Publicaciones
Esta sección incluye una lista de los últimos artículos científicos del IPNA publicados en revistas incluidas en el Science Citation Index (SCI).
En DIGITAL.CSIC, repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos desde 1962, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc. del centro. El objetivo de DIGITAL.CSIC es organizar, preservar y difundir en acceso abierto los resultados de nuestra investigación.
En el repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc.
Análisis de la Producción Científica del IPNA 2014-2019: análisis bibliométrico realizado a partir de datos recogidos en Scopus y Web of Science.

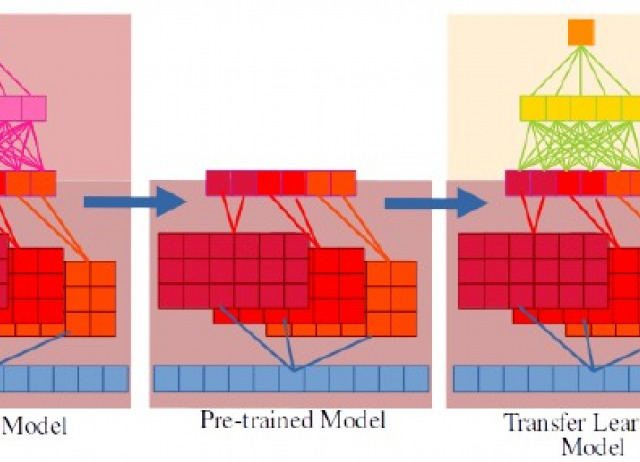
Prediction of Antifungal Activity of Antimicrobial Peptides by Transfer Learning from Protein Pretrained Models
Peptides with antifungal activity have gained significant attention due to their potential therapeutic applications. In this study, we explore the use of pretrained protein models as feature extractors to develop predictive models for antifungal peptide activity. Various machine learning classifiers were trained and evaluated. Our AFP predictor achieved comparable performance to current state-of-the-art methods. Overall, our study demonstrates the effectiveness of pretrained models for peptide analysis and provides a valuable tool for predicting antifungal peptide activity and potentially other peptide properties.
Lobo, Fernando; González, Maily Selena; Boto, Alicia; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
El conejo europeo y su impacto en la dispersión de semillas de las plantas nativas de Canarias
El conejo europeo (Oryctolaguscuniculus) es originario del suroeste de Europa y el Norte de África. Esta especie ha viajado con el ser humano hasta los lugares más remotos del mundo, como son las islas, donde ha sido introducido en al menos 800 de éstas, incluyendo la mayoría de las islas macaronésicas (Azores, Madeira, Salvajes y Canarias).
Guerrero Campos, María; González Mancebo, Juana Mª; Nogales, Manuel.
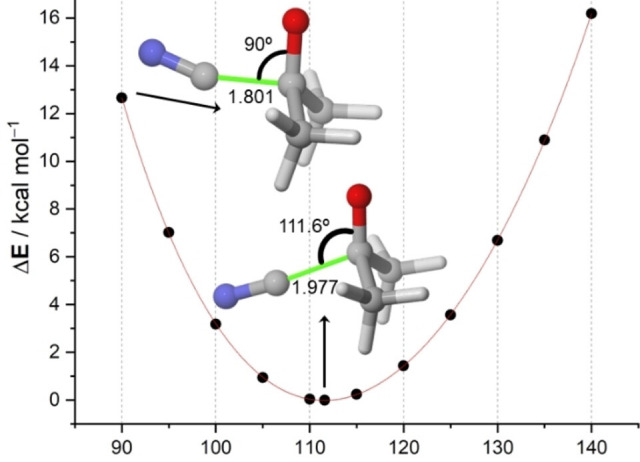
Origin of the Bürgi-Dunitz Angle
The Bürgi-Dunitz (BD) angle plays a pivotal role in organic chemistry to rationalize the nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups. Yet, the origin of the obtuse trajectory of the nucleophile remains incompletely understood. Herein, we quantify the importance of the underlying physical factors quantum chemically. The obtuse BD angle appears to originate from the concerted action of a reduced Pauli repulsion between the nucleophile HOMO and carbonyl π bond, a more stabilizing HOMO-π*-LUMO(C=O) interaction, as well as a more favorable electrostatic attraction.
Rodríguez, Humberto A.; Bickelhaupt, F. Matthias; Fernández, Israel.
