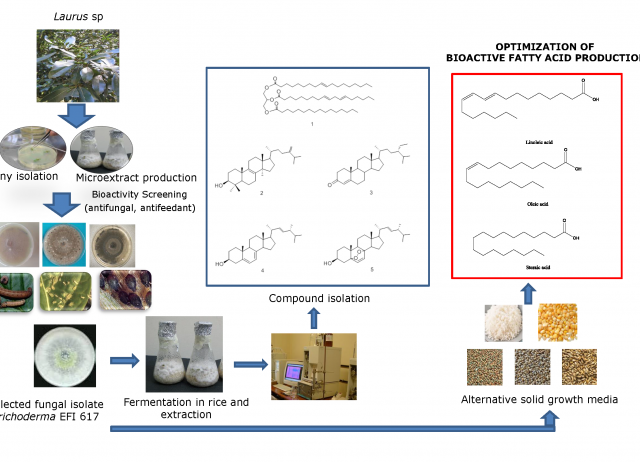
Chemical Composition of an Aphid Antifeedant Extract from an Endophytic Fungus, Trichoderma sp. EFI671
Botanical and fungal biopesticides, including endophytes, are in high demand given the current restrictive legislations on the use of chemical pesticides. As part of an ongoing search for new biopesticides, a series of fungal endophytes have been isolated from selected medicinal plants including Lauraceae species. In the current study, an extract from the endophytic fungus Trichoderma sp. EFI 671, isolated from the stem parts of the medicinal plant Laurus sp., was screened for bioactivity against plant pathogens (Fusarium graminearum, Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea), insect pests (Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae, Rhopalosiphum padi) and plant parasites (Meloidogyne javanica), with positive results against M. persicae. The chemical study of the neutral fraction of the active hexane extract resulted in the isolation of a triglyceride mixture (m1), eburicol (2), β-sitostenone (3), ergosterol (4) and ergosterol peroxide (5). The free fatty acids present in the acid fraction of the extract and in m1 (oleic, linoleic, palmitic and stearic) showed strong dose-dependent antifeedant effects against M. persicae. Liquid (potato dextrose broth, PDB and Sabouraud Broth, SDB) and solid (corn, sorghum, pearl millet and rice) growth media were tested in order to optimize the yield and bioactivity of the fungal extracts. Pearl millet and corn gave the highest extract yields. All the extracts from these solid media had strong effects against M. persicae, with sorghum being the most active. Corn media increased the methyl linoleate content of the extract, pearl millet media increased the oleic acid and sorghum media increased the oleic and linoleic acids compared to rice. The antifeedant effects of these extracts correlated with their content in methyl linoleate and linoleic acid. The phytotoxic effects of these extracts against ryegrass, Lolium perenne, and lettuce, Lactuca sativa, varied with culture media, with sorghum being non- toxic.
Kaushik, Nutan; Díaz, Carmen E.; Chhipa, Hemraj; Fernando Julio, L.; Fe Andrés, M.; González-Coloma, Azucena
Synthetic Approaches to Phosphasugars (2-oxo-1,2-oxaphosphacyclanes) Using the Anomeric Alkoxyl Radical β-Fragmentation Reaction as the Key Step
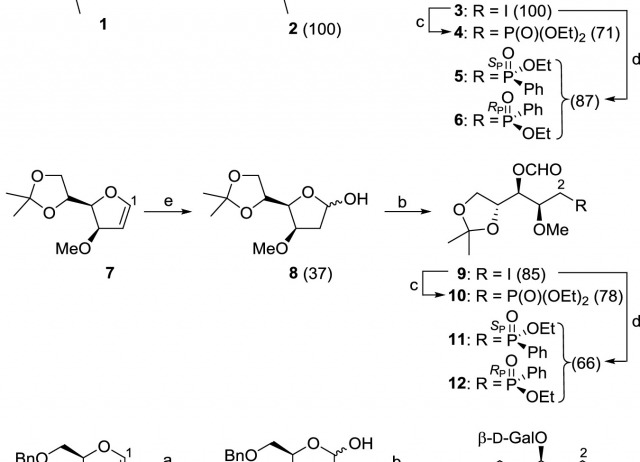
The anomeric alkoxyl radical β-fragmentation (ARF) of carbohydrates possessing an electron-withdrawing group (EWG) at C2, promoted by PhI(OAc)2/I2, gives rise to an acyclic iodide through which a pentavalent atom of phosphorus can be introduced via the Arbuzov reaction. After selective hydrolysis and subsequent cyclization, the phosphonate or phosphinate intermediates can be converted into 2-deoxy-1-phosphahexopyranose and 2-deoxy-1-phosphapentopyranose sugars. The ARF of carbohydrates with an electron-donor group (EDG) at C2 proceeds by a radical-polar crossover mechanism, and the cyclization occurs by nucleophilic attack of a conveniently positioned phosphonate or phosphinate group to the transient oxocarbenium ion. This alternative methodology leads to 5-phosphasugars with a 4-deoxy-5-phosphapentopyranose framework. The structure and conformation of the 2-oxo-1,2-oxaphosphinane and 2-oxo-1,2-oxaphospholane ring systems in different carbohydrate models have been studied by NMR and X-ray crystallography.
