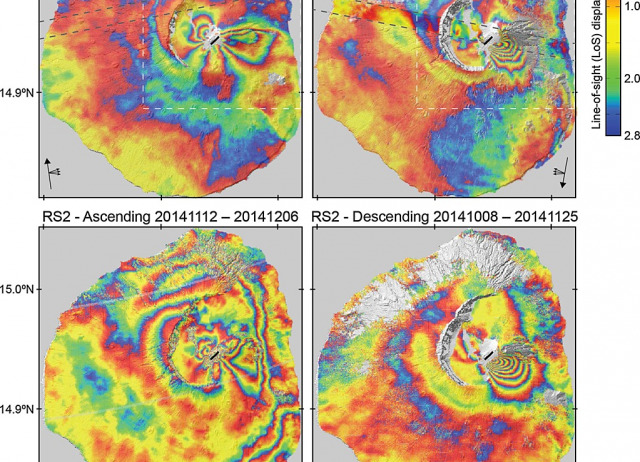
The 2014–2015 eruption of Fogo volcano: Geodetic modeling of Sentinel‐1 TOPS interferometry
After 20 years of quiescence, Fogo volcano erupted in November 2014. The eruption produced fast‐moving lava flows that traveled for several kilometers and destroyed two villages. This event represents the first episode of significant surface deformation imaged by the new European Space Agency's Sentinel‐1 satellite in its standard acquisition mode, Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans (TOPS), which differs from that of previous synthetic aperture radar (SAR) missions. We perform a Bayesian inversion of Sentinel‐1 TOPS SAR interferograms spanning the eruption and accurately account for variations in the TOPS line‐of‐sight vector when modeling displacements. Our results show that magma ascended beneath the Pico do Fogo cone and then moved laterally toward its southwestern flank, where the eruptive fissure opened. This study provides important insights into the inner workings of Fogo volcano and shows the potential of Sentinel‐1 TOPS interferometry for geophysical (e.g., volcano monitoring) applications.
González, Pablo J.; Bagnardi, Marco; Hooper, Andrew J.; Larsen, Yngvar; Marinkovic, Petar; Samsonov, Sergey V.; Wright, Tim J.
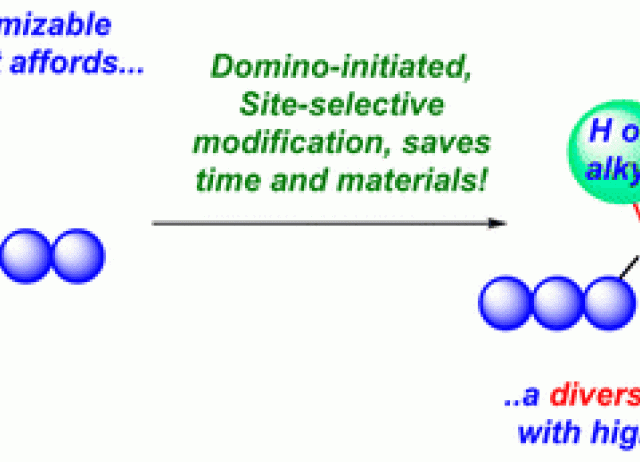
Domino Process Achieves Site-Selective Peptide Modification with High Optical Purity. Applications to Chain Diversification and Peptide Ligation
The development of peptide libraries by site-selective modification of a few parent peptides would save valuable time and materials in discovery processes but still is a difficult synthetic challenge. Herein, we introduce natural hydroxyproline as a convertible unit for the production of a variety of optically pure amino acids, including expensive N-alkyl amino acids, homoserine lactones, and Agl lactams, and to achieve the mild, efficient, and site-selective modification of peptides. A domino process is used to cleave the customizable Hyp unit under mild, metal-free conditions. Both terminal and internal positions can be modified, and similar customizable units can be differentiated. The resulting products possess two reactive chains which can be manipulated independently. The versatility and scope of this process is highlighted by its application to the ligation of two peptide chains, and the generation of peptides with several chains and peptides with conformational restrictions.