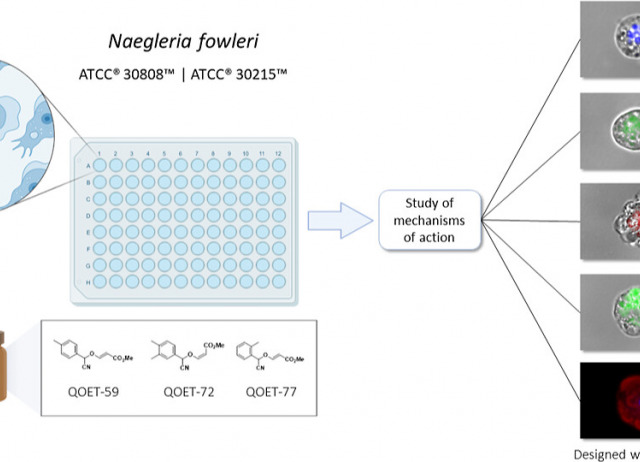
Cyanomethyl Vinyl Ethers Against Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri is a pathogenic amoeba that causes a fulminant and rapidly progressive disease affecting the central nervous system called primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). Moreover, the disease is fatal in more than 97% of the reported cases, mostly affecting children and young people after practicing aquatic activities in nontreated fresh and warm water bodies contaminated with these amoebae. Currently, the treatment of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis is based on a combination of different antibiotics and antifungals, which are not entirely effective and lead to numerous side effects. In the recent years, research against PAM is focused on the search of novel, less toxic, and fully effective antiamoebic agents. Previous studies have reported the activity of cyano-substituted molecules in different protozoa. Therefore, the activity of 46 novel synthetic cyanomethyl vinyl ethers (QOET-51 to QOET-96) against two type strains of N. fowleri (ATCC 30808 and ATCC 30215) was determined. The data showed that QOET-51, QOET-59, QOET-64, QOET-67, QOET-72, QOET-77, and QOET-79 were the most active molecules. In fact, the selectivity index (CC50/IC50) was sixfold higher when compared to the activities of the drugs of reference. In addition, the mechanism of action of these compounds was studied, with the aim to demonstrate the induction of a programmed cell death process in N. fowleri.
Chao-Pellicer, Javier; Arberas-Jiménez, Íñigo; Delgado-Hernández, Samuel; Sifaoui, Ines; Tejedor, David; García-Tellado, Fernando; Piñero, José E.; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob.
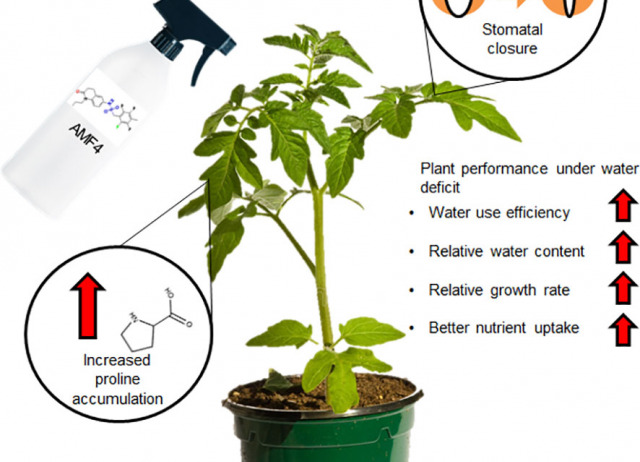
Abscisic acid mimic-fluorine derivative 4 alleviates water deficit stress by regulating ABA-responsive genes, proline accumulation, CO2 assimilation, water use efficiency and better nutrient uptake in tomato plants
Water deficit represents a serious limitation for agriculture and both genetic and chemical approaches are being used to cope with this stress and maintain plant yield. Next-generation agrochemicals that control stomatal aperture are promising for controlling water use efficiency. For example, chemical control of abscisic acid (ABA) signaling through ABA-receptor agonists is a powerful method to activate plant adaptation to water deficit. Such agonists are molecules able to bind and activate ABA receptors and, although their development has experienced significant advances in the last decade, few translational studies have been performed in crops. Here, we describe protection by the ABA mimic-fluorine derivative 4 (AMF4) agonist of the vegetative growth in tomato plants subjected to water restriction. Photosynthesis in mock-treated plants is markedly impaired under water deficit conditions, whereas AMF4 treatment notably improves CO2 assimilation, the relative plant water content and growth. As expected for an antitranspirant molecule, AMF4 treatment diminishes stomatal conductance and transpiration in the first phase of the experiment; however, when photosynthesis declines in mock-treated plants as stress persists, higher photosynthetic and transpiration parameters are recorded in agonist-treated plants. Additionally, AMF4 increases proline levels over those achieved in mock-treated plants in response to water deficit. Thus water deficit and AMF4 cooperate to upregulate P5CS1 through both ABA-independent and ABA-dependent pathways, and therefore, higher proline levels are produced Finally, analysis of macronutrients reveals higher levels of Ca, K and Mg in AMF4- compared to mock-treated plants subjected to water deficit. Overall, these physiological analyses reveal a protective effect of AMF4 over photosynthesis under water deficit and enhanced water use efficiency after agonist treatment. In summary, AMF4 treatment is a promising approach for farmers to protect the vegetative growth of tomatoes under water deficit stress.
