Publicaciones
Esta sección incluye una lista de los últimos artículos científicos del IPNA publicados en revistas incluidas en el Science Citation Index (SCI).
En DIGITAL.CSIC, repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos desde 1962, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc. del centro. El objetivo de DIGITAL.CSIC es organizar, preservar y difundir en acceso abierto los resultados de nuestra investigación.
En el repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc.
Análisis de la Producción Científica del IPNA 2014-2019: análisis bibliométrico realizado a partir de datos recogidos en Scopus y Web of Science.

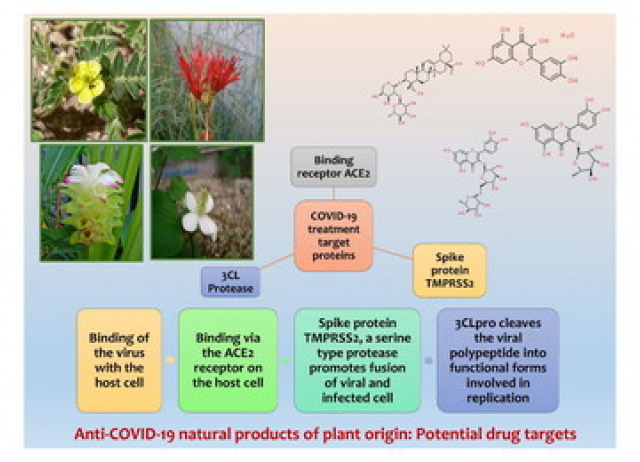
Harnessing and bioprospecting botanical-based herbal medicines against potential drug targets for COVID-19: a review coupled molecular docking studies
Since the end of February 2020, the world has come to a standstill due to the virus SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). Since then, the global scientific community has explored various remedies and treatments against this virus, including natural products that have always been a choice because of their many benefits. Various known phytochemicals are well documented for their antiviral properties. Research is being carried out to discover new natural plant products or existing ones as a treatment measure for this disease. The three important targets in this regard are—papain like protease (PLpro), spike protein, and 3 chymotrypsin like proteases (3CLpro). Various docking studies are also being elucidated to identify the phytochemicals that modulate crucial proteins of the virus. The paper is simultaneously a comprehensive review that covers recent advances in the domain of the effect of various botanically derived natural products as an alternative treatment approach against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, the docking analyses revealed that rutin (inhibitor of the major protease of SARS-CoV-2), gallocatechin (e.g., interacting with 03 hydrogen bonds with a spike-like protein), lycorine (showing the best binding affinity with amino acids GLN498, THR500 and GLY446 of the spike-like protein), and quercetrin (inhabiting at its residues ASP216, PHE219, and ILE259) are promising inhibitors of SARS‑CoV‑2.
Pal, Tarun; Anand, Uttpal; Mitrab, Shreya Sikdar; Biswasb, Protha; Tripathic, Vijay; Proćkówd, Jarosław; Deyb, Abhijit; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
Consumption of the lichen Roccella Gracilis by the large ground-finch Geospiza Magnirostris on the island of Daphne Major (Galápagos)
This note reports a trophic interaction of a passerine consuming lichens. On the islet of Daphne Major (Galápagos Archipelago), we made five observations of the Large Ground-Finch Geospiza magnirostris eating the fruticose lichen Roccella gracilis. This is an example of how island birds broaden their feeding niche in resource-poor environments.
Manuel Nogales, Sandra Hervías-Parejo.