Romero Estudillo, Iván Omar; Boto, Alicia
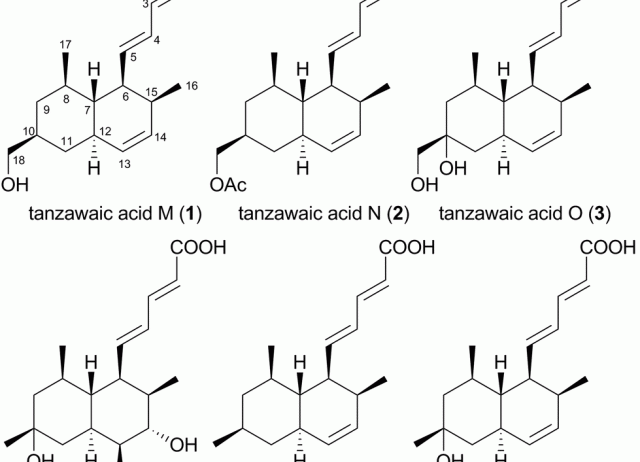
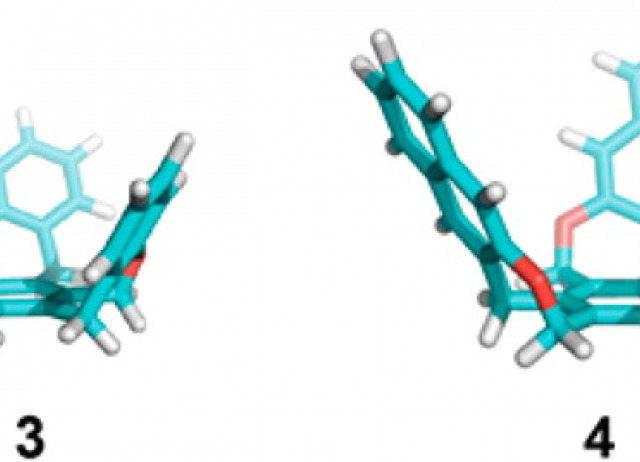
Tanzawaic acids isolated from a marine-derived fungus of the genus Penicillium with cytotoxic activities
Tanzawaic acids M (1), N (2), O (3) and P (4) and the known tanzawaic acids B (5) and E (6), have been isolated from an extract of a cultured marine-derived fungus (strain CF07370) identified as a member of the genus Penicillium. The structures of 1–4 were determined based on spectroscopic evidence. The antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of compounds 1–6 were evaluated.
Cardoso-Martínez, F.; Rosa, José M. de la; Díaz-Marrero, Ana R.; Darias, José; Cerella, Claudia; Diederich, Marc; Cueto, Mercedes
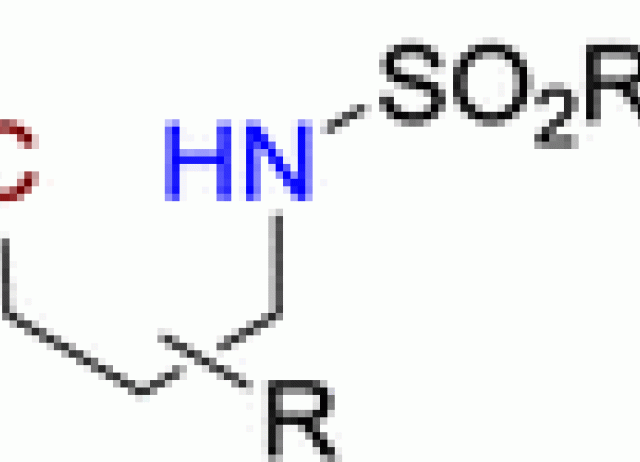
Chemoselective Intramolecular Functionalization of Methyl Groups in Nonconstrained Molecules Promoted by N-Iodosulfonamides
Mechanistic evidence observed in Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag-type reactions has been crucial to achieve the chemoselective functionalization of methyl groups under mild conditions. Radical-mediated methyl iodination and subsequent oxidative deiodination are the key steps in this functionalization, where iodine chemistry has a pivotal role on the formation of the C–N bond. The concepts of single hydrogen atom transfer (SHAT) and multiple hydrogen atom transfer (MHAT) are introduced to describe the observed chemoselectivity.
Paz, Nieves R.; Rodríguez Sosa, Dionisio; Valdés, Haydée; Marticorena, Ricardo; Melián, Daniel; Copano, Belén; González Martín, Concepción C.; Herrera, Antonio J.
Oxidation with air by ascorbate-driven quinone redox cycling
Transition metal-free oxidation with air at room temperature has been achieved by simply using ascorbate (vitamin C) and catalytic amounts of menadione (vitamin K3). A combination of the mentioned vitamins transforms atmospheric oxygen into hydrogen peroxide, which is able to oxidize arylboronic acids and other chemical moieties.
