans to the most remote archipelagos, having been introduced on at least 800 islands worldwide. This herbivore has caused a devastating effect on endemic insular plants, causing changes in species composition, cascading extinctions and disruption of native seed dispersal systems worldwide. However, its ecological impacts as disrupting native seed dispersal systems have not been studied from a holistic perspective in any of the archipelagos where rabbits were introduced. Here, we assess the role of rabbits as frugivores and seed-dispersers on the most extensive and diverse island of the Canary Archipelago, Tenerife, across its five main vegetation zones represented in an altitudinal gradient 0–3715 m a.s.l. To this end, 120 transects per vegetation zone were conducted (August 2020–November 2021) to collect fresh faecal samples from a total of 244 latrines. They consisted of 29,538 droppings in which we found seeds from 73 plant species, 29 of which were identified to species level (13 endemic, eight natives and eight introduced by humans). About 70% of the seeds were identified as fleshy-fruited plant species while the remaining nine were dry fruits. Of the former, only nine showed a percentage of intact seeds greater than 75%, another nine species between 50 and 75%, and three lower than 50%. The digestive effect of rabbits on seedling emergence was generally low, compared to that produced by native seed dispersers. Since fleshy-fruited plants and rabbits have not been linked in their evolutionary history in the Canaries, the former seems to have their own legitimate seed dispersers.
Guerrero-Campos, María; Beatriz Mendes, Sara; Marrero, Patricia; Romero, Javier; Nieves, Concepción; Hervías-Parejo, Sandra; González-Mancebo, Juana María; Nogales, Manuel.
Evolutionary genomics of oceanic island radiations
A recurring feature of oceanic archipelagos is the presence of adaptive radiations that generate endemic, species-rich clades that can offer outstanding insight into the links between ecology and evolution. Recent developments in evolutionary genomics have contributed towards solving long-standing questions at this interface. Using a comprehensive literature search, we identify studies spanning 19 oceanic archipelagos and 110 putative adaptive radiations, but find that most of these radiations have not yet been investigated from an evolutionary genomics perspective. Our review reveals different gaps in knowledge related to the lack of implementation of genomic approaches, as well as undersampled taxonomic and geographic areas. Filling those gaps with the required data will help to deepen our understanding of adaptation, speciation, and other evolutionary processes.
Cerca, José; Cotoras, Darko D.; Bieker, Vanessa C.; De-Kayne, Rishi; Vargas, Pablo; Fernández-Mazuecos, Mario; López-Delgado, Julia; White, Oliver; Stervander, Martin; Geneva, Anthony J.; Guevara Andino, Juan Ernesto; Meier, Joana Isabel; Roeble, Lizzie; Brée, Baptiste; Patiño, Jairo; Guayasamin, Juan M.; Torres, María de Lourdes; Valdebenito, Hugo; Castañeda María del Rosario; Chaves, Jaime A.; Jaramillo Díaz, Patricia; Valente, Luis; Knope, Matthew L.; Price, Jonathan P.; Rieseberg, Loren H.; Baldwin, Bruce G.; Emerson, Brent C.; Rivas-Torres, Gonzalo; Gillespie, Rosemary; Martin, Michael D.
Patterns and drivers of beta diversity across geographic scales and lineages in the Macaronesian flora
Aim: How spatial, historical and ecological processes drive diversity patterns remains one of the main foci of island biogeography. We determined how beta diversity varies across spatial scales and among organisms, disentangled the drivers of this variation, and examined how, consequently, biogeographic affinities within and among archipelagos vary among land plants.
Mouton, Lea; Patiño, Jairo; Carine, Mark; Rumsey, Fred; Menezes de Sequeira, Miguel; González-Mancebo, Juana María; de Almeida Gabriel, Rosalina Maria; Hardy, Olivier J.; Sim-Sim, Manuela; Reyes-Betancort, J. Alfredo; Collart, Flavien; Vanderpoorten, Alain.