Spatial ecology to strengthen invasive snake management on islands
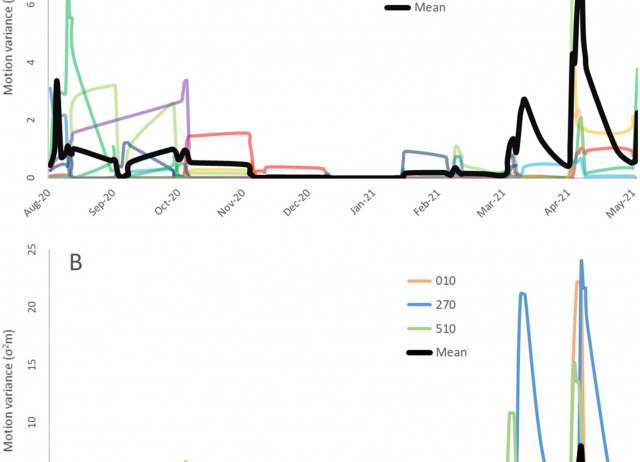
Knowledge on the spatial ecology of invasive predators positively contributes to optimizing their management, especially when involving cryptic and secretive species, such as snakes. However, this information is lacking for most invasive snakes, particularly on islands, where they are known to cause severe ecological and socio-economic impacts. This research is focused on assessing the spatial ecology of the California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) on Gran Canaria to strengthen management actions. We monitored 15 radio-tagged individuals once per day on 9–11 days per month from July 2020 to June 2021 to calculate the species' home range and describe annual activity patterns in the invaded range. To account for the species' diel activity during the emergence period, we additionally monitored snakes from January to May 2021 during three consecutive days per month in four different time intervals each day. We detected movement (consecutive detections at least 6 m apart) in 31.68% of the 1146 detections during the whole monitoring period. Movements most frequently detected were shorter than 100 m (82.24%), and among them the range 0–20 m was the most recurrent (27.03%). The mean distance of movement was 62.57 ± 62.62 m in 1–2 days. Average home range was 4.27 ± 5.35 ha—calculated with the Autocorrelated Kernel Density Estimator (AKDE) at 95%—and did not significantly vary with SVL nor sex. We detected an extremely low value of motion variance (0.76 ± 2.62 σ2m) compared to other studies, with a general inactivity period from November to February, January being the less active month of the year. Diel activity was higher during central and evening hours than during early morning and night. Our results should be useful to improve control programs for this invasive snake (e.g., trap placement and visual survey guidance) on Gran Canaria. Our research highlights the importance of gathering spatial information on invasive snakes to enhance control actions, which can contribute to the management of secretive invasive snakes worldwide.
Maestresalas, Borja; Piquet, Julien C.; López-Darias, Marta.
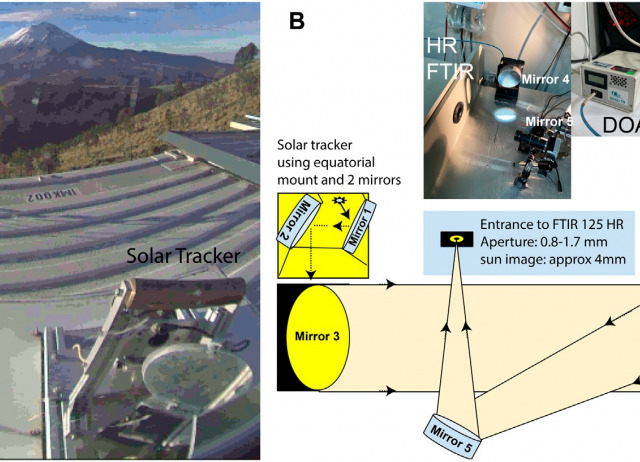
Combined direct-sun ultraviolet and infrared spectroscopies at Popocatépetl volcano (Mexico)
Volcanic plume composition is strongly influenced by both changes in magmatic systems and plume-atmosphere interactions. Understanding the degassing mechanisms controlling the type of volcanic activity implies deciphering the contributions of magmatic gases reaching the surface and their posterior chemical transformations in contact with the atmosphere. Remote sensing techniques based on direct solar absorption spectroscopy provide valuable information about most of the emitted magmatic gases but also on gas species formed and converted within the plumes. In this study, we explore the procedures, performances and benefits of combining two direct solar absorption techniques, high resolution Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and Ultraviolet Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (UV-DOAS), to observe the composition changes in the Popocatépetl’s plume with high temporal resolution. The SO2 vertical columns obtained from three instruments (DOAS, high resolution FTIR and Pandora) were found similar (median difference <12%) after their intercalibration. We combined them to determine with high temporal resolution the different hydrogen halide and halogen species to sulfur ratios (HF/SO2, BrO/SO2, HCl/SO2, SiF4/SO2, detection limit of HBr/SO2) and HCl/BrO in the Popocatépetl’s plume over a 2.5-years period (2017 to mid-2019). BrO/SO2, BrO/HCl, and HCl/SO2 ratios were found in the range of (0.63 ± 0.06 to 1.14 ± 0.20) × 10−4, (2.6 ± 0.5 to 6.9 ± 2.6) × 10−4, and 0.08 ± 0.01 to 0.21 ± 0.01 respectively, while the SiF4/SO2 and HF/SO2 ratios were found fairly constant at (1.56 ± 0.25) × 10−3 and 0.049 ± 0.001. We especially focused on the full growth/destruction cycle of the most voluminous lava dome of the period that took place between February and April 2019. A decrease of the HCl/SO2 ratio was observed with the decrease of the extrusive activity. Furthermore, the short-term variability of BrO/SO2 is measured for the first time at Popocatépetl volcano together with HCl/SO2, revealing different behaviors with respect to the volcanic activity. More generally, providing such temporally resolved and near-real-time time series of both primary and secondary volcanic gaseous species is critical for the management of volcanic emergencies, as well as for the understanding of the volcanic degassing processes and their impact on the atmospheric chemistry.