G. Silveira-Dorta, D. M. Monzón, F. P. Crisóstomo, T. Martín, V. S. Martín, R. Carrillo
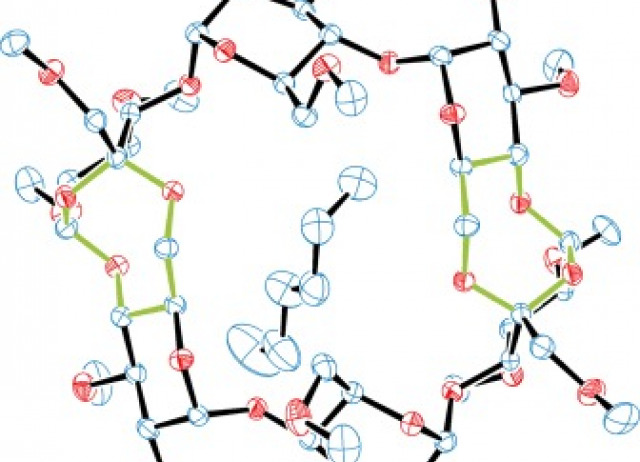
Easy access to modified cyclodextrins by an intramolecular radical approach
A simple method to modify the primary face of cyclodextrins (CDs) is described. The 6I‐O‐yl radical of α‐, β‐, and γ‐CDs regioselectively abstracts the H5II, located in the adjacent D‐glucose unit, by an intramolecular 1,8‐hydrogen‐atom‐transfer reaction through a geometrically restricted nine‐membered transition state to give a stable 1,3,5‐trioxocane ring. The reaction has been extended to the 1,4‐diols of α‐ and β‐CD to give the corresponding bis(trioxocane)s. The C2‐symmetric bis(trioxocane) corresponding to the α‐CD is a stable crystalline solid whose structure was confirmed by X‐ray diffraction analysis. The calculated geometric parameters confirm that the primary face is severely distorted toward a narrower elliptical shape for this rim.
Álvarez-Dorta, Dimitri; León, Elisa I.; Kennedy, Alan R.; Martín, Ángeles; Pérez-Martín, Inés; Suárez, Ernesto
Synthesis of New Benzocyclotrimer Analogues: New Receptors for Tetramethylammonium Ion Recognition
Using a [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition/Mitsunobu reaction sequence, a convenient synthesis to access new benzocyclotrimer analogues has been developed. The new receptors have the geometry and functionality capable of recognizing the tetramethylammonium ion in the gas phase and in solution.
Carrillo Fumero, Romen; Hynes, Michael J.; Martín, Víctor S.; Martín, Tomás; Pinacho Crisóstomo, Fernando R.
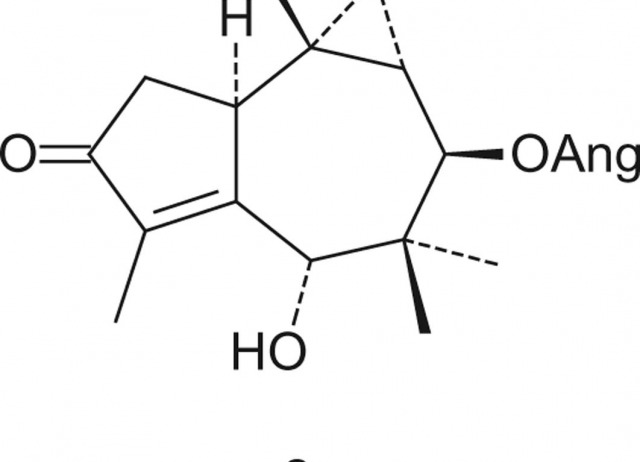
Bioactive compounds from transformed root cultures and aerial parts of Bethencourtia hermosae
A chemical study of Bethencourtia hermosae, aerial parts and in vitro root cultures, transformed by Agrobacterium rhizogenes, afforded the hitherto unreported sesquiterpenes ceratopicanol angelate (1), 8β-hydroxy-african-4(5)-en-3-one tiglate (4), 8β-hydroxy-african-4(5)-en-3-one 3′-angeloxy-2′-methylbutanoate (5), 1α,8β-dihydroxy-african-4(5)-en-3-one 8β-angelate (7) and 6α,8β-dihydroxy-african-4(5)-en-3-one 8β-angelate (8). In addition, 8β-hydroxy-african-4(5)-en-3-one (6) was isolated for the first time from a natural source, along with the rare sesquiterpenoid senecrassidiol (10) and two jacaranone derivatives 14 and 16. Known pyrrolizidine alkaloids, together with previously unreported hermosine (23), have also been isolated from this plant. The insect antifeedant activities of the extracts and compounds were studied together with their cytotoxic effects against insect (Sf9) and mammalian (CHO) cell lines.