Jiménez-Arias, David; Morales-Sierra, Sarai; Suárez, Emma; Lozano-Juste, Jorge; Coego, Alberto; Estevez, Juan C.; Borges, Andrés A. ; Rodriguez, Pedro L.
Lava dome cycles reveal rise and fall of magma column at Popocatépetl volcano
Lava domes exhibit highly unpredictable and hazardous behavior, which is why imaging their morphological evolution to decipher the underlying governing mechanisms remains a major challenge. Using high-resolution satellite radar imagery enhanced with deep-learning, we image the repetitive dome construction-subsidence cycles at Popocatépetl volcano (Mexico) with very high temporal and spatial resolution. We show that these cycles resemble gas-driven rise and fall of the upper magma column, where buoyant bubble-rich magma is extruded from the conduit (in ~hours-days), and successively drained back (in ~days-months) as magma degasses and crystallizes. These cycles are superimposed on a progressive decadal crater deepening, accompanied by heat and gas flux decrease, which could be partially explained by gas depletion within the magma plumbing system. Results reinforce the idea that gas retention and escape from the magma column play a key role in the short- and long-term morphological evolution of low-viscosity lava domes and their associated hazards.
Valade, Sébastien; Coppola, Diego; Campion, Robin; Ley, Andreas; Boulesteix, Thomas; Taquet, Noémie; Legrand, Denis; Laiolo, Marco; Walter, Thomas R.; De la Cruz-Reyna, Servando.
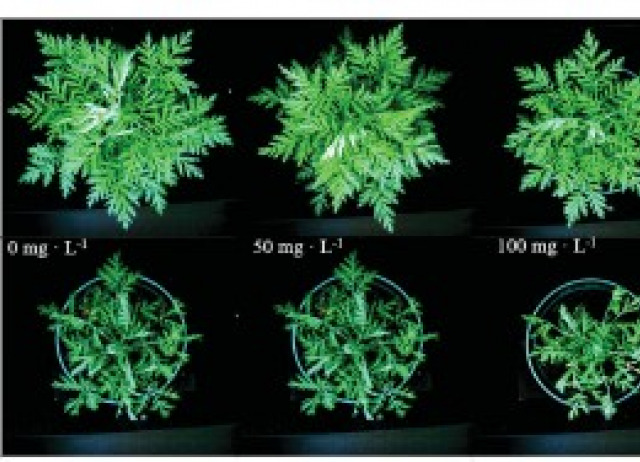
The use of chitosan oligosaccharide to improve artemisinin yield in well-watered and drought-stressed plants
ntroduction: Artemisinin is a secondary metabolite well-known for its use in the treatment of malaria. It also displays other antimicrobial activities which further increase its interest. At present, Artemisia annua is the sole commercial source of the substance, and its production is limited, leading to a global deficit in supply. Furthermore, the cultivation of A. annua is being threatened by climate change. Specifically, drought stress is a major concern for plant development and productivity, but, on the other hand, moderate stress levels can elicit the production of secondary metabolites, with a putative synergistic interaction with elicitors such as chitosan oligosaccharides (COS). Therefore, the development of strategies to increase yield has prompted much interest. With this aim, the effects on artemisinin production under drought stress and treatment with COS, as well as physiological changes in A. annua plants are presented in this study. Methods: Plants were separated into two groups, well-watered (WW) and drought-stressed (DS) plants, and in each group, four concentrations of COS were applied (0, 50,100 and 200 mg•L-1). Afterwards, water stress was imposed by withholding irrigation for 9 days. Results: Therefore, when A. annua was well watered, COS did not improve plant growth, and the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes hindered the production of artemisinin. On the other hand, during drought stress, COS treatment did not alleviate the decline in growth at any concentration tested. However, higher doses improved the water status since leaf water potential (YL) improved by 50.64% and relative water content (RWC) by 33.84% compared to DS plants without COS treatment. Moreover, the combination of COS and drought stress caused damage to the plant’s antioxidant enzyme defence, particularly APX and GR, and reduced the amount of phenols and flavonoids. This resulted in increased ROS production and enhanced artemisinin content by 34.40% in DS plants treated with 200 mg•L-1 COS, compared to control plants. Conclusion: These findings underscore the critical role of ROS in artemisinin biosynthesis and suggest that COS treatment may boost artemisinin yield in crop production, even under drought conditions.