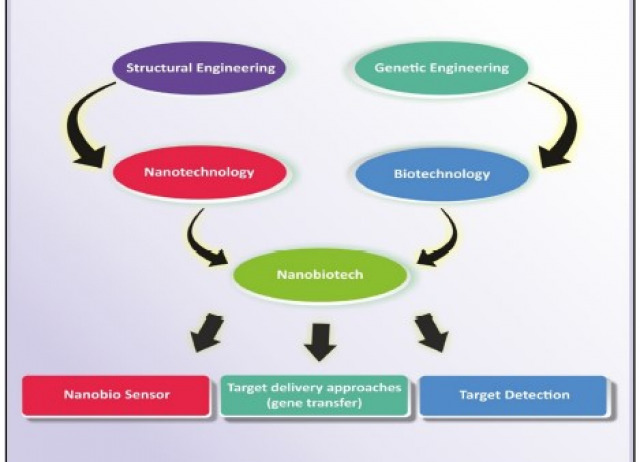
Nano-biotechnology in tumour and cancerous disease: A perspective review
In recent years, drug manufacturers and researchers have begun to consider the nanobiotechnology approach to improve the drug delivery system for tumour and cancer diseases. In this article, we review current strategies to improve tumour and cancer drug delivery, which mainly focuses on sustaining biocompatibility, biodistribution, and active targeting. The conventional therapy using cornerstone drugs such as fludarabine, cisplatin etoposide, and paclitaxel has its own challenges especially not being able to discriminate between tumour versus normal cells which eventually led to toxicity and side effects in the patients. In contrast to the conventional approach, nanoparticle-based drug delivery provides target-specific delivery and controlled release of the drug, which provides a better therapeutic window for treatment options by focusing on the eradication of diseased cells via active targeting and sparing normal cells via passive targeting. Additionally, treatment of tumours associated with the brain is hampered by the impermeability of the blood–brain barriers to the drugs, which eventually led to poor survival in the patients. Nanoparticle-based therapy offers superior delivery of drugs to the target by breaching the blood–brain barriers. Herein, we provide an overview of the properties of nanoparticles that are crucial for nanotechnology applications. We address the potential future applications of nanobiotechnology targeting specific or desired areas. In particular, the use of nanomaterials, biostructures, and drug delivery methods for the targeted treatment of tumours and cancer are explored.
Soni, Ambikesh; Bhandari, Manohar Prasad; Tripathi, Gagan Kant; Bundela, Priyavand; Khiriya, Pradeep Kumar; Khare, Purnima Swarup; Kashyap, Manoj Kumar; Dey, Abhijit; Vellingiri, Balachandar; Sundaramurthy, Suresh; Suresh, Arisutha; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
How genomics can help biodiversity conservation
The availability of public genomic resources can greatly assist biodiversity assessment, conservation, and restoration efforts by providing evidence for scientifically informed management decisions. Here we survey the main approaches and applications in biodiversity and conservation genomics, considering practical factors, such as cost, time, prerequisite skills, and current shortcomings of applications. Most approaches perform best in combination with reference genomes from the target species or closely related species. We review case studies to illustrate how reference genomes can facilitate biodiversity research and conservation across the tree of life. We conclude that the time is ripe to view reference genomes as fundamental resources and to integrate their use as a best practice in conservation genomics.
Theissinger, Kathrin; Fernandes, Carlos; Formenti, Giulio; Bista, Iliana; Berg, Paul R.; Bleidorn, Christoph; Bombarely, Aureliano; Crottini, Angelica; Gallo, Guido R.; Godoy, José A.; Jentoft, Sissel; Malukiewicz, Joanna; Mouton, Alice; Oomen, Rebekah A.; Paez, Sadye; Palsbøll, Per J.; Pampoulie, Christophe; Ruiz-López, María J.; Secomandi, Simona; Svardal, Hannes; Theofanopoulou, Constantina; de Vries, Jan; Waldvogel, Ann-Marie; Zhang, Guojie; Jarvis, Erich D.; Bálint, Miklós; Ciofi, Claudio; Waterhouse, Robert M.; Mazzoni, Camila J.; Höglund, Jacob; Arribas, Paula; The European Reference Genome Atlas Consortium.