Fraga, Braulio M.; Díaz, Carmen E.; Amador, Leonardo J.; Reina, Matías; Santana, Omar; González-Coloma, Azucena.
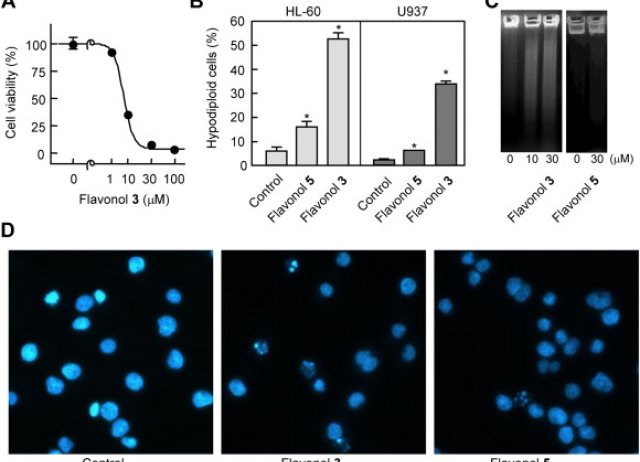
Synthesis and effects on cell viability of flavonols and 3-methyl ether derivatives on human leukemia cells
Flavonoids are polyphenolic compounds which display an array of biological activities and are considered potential antitumor agents. Here we evaluated the antiproliferative activity of selected synthetic flavonoids against human leukemia cell lines. We found that 4′-bromoflavonol (flavonol 3) was the most potent. This compound inhibited proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner, induced apoptosis and blocked cell cycle progression at the S phase. Cell death was found to be associated with the cleavage and activation of multiple caspases, the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and the up-regulation of two death receptors (death receptor 4 and death receptor 5) for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Moreover, combined treatments using 4′-bromoflavonol and TRAIL led to an increased cytotoxicity compared to single treatments. These results provide a basis for further exploring the potential applications of this combination for the treatment of cancer.
Burmistrova, Olga; Marrero, María Teresa; Estévez, Sara; Welsch, Isabel; Brouard, Ignacio; Quintana, José; Estévez, Francisco
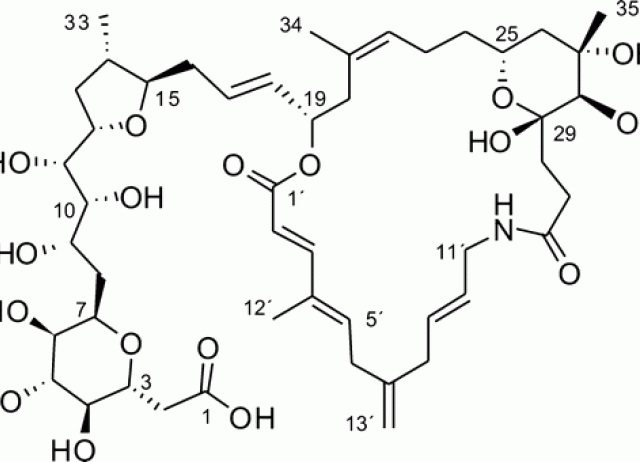
Belizentrin, a Highly Bioactive Macrocycle from the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum belizeanum
Belizentrin (1), a novel 25-membered polyketide-derived macrocycle, was isolated from cultures of the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum belizeanum. This metabolite is the first member of an unprecedented class of polyunsaturated and polyhydroxylated macrolactams. The structure of 1 was primarily determined by NMR and computational methods. Pharmacological assays with cerebellar cells showed that 1 produces important changes in neuronal network integrity at nanomolar concentrations.
Domínguez, Humberto J.; Napolitano, José G.; Fernández-Sánchez, M. Teresa; Cabrera-García, David, Novelli, Antonello; Norte, Manuel; Fernández, José J.; Hernández Daranas, Antonio