García-García, Ana L.; Rita Matos, Ana; Feijão, Eduardo; Cruz de Carvalho, Ricardo; Boto, Alicia; Marques da Silva, Jorge; Jiménez-Arias, David.
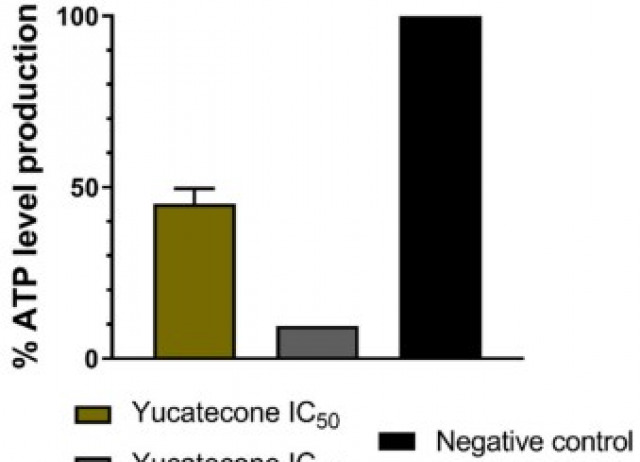
Identification and characterization of novel marine oxasqualenoid yucatecone against Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria fowleri is an opportunistic protozoan, belonging to the free-living amoeba group, that can be found in warm water bodies. It is causative agent the primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, a fulminant disease with a rapid progression that affects the central nervous system. However, no 100% effective treatments are available and those that are currently used involve the appearance of severe side effects, therefore, there is an urgent need to find novel antiamoebic compounds with low toxicity. In this study, the in vitro activity of six oxasqualenoids obtained from the red algae Laurencia viridis was evaluated against two different strains of N. fowleri (ATCC® 30808 and ATCC® 30215) as well as their cytotoxicity against murine macrophages. Yucatecone was the molecule with the highest selectivity index (>2.98 and 5.23 respectively) and it was selected to continue with the cell death type determination assays. Results showed that yucatone induced programmed cell death like responses in treated amoebae causing DNA condensation and cellular membrane damage among others. In this family of oxasqualenoids, it seems that the most significative structural feature to induce activity against N. fowleri is the presence of a ketone at C-18. This punctual oxidation transforms an inactive compound into a lead compound as the yucatecone and 18-ketodehydrotyrsiferol with IC50 values of 16.25 and 12.70 μM, respectively. The assessment of in silico ADME/Tox analysis revealed that the active compounds showed good Human Oral Absorption and demonstrate that are found to be within the limit of approved drug parameter range. Hence, the study highlights promising potential of yucatone to be tested for therapeutic use against primary amoebic meningoencephalitis.
Arberas-Jiménez, Íñigo; Cen-Pacheco, Francisco; Chao-Pellicer, Javier; Sifaoui, Ines; Rizo-Liendo, Aitor; Morales, Ezequiel Q.; Hernández Daranas, Antonio; Díaz Marrero, Ana Raquel; Piñero, José E.; Fernández, José J.; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob.