Taquet, N.; Rivera Cárdenas, C.; Stremme, W.; Boulesteix, Thomas; Bezanilla, A.; Grutter, M.; García, O.; Hase, F.; Blumenstock, T.
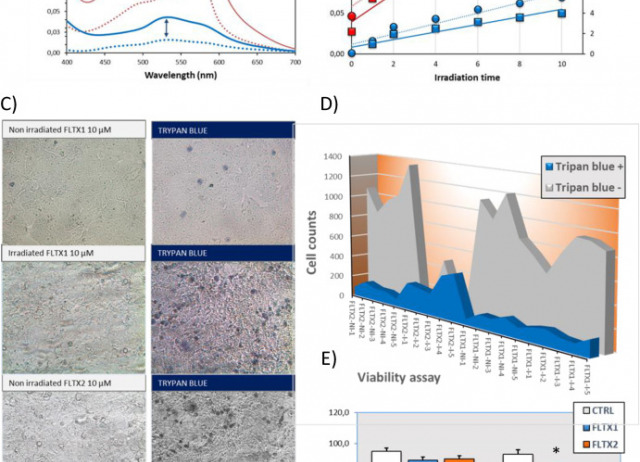
Fluorescent tamoxifen derivatives as biophotonic probes for the study of human breast cancer and estrogen-receptor directed photosensitizers
Currently, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer worldwide, being the so-called estrogen receptor (ER) positive the subtype with highest prevalence. For decades, the most successful strategy to prevent recurrence of ER + breast cancers is tamoxifen coadjuvant therapy. However, the involvement of the different estrogen receptors (ERα, ERβ and GPER) and the interaction in their signaling pathways, the evidence for side-effects in chronic tamoxifen treatments, as well as the appearance of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancers, have encouraged the need for novel receptor-targeted fluorescent probes. In line with this, multifunctional antiestrogen conjugates, exhibiting fluorescent properties while retaining the ability to antagonize estrogen actions, have been synthesized and proven to be particularly useful in the study of the molecular biology of ER + breast cancers. These novel fluorescent tamoxifen derivatives (FTDs) exhibit pharmacological features of pure antiestrogens, with similar or even greater affinity for ERα than tamoxifen, inhibit ER-dependent gene transcription and cell proliferation, and are devoid of uterotrophic effects. In the present study we have aim at providing a detailed view of their biophotonic potential, including their spectroscopic properties, their usefulness for fluorescent labelling of cellular compartments and intracellular targets, their application in the identification of non-ER antiestrogen binding sites thought fluorescence competition assays, and finally, in their ability to function as efficient ER-targeted photosensitizers.
Díaz, Mario; Hernández, Dácil; Valdés-Baizabal, Catalina; Lobo, Fernando; Marín, Raquel; Canerina-Amaro, Ana; Boto, Alicia; Lahoz, Fernando.
