Publicaciones
Esta sección incluye una lista de los últimos artículos científicos del IPNA publicados en revistas incluidas en el Science Citation Index (SCI).
En DIGITAL.CSIC, repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos desde 1962, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc. del centro. El objetivo de DIGITAL.CSIC es organizar, preservar y difundir en acceso abierto los resultados de nuestra investigación.
En el repositorio institucional del CSIC, pueden encontrar el listado completo de artículos científicos, así como otras colecciones de interés como congresos, tesis, libros, material divulgativo, etc.
Análisis de la Producción Científica del IPNA 2014-2019: análisis bibliométrico realizado a partir de datos recogidos en Scopus y Web of Science.

Class or community? Marx, the Russian commune, and contemporary critical theory
This article explores the relationship between class and community through a discussion of peasant struggles and the commune during the Russian Revolution. Doing so, we show how Marx's class-oriented reflections on community can help us to understand the role that the peasantry plays (or should play) in processes of social transformation. This enables us, first, to understand the relevance of communal forms for Marx, who believed that communitarian ways of life were crucial for overcoming a value-based society. It is, in fact, a mistake to divide Marx's intellectual trajectory into two periods: a categorical Marx, who authored Capital and critically analyzed the classical theory of value, and a phenomenological, empirical Marx, who in the last years of his life abandoned writing Capital and focused instead on studying the Russian peasantry. Second, it enables us to discuss new externalist visions, such as postcolonial and decolonial theories, which postulate that the subordination of contemporary peasant communities is rooted in epistemology, culture, and local power relations. These theories are related to the old social-democratic canon, which conceives of social classes as preconstituted entities and of capital as a parasitic externality that is incommensurable with social dynamics. The experience of the Russian peasantry calls into question all externalist and ontological perspectives.
Macías Vázquez, Alfredo; Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva.
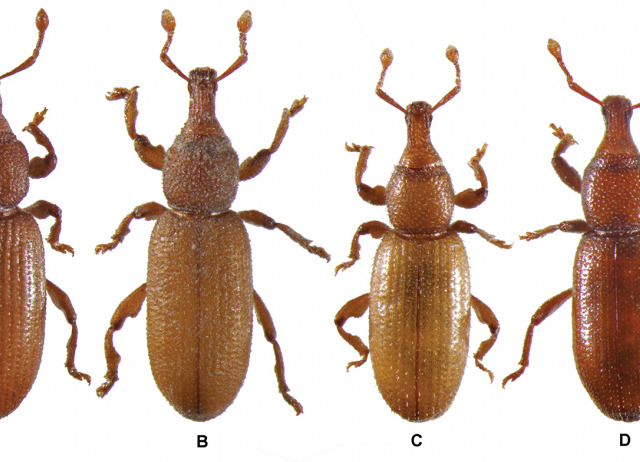
Three new subterranean species of Baezia (Curculionidae, Molytinae) for the Canary Islands
The genus Baezia Alonso-Zarazaga & García, 1999 is endemic to the Canary Islands, where four species were known to date. Based on morphological evidence, three new species of Baezia are described in this study: Baezia aranfaybo García & López, sp. nov. from El Hierro island, and Baezia madai García & Oromí sp. nov. and Baezia tizziri García & Andújar, sp. nov. from La Palma island. Notes on their biology, habitat, and distribution are presented. The number of taxa in this endemic Canarian genus increases to seven eyeless species. One species has been reported from the soil (endogean environment), with the other six associated with caves and the mesovoid shallow substratum (hypogean or subterranean environment). Frequent association with the presence of roots suggests that species of Baezia may inhabit the continuum represented by the endogean and hypogean environments. Identification key to the seven species are provided.