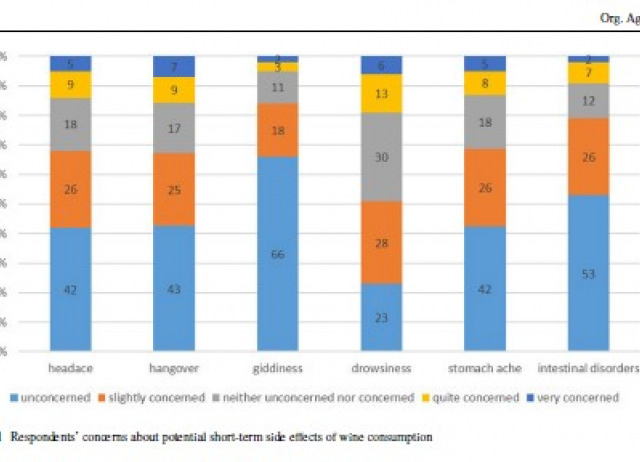
Drivers of consumer willingness to pay for sustainable wines: natural, biodynamic, and organic
This study analysed consumers’ willingness to pay (WTP) for wines with different sustainability features, namely natural, biodynamic, and organic, and explored the drivers of individual preferences for these wines. An online survey was conducted with a sample of 501 Italian regular wine consumers. To elicit WTP for natural, organic, and biodynamic wines, a multiple price list (MPL) was applied. The drivers of consumers’ preferences for the three wines were then investigated by means of a seemingly unrelated regression model (SUR). Results reveal a higher WTP for organic, followed by natural and biodynamic wines. The same core drivers of individual preferences were revealed for the three wine types: wine drinking frequency, naturalness perception, and wine health concerns. Wineries interested in commercialising sustainable wines should develop targeted communication campaigns to increase consumer awareness and understanding of the different sustainable production methods.
Vecchio, Riccardo; Annunziata, Azzurra; Parga-Dans, Eva; Alonso-González, Pablo.
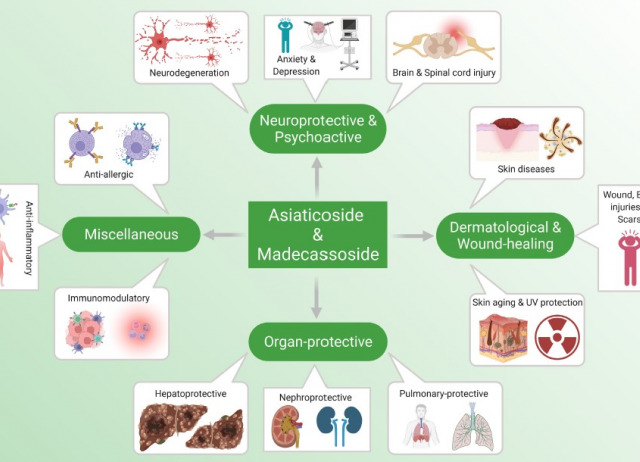
Therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities of asiaticoside and madecassoside: A review
Centella asiatica is an ethnomedicinal herbaceous species that grows abundantly in tropical and sub-tropical regions of China, India, South-Eastern Asia and Africa. It is a popular nutraceutical that is employed in various forms of clinical and cosmetic treatments. C. asiatica extracts are reported widely in Ayurvedic and Chinese traditional medicine to boost memory, prevent cognitive deficits and improve brain functions. The major bioactive constituents of C. asiatica are the pentacyclic triterpenoid glycosides, asiaticoside and madecassoside, and their corresponding aglycones, asiatic acid and madecassic acid. Asiaticoside and madecassoside have been identified as the marker compounds of C. asiatica in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and these triterpene compounds offer a wide range of pharmacological properties, including neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, wound healing, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-allergic, anti-depressant, anxiolytic, antifibrotic, antibacterial, anti-arthritic, anti-tumour and immunomodulatory activities. Asiaticoside and madecassoside are also used extensively in treating skin abnormalities, burn injuries, ischaemia, ulcers, asthma, lupus, psoriasis and scleroderma. Besides medicinal applications, these phytocompounds are considered cosmetically beneficial for their role in anti-ageing, skin hydration, collagen synthesis, UV protection and curing scars. Existing reports and experimental studies on these compounds between 2005 and 2022 have been selectively reviewed in this article to provide a comprehensive overview of the numerous therapeutic advantages of asiaticoside and madecassoside and their potential roles in the medical future.
Bandopadhyay, Shinjini; Mandal, Sujata; Ghorai, Mimosa; Kumar Jha, Niraj; Kumar, Manoj; Radha; Ghosh, Arabinda; Proćków, Jarosław; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Dey, Abhijit.
