Major components of Spanish cultivated Artemisia absinthium populations: Antifeedant, antiparasitic, and antioxidant effects
The objective of this study was the valorization of Spanish Artemisia absinthium populations from Teruel (Aragón) and Sierra Nevada (Granada). These populations were experimentally cultivated in the field and under controlled conditions. Three major components were isolated from a two year-old population obtained from the Teruel population cultivated in Ejea-Zaragoza in 2003, and identified by NMR experiments as the sequiterpene lactone hydroxypelenolide (I) and the flavones artemetin (II) and casticin (III). The I–III content of the plant extracts was analyzed by HPLC-DAD. The insect antifeedant properties of plant extracts from different years and crops were tested against Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae and Rhopalosiphum padi. Additionally we studied their antioxidant, phytotoxic and antiparasitic effects.
Gonzalez-Coloma, Azucena; Bailen, Maria; Diaz, Carmen E.; Fraga, Braulio M.; Martínez-Díaz, Rafael; Zuñiga, Gustavo E.; Contreras, Rodrigo A.; Cabrera, Raimundo; Burillo, Jesus
Plant-defensive sesquiterpenoids from Senecio species with biopesticide potential
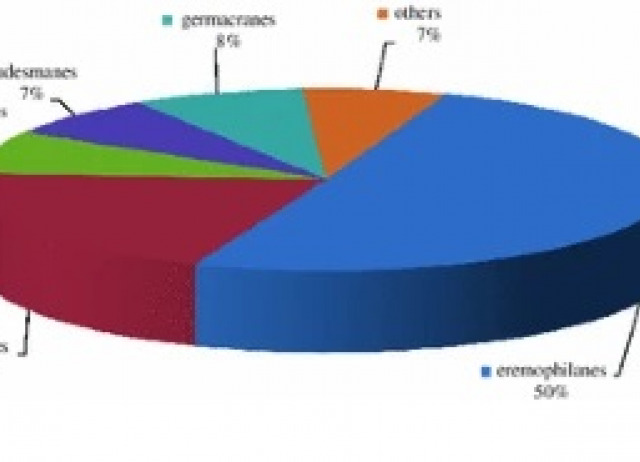
Senecio species have been used in folk medicine for treatment of wounds, as antiemetic, antiinflammatory and their crude extract or dry powder as crop protection agents. The toxicity exhibited to livestock by these plants has been attributed to their content in pyrrolizidine alkaloids and furanoeremophilane type sesquiterpenes. Sesquiterpenoids with eremophilane, cacalol, bisabolane, silphinene, caryophillane, humulane, germacrane and benzofurane skeletons have been isolated from this genus. Here we focus on bioactive sesquiterpenoids with plant defensive properties isolated from Senecio.
Portero, A. G.; González-Coloma, Azucena; Reina, Matías; Díaz, Carmen E.
Supercritical CO2 extraction of Persea indica: Effect of extraction parameters, modelling and bioactivity of its extracts
The objective of the work was to optimize the extraction of Persea indica L. bioactive compounds by means of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) and analyze their insecticidal effects. P. indica L. is one of the dominant species of the Canarian laurel forest, a relict of the Tertiary flora. Different extraction conditions (pressure, plant material particle size, temperature, CO2 flow) and the influence of entrainer were tested and the evolution of the extracted compounds was screened by HPLC–MS. A comparison with conventional techniques such as hydrodistillation (HD) or organic solvent extraction (OSE) was also presented. Particularly, four CO2 densities ranging from 628.61 kg/m3 to 839.81 kg/m3 were studied in the range of 10.0–20.0 MPa and 40–50 °C. The extracts contained insecticidal ryanodanes of great interest, previously described as insecticidal components of P. indica. The insecticidal antifeedant activity of selected extracts was inspected. A model based on mass transfer equations, the Sovová model, was successfully applied to correlate the experimental data.
Martín, L; González-Coloma, A.; Díaz, C. E.; Mainara, A. M.; Urieta, J. S.
A New Catalytic Prins Cyclization Leading to Oxa- and Azacycles
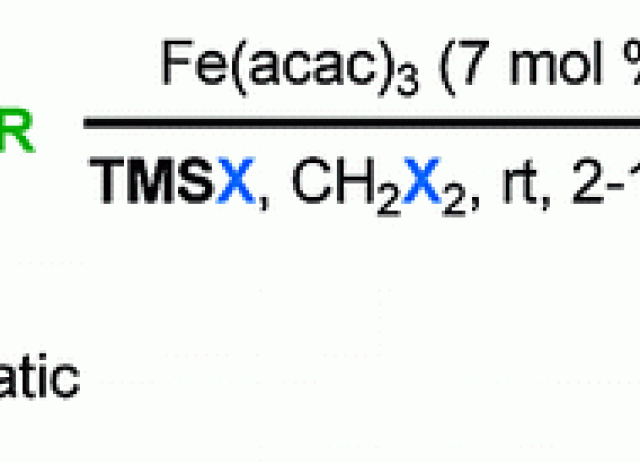
A new Prins cyclization process that builds up one carbon−carbon bond, one heteroatom-carbon bond, and one halogen-carbon bond, (in an oxa- and azacycle) relies on an iron catalyst system formed from Fe(acac)3 and trimethylsilyl halide. The method displays a broad substrate scope and is economical, environmentally friendly, and experimentally simple. This catalytic method permits the construction of chloro, bromo and iodo heterocycles, by the suitable combination of iron(III) source, the corresponding trimethylsilyl halide and the solvent, in high yields.
Miranda, Pedro O.; Carballo, Ruben M.; Martín, Víctor S.; Padrón, Juan I.