García, Rafael; Andújar, Carmelo; Oromí, Pedro; Emerson, Brent C.; López, Heriberto
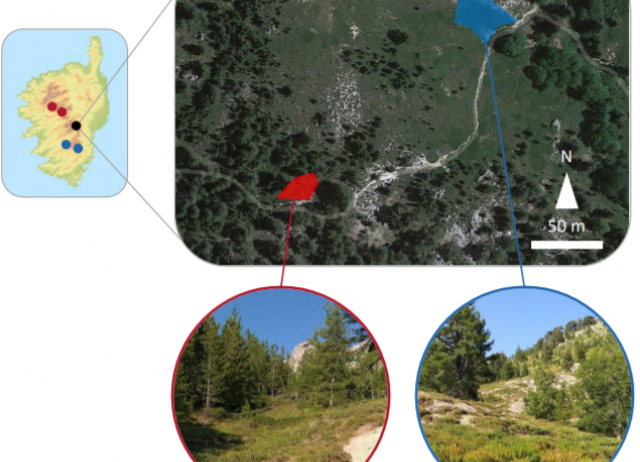
Demographic consequences of dispersal‐related trait shift in two recently diverged taxa of montane grasshoppers
Although the pervasiveness of intraspecific wing‐size polymorphism and transitions to flightlessness have long captivated biologists, the demographic outcomes of shifts in dispersal ability are not yet well understood and have been seldom studied at early stages of diversification. Here, we use genomic data to infer the consequences of dispersal‐related trait variation in the taxonomically controversial short‐winged (Chorthippus corsicus corsicus) and long‐winged (Chorthippus corsicus pascuorum) Corsican grasshoppers. Our analyses revealed lack of contemporary hybridization between sympatric long‐ and short‐winged forms and phylogenomic reconstructions supported their taxonomic distinctiveness, rejecting the hypothesis of intraspecific wing polymorphism. Statistical evaluation of alternative models of speciation strongly supported a scenario of Pleistocene divergence (<1.5 Ma) with ancestral gene flow. According to neutral expectations from differences in dispersal capacity, historical effective migration rates from the long‐ to the short‐winged taxon were threefold higher than in the opposite direction. Although populations of the two taxa present a marked genetic structure and have experienced parallel demographic histories, our coalescent‐based analyses suggest that reduced dispersal has fueled diversification in the short‐winged C. c. corsicus. Collectively, our study illustrates how dispersal reduction can speed up geographical diversification and increase the opportunity for allopatric speciation in topographically complex landscapes.
Ortego, Joaquín; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, Jorge; Noguerales, Víctor
Trophic ecology of an introduced top predator (Felis catus) on a small African oceanic islet (Santa Luzia, Cabo Verde Islands)
Studies on feral cat diet offer important ecological information and are the first step towards determining their impact upon endangered species. However, in comparing seasonal changes in diet with seasonal prey availability, the scarce amount of research into oceanic islands worldwide must be considered when deciding if a specific population is actually affected by cat predation. Cat diet was analysed on Santa Luzia (Cabo Verde Islands) since this invasive predator is considered one of the main threats to native endangered species that require conservation measures. These previous studies were carried out in different seasons, providing contrasting results, skinks being more preyed upon in the rainy season and mice in the driest periods. To check these different results, we focussed on how cat diet varied seasonally in response to changes in prey abundance. Saurians were the most important prey group, followed by mice, invertebrates and birds. No seasonal differences were, however, observed in the different prey groups consumed, saurians being the main prey in both seasons. All cases reflected their respective abundances. Results corroborate the generalist and opportunistic trophic ecology of feral cats, providing important information to assess their impact on prey populations and design future eradication programmes.
Medina, Félix M.; Melo, Tommy; Oliveira, Paulo; Nogales, Manuel; Geraldes, Pedro
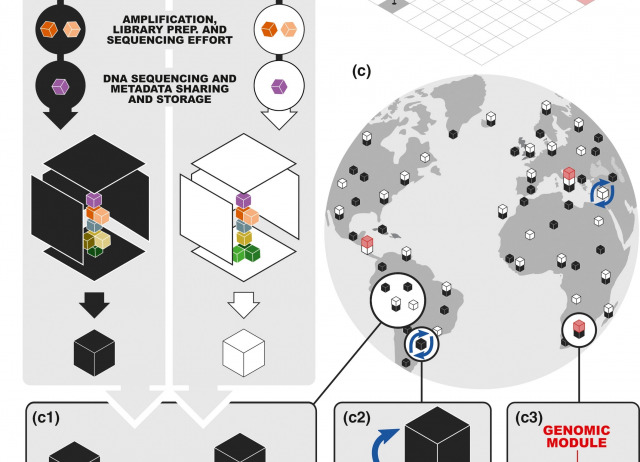
Connecting high‐throughput biodiversity inventories: Opportunities for a site‐based genomic framework for global integration and synthesis
High‐throughput sequencing (HTS) is increasingly being used for the characterization and monitoring of biodiversity. If applied in a structured way, across broad geographical scales, it offers the potential for a much deeper understanding of global biodiversity through the integration of massive quantities of molecular inventory data generated independently at local, regional and global scales. The universality, reliability and efficiency of HTS data can potentially facilitate the seamless linking of data among species assemblages from different sites, at different hierarchical levels of diversity, for any taxonomic group and regardless of prior taxonomic knowledge. However, collective international efforts are required to optimally exploit the potential of site‐based HTS data for global integration and synthesis, efforts that at present are limited to the microbial domain. To contribute to the development of an analogous strategy for the nonmicrobial terrestrial domain, an international symposium entitled “Next Generation Biodiversity Monitoring” was held in November 2019 in Nicosia (Cyprus). The symposium brought together evolutionary geneticists, ecologists and biodiversity scientists involved in diverse regional and global initiatives using HTS as a core tool for biodiversity assessment. In this review, we summarize the consensus that emerged from the 3‐day symposium. We converged on the opinion that an effective terrestrial Genomic Observatories network for global biodiversity integration and synthesis should be spatially led and strategically united under the umbrella of the metabarcoding approach. Subsequently, we outline an HTS‐based strategy to collectively build an integrative framework for site‐based biodiversity data generation.