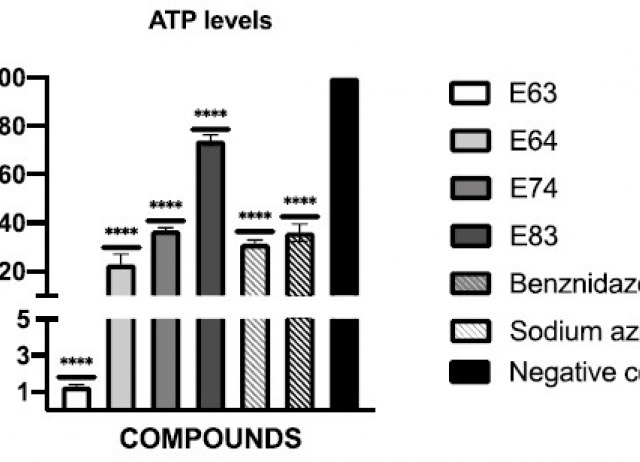
In vitro activity and mechanism of cell death induction of cyanomethyl vinyl ethers derivatives against Trypanosoma cruzi
Chagas disease causes a problematic pathology that can lead to megacolon and heart disease, and can even cause the death of the patient. Current therapies for this disease are the same as they were 50 years ago, are not fully effective and have strong side effects. The lack of a safe and effective therapy makes it necessary to search for new, less toxic and totally effective compounds against this parasite. In this work, the antichagasic activity of 46 novel cyanomethyl vinyl ether derivatives was studied. In addition, to elucidate the type of cell death that these compounds produce in parasites, several events related to programmed cell death were studied. The results highlight four more selective compounds, E63, E64, E74 and E83, which also appear to trigger programmed cell death, and are therefore postulated as good candidates to use in future therapeutics for Chagas disease.
Bethencourt-Estrella, Carlos J.; Delgado-Hernández,Samuel; López-Arencibia, Atteneri; San Nicolás-Hernández, Desirée; Tejedor, David; García-Tellado, Fernando; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob; Piñero, José E.
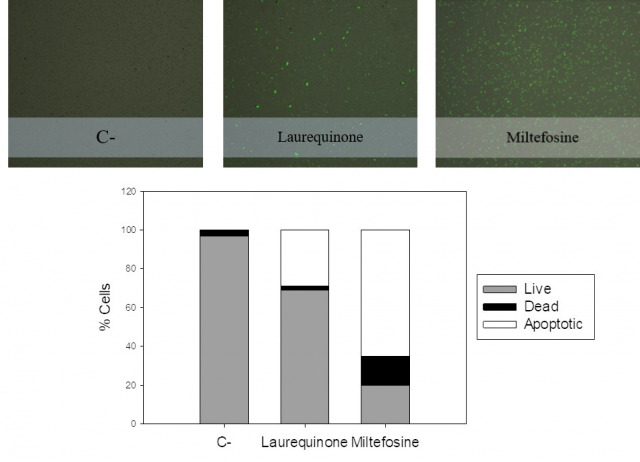
Laurequinone, a Lead Compound against Leishmania
Among neglected tropical diseases, leishmaniasis is one of the leading causes, not only of deaths but also of disability-adjusted life years. This disease, caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania, triggers different clinical manifestations, with cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral forms. As existing treatments for this parasitosis are not sufficiently effective or safe for the patient, in this work, different sesquiterpenes isolated from the red alga Laurencia johnstonii have been studied for this purpose. The different compounds were tested in vitro against the promastigote and amastigote forms of Leishmania amazonensis. Different assays were also performed, including the measurement of mitochondrial potential, determination of ROS accumulation, and chromatin condensation, among others, focused on the detection of the cell death process known in this type of organism as apoptosis-like. Five compounds were identified that displayed leishmanicidal activity: laurequinone, laurinterol, debromolaurinterol, isolaurinterol, and aplysin, showing IC50 values against promastigotes of 1.87, 34.45, 12.48, 10.09, and 54.13 µM, respectively. Laurequinone was the most potent compound tested and was shown to be more effective than the reference drug miltefosine against promastigotes. Different death mechanism studies carried out showed that laurequinone appears to induce programmed cell death or apoptosis in the parasite studied. The obtained results underline the potential of this sesquiterpene as a novel anti-kinetoplastid therapeutic agent.
García-Davis, Sara; López-Arencibia, Atteneri; Bethencourt-Estrella, Carlos J.; San Nicolás-Hernández, Desirée; Viveros-Valdez, Ezequiel; Díaz Marrero, Ana Raquel ; Fernández, José J.; Lorenzo-Morales, Jacob; Piñero, José E.