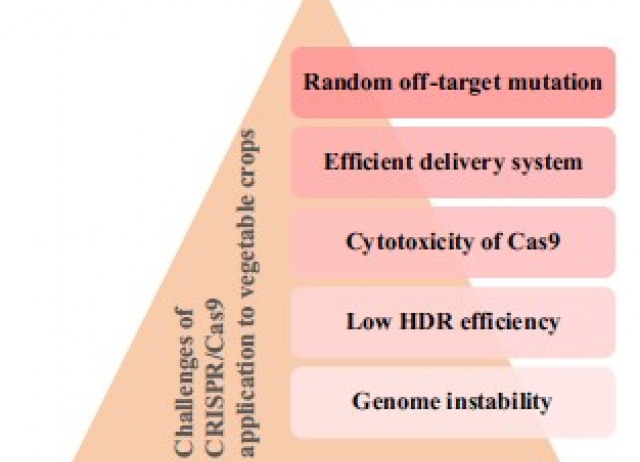
Exploring the potential of CRISPR/Cas genome editing for vegetable crop improvement: An overview of challenges and approaches
Vegetables provide many nutrients in the form of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which make them an important part of our diet. Numerous biotic and abiotic stresses can affect crop growth, quality, and yield. Traditional and modern breeding strategies to improve plant traits are slow and resource intensive. Therefore, it is necessary to find new approaches for crop improvement. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR associated 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) is a genome editing tool that can be used to modify targeted genes for desirable traits with greater efficiency and accuracy. By using CRISPR/Cas9 editing to precisely mutate key genes, it is possible to rapidly generate new germplasm resources for the promotion of important agronomic traits. This is made possible by the availability of whole genome sequencing data and information on the function of genes responsible for important traits. In addition, CRISPR/Cas9 systems have revolutionized agriculture, making genome editing more versatile. Currently, genome editing of vegetable crops is limited to a few vegetable varieties (tomato, sweet potato, potato, carrot, squash, eggplant, etc.) due to lack of regeneration protocols and sufficient genome sequencing data. In this article, we summarize recent studies on the application of CRISPR/Cas9 in improving vegetable trait development and the potential for future improvement.
Das, Tuyelee; Anand, Uttpal; Pal, Tarun; Mandal, Sayanti; Kumar, Manoj; Radha; Gopalakrishnan, Abilash Valsala; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel CSIC; Dey, Abhijit.
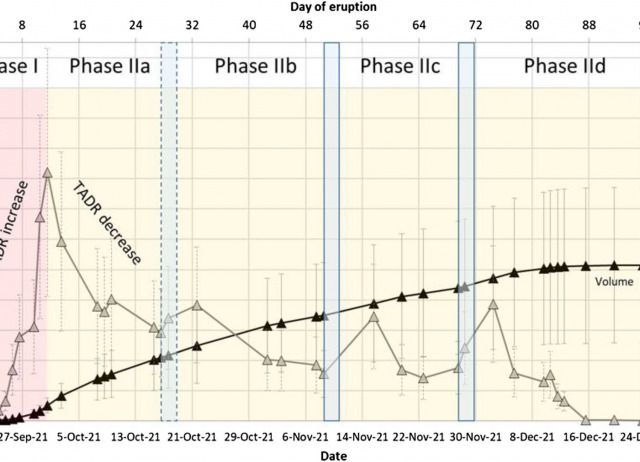
Combining thermal, tri-stereo optical and bi-static InSAR satellite imagery for lava volume estimates: the 2021 Cumbre Vieja eruption, La Palma
Determining outline, volume and effusion rate during an effusive volcanic eruption is crucial as it is a major controlling factor of the lava flow lengths, the prospective duration and hence the associated hazards. We present for the first time a multi-sensor thermal-and-topographic satellite data analysis for estimating lava effusion rates and volume. At the 2021 lava field of Cumbre Vieja, La Palma, we combine VIIRS + MODIS thermal data-based effusion rate estimates with DSMs analysis derived from optical tri-stereo Pléiades and TanDEM-X bi-static SAR-data. This multi-sensor-approach allows to overcome limitations of single-methodology-studies and to achieve both, high-frequent observation of the relative short-term effusion rate trends and precise total volume estimates. We find a final subaerial-lava volume of 212×106±13×106m3 with a MOR of 28.8 ± 1.4 m3/s. We identify an initially sharp eruption-rate-peak, followed by a gradually decreasing trend, interrupted by two short-lived-peaks in mid/end November. High eruption rate accompanied by weak seismicity was observed during the early stages of the eruption, while during later stage the lava effusion trend coincides with seismicity. This article demonstrates the geophysical monitoring of eruption rate fluctuations, that allows to speculate about changes of an underlying pathway during the 2021 Cumbre Vieja eruption.
Plank, Simon; Shevchenko, Alina V.; d’Angelo, Pablo; Gstaiger, Veronika; González, Pablo J.; Cesca, Simone; Martinis, Sandro; Walter, Thomas R.