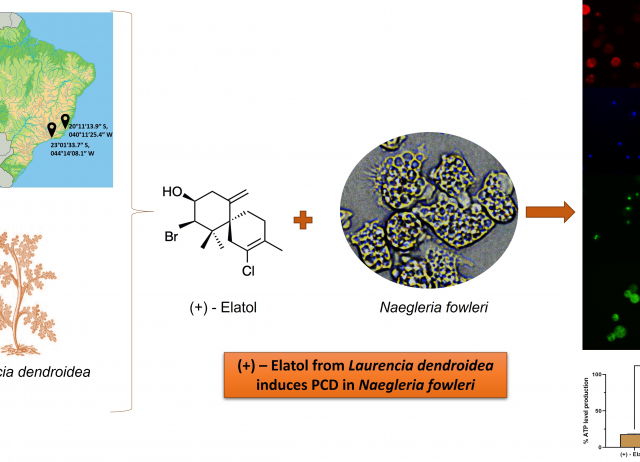
Chamigrane-Type Sesquiterpenes from Laurencia dendroidea as Lead Compounds against Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri is an opportunistic protozoon that can be found in warm water bodies. It is the causative agent of the primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Focused on our interest to develop promising lead structures for the development of antiparasitic agents, this study was aimed at identifying new anti-Naegleria marine natural products from a collection of chamigrane-type sesquiterpenes with structural variety in the levels of saturation, halogenation and oxygenation isolated from Laurencia dendroidea. (+)-Elatol (1) was the most active compound against Naegleria fowleri trophozoites with IC50 values of 1.08 μM against the ATCC 30808™ strain and 1.14 μM against the ATCC 30215™ strain. Furthermore, the activity of (+)-elatol (1) against the resistant stage of N. fowleri was also assessed, showing great cysticidal properties with a very similar IC50 value (1.14 µM) to the one obtained for the trophozoite stage. Moreover, at low concentrations (+)-elatol (1) showed no toxic effect towards murine macrophages and could induce the appearance of different cellular events related to the programmed cell death, such as an increase of the plasma membrane permeability, reactive oxygen species overproduction, mitochondrial malfunction or chromatin condensation. Its enantiomer (−)-elatol (2) was shown to be 34-fold less potent with an IC50 of 36.77 μM and 38.03 μM. An analysis of the structure–activity relationship suggests that dehalogenation leads to a significant decrease of activity. The lipophilic character of these compounds is an essential property to cross the blood-brain barrier, therefore they represent interesting chemical scaffolds to develop new drugs.
Arberas-Jiménez, Íñigo; Nocchi, Nathália; Chao-Pellicer, Javier; Sifaoui, Ines; Ribeiro Soares, Angélica; DIAZ MARRERO, ANA RAQUEL ; Fernández, José J.; Piñero, José E.; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob.
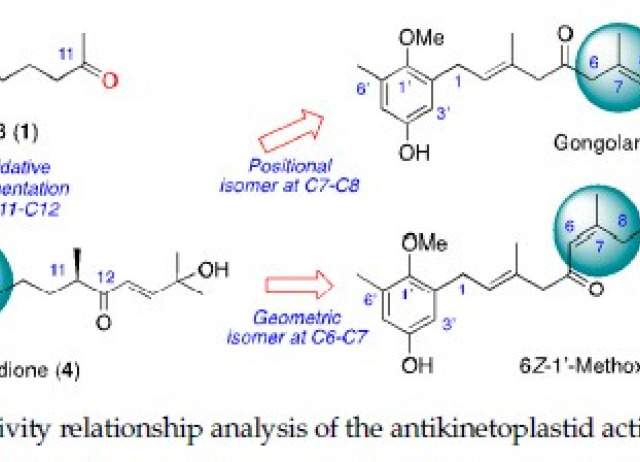
Meroterpenoids from Gongolaria abies-marina against Kinetoplastids: In Vitro Activity and Programmed Cell Death Study
Leishmaniasis and Chagas disease affect millions of people worldwide. The available treatments against these parasitic diseases are limited and display multiple undesired effects. The brown alga belonging to the genus Gongolaria has been previously reported as a source of compounds with different biological activities. In a recent study from our group, Gongolaria abies-marine was proven to present antiamebic activity. Hence, this brown alga could be a promising source of interesting molecules for the development of new antiprotozoal drugs. In this study, four meroterpenoids were isolated and purified from a dichloromethane/ethyl acetate crude extract through a bioguided fractionation process targeting kinetoplastids. Moreover, the in vitro activity and toxicity were evaluated, and the induction of programmed cell death was checked in the most active and less toxic compounds, namely gongolarone B (2), 6Z-1′-methoxyamentadione (3) and 1′-methoxyamentadione (4). These meroterpenoids triggered mitochondrial malfunction, oxidative stress, chromatin condensation and alterations of the tubulin network. Furthermore, a transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image analysis showed that meroterpenoids (2–4) induced the formation of autophagy vacuoles and ER and Golgi complex disorganization. The obtained results demonstrated that the mechanisms of action at the cellular level of these compounds were able to induce autophagy as well as an apoptosis-like process in the treated parasites.
San Nicolás-Hernández, Desirée; Rodríguez-Expósito, Rubén L.; López-Arencibia, Atteneri; Bethencourt-Estrella, Carlos J.; Sifaoui, Ines; Salazar-Villatoro, Lizbeth; Omaña-Molina, Maritza; Fernández, José J.; DIAZ MARRERO, ANA RAQUEL ; Piñero, José E.; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob.