Arribas, Paula; Andújar, Carmelo; Bidartondo, Martin I.; Bohmann, Kristine; Coissac, Éric; Creer, Simon; deWaard, Jeremy R.; Elbrecht, Vasco; Ficetola, Gentile F.; Goberna, Marta; Kennedy, Susan; Krehenwinkel, Henrik; Leese, Florian; Novotny, Vojtech; Ronquist, Fredrik; Yu, Douglas W.; Zinger, Lucie; Creedy, Thomas J.; Meramveliotakis, Emmanouil; Noguerales, Víctor; Overcast, Isaac; Morlon, Hélène; Vogler, Alfried P.; Papadopoulou, Anna; Emerson, Brent C.
Sharing and Reporting Benefits from Biodiversity Research
The most remarkable feature of our planet is the diversity of its life forms, ranging from viruses and nanobacteria to blue whales and giant sequoias to satanic leaf‐tailed geckos and leafy seadragons (look them up!). Life is found in essentially all environments on earth, and the number of species living on our planet is many times greater than we could have imagined a century ago. A well‐regarded estimate pegs the number of eukaryotic species on earth at 8.7 million (±1.3 million), of which fewer than 15% are currently described (Mora et al., 2011). The diversity of prokaryotes is less clear (and highly controversial), but an analysis of 1.6 billion 16S ribosomal RNA sequences estimated that 0.8–1.6 million prokaryotic operational taxonomic units exist globally (Louca et al., 2019). While we do not know how many species are currently extant, or have existed in the past, we do know that this biodiversity is valuable, providing food, fibre and medicine, furnishing ecosystem services such as water and air purification, nutrient cycling, pollination and carbon uptake, and contributing to technological innovations ranging from biotechnology to robotics to material science. Moreover, biodiversity underlies the cultural identity of human populations and is important to human health and well‐being. Geographically, species richness increases from the Polar Regions to the tropics in terrestrial and surface marine ecosystems. Thus, some countries, especially those in tropical and subtropical regions, are endowed with much greater biodiversity than others. Unfortunately, benefits arising from the access and utilization of this biodiversity have been unequally shared, with (paradoxically) biodiversity‐poor countries often accruing the lion's share of economic gains. There can be imbalances within countries as well, wherein some segments of the population obtain greater economic benefits from biodiversity and associated traditional knowledge than indigenous peoples. The “Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization,” which came into force in 2014, is an international agreement designed to ensure that the benefits arising from biodiversity are shared equitably (https://www.cbd.int/abs/). However, few scientific journals require compliance with the Nagoya Protocol or the reporting of benefits from biodiversity research. In this editorial, we (the editors of Molecular Ecology and Molecular Ecology Resources) express support for the Nagoya Protocol and the principle of benefit sharing. We believe that scientific journals publishing research on biodiversity can play an important role in implementing the Nagoya Protocol and in reporting on benefits generated from such research. Below, we provide background on the Nagoya Protocol, discuss the kinds of benefits that may arise from biodiversity research, describe the rationale for reporting on these benefits and introduce changes to the journals’ Data Accessibility Statements to incorporate the requirements and goals of the Nagoya Protocol.