Editorial: Marine microalgae and biotoxins
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their impact in aquaculture, services and aquatic ecosystems in coastal areas are a major concern. The occurrence of these natural phenomena is expected to increase due to the growing pressure of anthropogenic activities, the projected climate trends, and their effects in the marine environment (Kazmi et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022). Methodological advances in monitoring systems for a fast and precise detection of biotoxins, together with a better knowledge on oceanographic conditions suitable for development of HABs, contributed to a more efficient and cost-effective management of aquaculture and fishery resources (Ruiz-Villarreal et al., 2022).
DIAZ MARRERO, ANA RAQUEL ; Fernandez, José J.; Rodríguez, Francisco; Band-Schmidt, Christine J.; Diogène, Jorge; Novelli, Antonello.
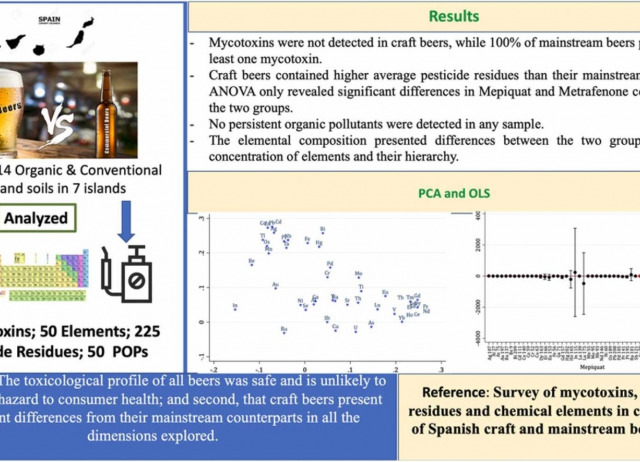
Comparative analysis of mycotoxin, pesticide, and elemental content of Canarian craft and Spanish mainstream beers
The number of craft breweries and the volume of craft beer produced globally is growing exponentially. However, little is known about their differences with mainstream beers regarding mycotoxin profile, pesticide and pollutant residues and elemental composition. Given that beer is one of the most consumed beverages worldwide, it is important to shed light on its toxicological profile. In this study, samples of 23 craft beers and 19 mainstream Spanish beers were collected to perform a comparative analysis including 8 mycotoxins, 225 pesticide residues and 50 POPs, and 50 elements. Mycotoxins were not detected in craft beers, while 100% of mainstream beers presented at least one mycotoxin. In contrast, craft beers contained higher average pesticide residues than their mainstream counterparts, although significant differences were only found in Mepiquat and Metrafenone content. No persistent organic pollutants were detected in any sample. The elemental composition presented differences between the two groups both in the concentration of elements and their hierarchy. In conclusion, the toxicological profile of all beers was safe and is unlikely to constitute a hazard to consumer health. Craft beers present significant differences from their mainstream counterparts in all the dimensions explored.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva; de las Heras Tranche, Iván; Acosta-Dacal, Andrea Carolina; Rodríguez Hernández, Ángel; Macías Montes, Ana; Zumbado Peña, Manuel; Pérez Luzardo, Octavio.
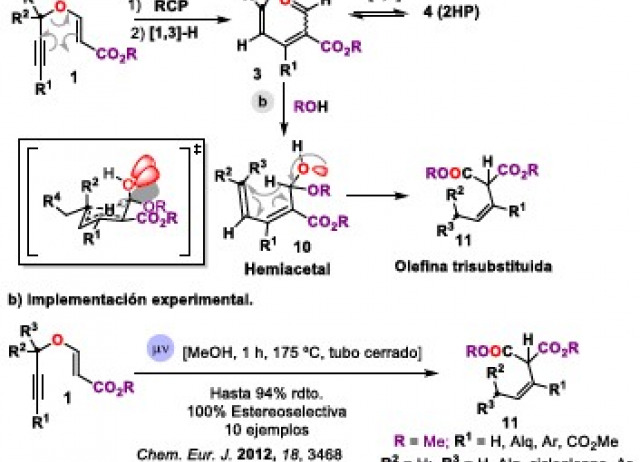
Control de la reactividad en plataformas moleculares multifuncionales y su aplicación a la construcción molecular orientada a la diversidad. Éteres propargílicos vinílicos como un caso de estudio
En este tutorial se muestra con el ejemplo de los éteres propargílicos vinílicos, bloques sintéticos multifuncionales, como es posible instrumentalizar la reactividad emergente de la combinación de sus grupos funcionales para el diseño y desarrollo de procesos dominó (cascada) ramificados para la generación de complejidad molecular orientada a la diversidad.
Tejedor, David; García-Tellado, Fernando.