Marden, Emily; Abbott, Richard J.; Austerlitz, Frédéric; Ortiz Barrientos, Daniel; Baucom, Regina S.; Bongaerts, Pim; Bonin, Aurélie; Bonneaud, Camille; Browne, Luke; Buerkle, C. Alex; Caicedo, Ana L.; Coltman, David W.; Cruzan, Mitchell B.; Davison, Angus; DeWoody, J. Andrew; Dumbrell, Alex J.; Emerson, Brent C.; Fountain-Jones, Nicholas M.; Gillespie, Rosemary; Giraud, Tatiana; Hansen, Michael M.; Hodgins, Kathryn A.; Heuertz, Myriam; Hirase, Shotaro; Hooper, Rebecca; Hohenlohe, Paul; Kane, Nolan C.; Kelley, Joanna L.; Kinziger, Andrew P.; McKenzie, Valerie J.; Moreau, Corrie S.; Nazareno, Alison G.; Pelletier, Tara A.; Pemberton, Josephine M.; Qu, Yanhua; Renaut, Sébastien; Riginos, Cynthia; Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, Naiara; Rogers, Sean M.; Russell, Jacob A.; Schoville, Sean D.; Shi, Suhua; Smith, Megan; Sork, Victoria L.; Stone, Graham N.; Taberlet, Pierre; Videvall, Elin; Waits, Lisette; Warschefsky, Emily; Wayne, Robert K.; Whibley, Annabel; Willoughby, Janna; Yoder, Jeremy B.; Zinger, Lucie; Sibbett, Benjamin; Narum, Shawn; Rieseberg, Loren H.
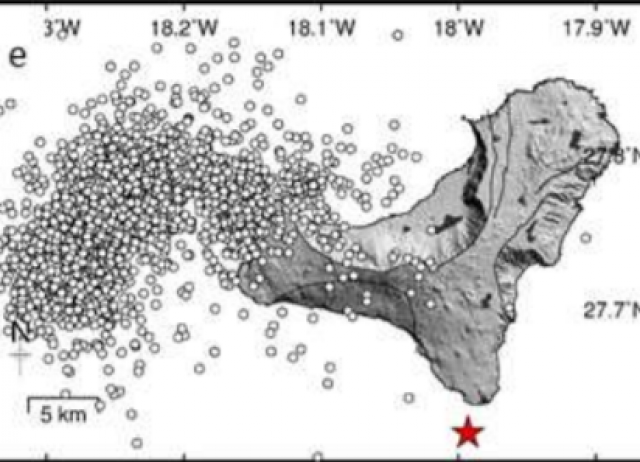
Tidal Influence on Seismic Activity During the 2011–2013 El Hierro Volcanic Unrest
The El Hierro volcanic unrest started in July 2011, with an increase in observed seismicity rates and surface deformation. After the initial onset, hypocenters migrated southward through September 2011, culminating in a submarine eruption beginning on October 10, 2011 and finishing in February 2012. The seismic activity continued, with remarkable periods of unrest through 2012 and 2013. The most significant episodes of seismic activity during this unrest are related to magma migration at depth. In this work, we compute tidal stress for each earthquake, at its hypocenter depth, and assign them a tidal stress phase angle. We have found statistically significant correlations between the occurrence of earthquakes and tidal stress phase angles, corresponding mainly to increasing tidal stress change rates. We found primarily that the magnitude of vertical and E‐W horizontal tidal stress values and their changing rates with time were correlated with earthquake occurrence times. We also found that there is no correlation between tides and seismicity at times with no observed surface displacements, suggesting that tidal modulation might be related to overpressure during migration of magma. Tidal modulation changes with depth and the influence of ocean‐loading tides is stronger than the influence of solid Earth tides. Our results support the hypothesis that tidal stress may modulate the seismicity during volcanic unrest, particularly during shallow depth magma migration.
Miguelsanz, Luis; González, Pablo J.; Tiampo, Kristy F.; Fernández Torres, José
Flightlessness in insects enhances diversification and determines assemblage structure across whole communities
Dispersal limitation has been recurrently suggested to shape both macroecological patterns and microevolutionary processes within invertebrates. However, because of potential interactions among biological, environmental, temporal, and spatial variables, causal links among flight-related traits, diversification and spatial patterns of community assembly remain elusive. Integrating genetic variation within species across whole insect assemblages, within a simplified spatial and environmental framework, can be used to reduce the impact of these potentially confounding variables. Here, we used standardized sampling and mitochondrial DNA sequencing for a whole-community characterization of the beetle fauna inhabiting a singular forested habitat (laurel forest) within an oceanic archipelago setting (Canary Islands). The spatial structure of species assemblages together with species-level genetic diversity was compared at the archipelago and island scales for 104 winged and 110 wingless beetle lineages. We found that wingless beetle lineages have: (i) smaller range sizes at the archipelago scale, (ii) lower representation in younger island communities, (iii) stronger population genetic structure, and (iv) greater spatial structuring of species assemblages between and within islands. Our results reveal that dispersal limitation is a fundamental trait driving diversity patterns at multiple hierarchical levels by promoting spatial diversification and affecting the spatial configuration of entire assemblages at both island and archipelago scales.
Salces-Castellano, Antonia; Andújar, Carmelo; López, Heriberto; Pérez-Delgado, Antonio J.; Arribas, Paula; Emerson, Brent C.
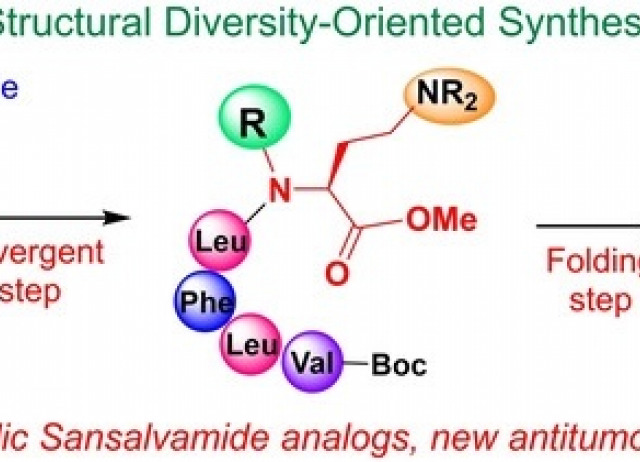
Structural Diversity using Hyp “Customizable Units”: Proof‐of‐Concept Synthesis of Sansalvamide‐Related Antitumoral Peptides
The potential of “customizable units” to generate structural diversity for biological screenings is highlighted in this proof‐of‐concept synthesis of new peptides related to the potent antitumoral Sansalvamide A. Using L‐4‐hydroxyproline (Hyp) as a customizable unit in a linear parent peptide, an improved procedure for selective peptide modification was developed. A divergent Hyp scission‐reductive amination process was carried out, affording five linear peptides with cationic residues, and notably, an N‐alkyl moiety that affected the conformation of the peptide. After two steps (saponification and macrocyclization), sixteen differently N1‐substituted linear and cyclic peptides were obtained. For the first time, the activity of the linear and cyclic compounds was compared. Not only some linear analogs but also cyclic compounds with scarcely studied cationic residues were active against MCF7 breast cancer line. Thus, the structural diversity generated from customizable units can be valuable in drug discovery.
Cuevas, Fernando; Saavedra, Carlos J.; Romero-Estudillo, Iván; Boto, Alicia; Ordóñez, Mario; Vergara, Irene
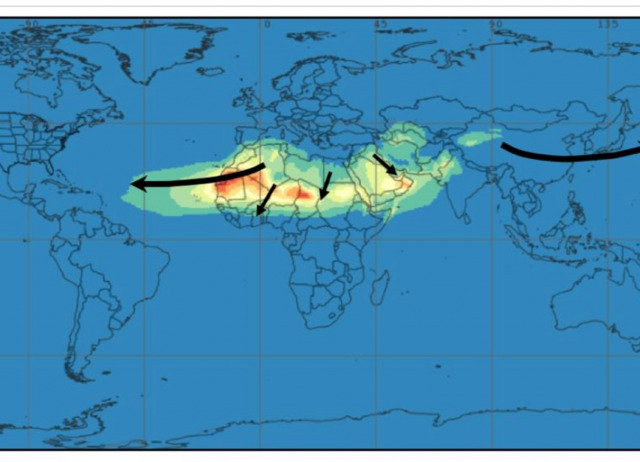
Impact of Desert Dust Events on the Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Background: Whether or not inhalation of airborne desert dust has adverse health effects is unknown. The present study, based on a systematic review and meta-analysis, was carried out to assess the influence desert dust on cardiovascular mortality, acute coronary syndrome, and heart failure. Methods: A systematic search was made in PubMed and Embase databases for studies published before March 2020. Studies based on daily measurements of desert dust were identified. The meta-analysis evaluated the impact of desert dust on cardiovascular events the same day (lag 0) of the exposure and during several days after the exposure (lags 1 to 5). The combined impact of several days of exposure was also evaluated. The incidence rate ratio (IRR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) was calculated using the inverse variance random effects method. Results: Of the 589 identified titles, a total of 15 studies were selected. The impact of desert dust on the incidence of cardiovascular mortality was statistically significant (IRR = 1.018 (95%CI 1.008–1.027); p < 0.001) in lag 0 of the dust episode, in the following day (lag 1) (IRR = 1.005 (95%CI 1.001–1.009); p = 0.022), and during both days combined (lag 0–1) (IRR = 1.015 (95%CI 1.003–1.028); p = 0.014). Conclusions: The inhalation to desert dust results in a 2% increase (for every 10 µg/m3) in cardiovascular mortality risk.
Domínguez-Rodríguez, Alberto; Báez-Ferrer, Néstor; Abreu-González, Pedro; Rodríguez, Sergio; Díaz, Rocío; Avanzas, Pablo; Hernández-Vaquero, Daniel