Hernández-Guerra, Daniel; Kennedy, Alan R.; León, Elisa I.; Martín, Ángeles; Pérez-Martín, Inés; Rodríguez Morales, María S.; Suárez, Ernesto
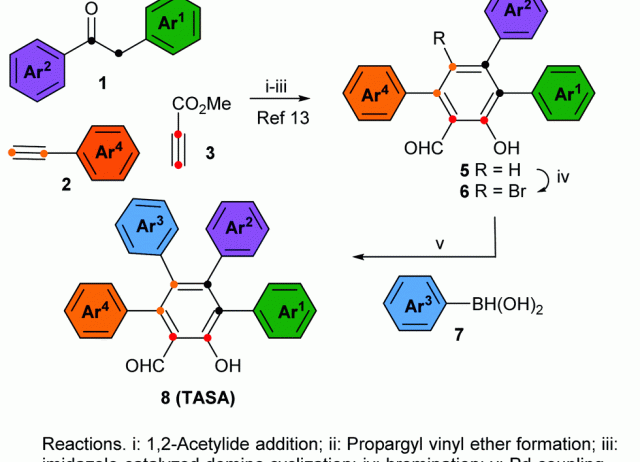
Short and modular synthesis of tetraarylsalicylaldehydes
In this study, we describe a novel strategy that allows the obtention of all 15 possible substitution geometries of perarylated salicylaldehydes with total control of the regioselectivity. This strategy entitles the formation of the salicylaldehyde core via a Claisen rearrangement of propargyl vinyl ethers, followed by bromination and Pd-catalyzed aryl–aryl cross-coupling reactions.
Tejedor, David; Delgado-Hernández, Samuel; Santamaría-Peláeza, Blanca; García-Tellado, Fernando
BPEC: An R Package for Bayesian Phylogeographic and Ecological Clustering
BPEC is an R package for Bayesian phylogeographic and ecological clustering which allows geographical, environmental and phenotypic measurements to be combined with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences in order to reveal geographic structuring of DNA sequence clusters consistent with migration events. DNA sequences are modelled using a collapsed version of a simplified coalescent model projected onto haplotype trees, which subsequently give rise to constrained clusterings as migrations occur. Within each cluster, a multivariate Gaussian distribution of the covariates (geographical, environmental, phenotypic) is used. Inference follows tailored reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling so that the number of clusters (i.e., migrations) does not need to be pre-specified. A number of output plots and visualizations are provided which reflect the posterior distribution of the parameters of interest. BPEC also includes functions that create output files which can be loaded into Google Earth. The package commands are illustrated through an example dataset of the polytypic Near Eastern brown frog Rana macrocnemis analyzed using BPEC.
Manolopoulou, Ioanna; Hille, Alex; Emerson, Brent C.
Impact of Saharan dust on the incidence of acute coronary syndrome
Introduction and objectives: Asian desert dust has recently been recognized as a trigger for acute myocardial infarction. The inflow of dust from the Sahara into Spain impairs air quality due to an increase in particulate matter concentrations in the ambient air. The aim of the present study was to elucidate whether Saharan dust events are associated with the incidence of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in patients living near North Africa, the major global dust source. Methods: We prospectively collected data on hospitalizations due to ACS in 2416 consecutive patients from a tertiary care hospital (Canary Islands, Spain) from December 2012 to December 2017. Concentrations of particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter 10 microns or smaller (PM10) and reactive gases were measured in the European Air Quality Network implemented in the Canary Islands. We applied the time-stratified case crossover design using conditional Poisson regression models to estimate the impact of PM10 Saharan dust events on the incidence of ACS. Results: The occurrence of Saharan dust events observed 0 to 5 days before the onset of ACS was not significantly associated with the incidence of ACS. Incidence rate ratios (IRR) of PM10 levels 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days before ACS onset (for changes in 10 mg/m3) were 1.27 (95%CI, 0.87-1.85), 0.92 (95%CI, 0.84-1.01), 0.74 (95%CI, 0.45-1.22), 0.98 (95%CI, 0.87-1.11), and 0.95 (95%CI, 0.84-1.06), respectively. Conclusions: Exposure to Saharan desert dust is unlikely to be associated with the incidence of ACS.
Domínguez-Rodríguez, Alberto; Rodríguez, Sergio; Baez-Ferrer, Nestor; Avanzas, Pablo; Abreu-González, Pedro; Silva, Jacob; Morís, César; Hernández-Vaquero, Daniel
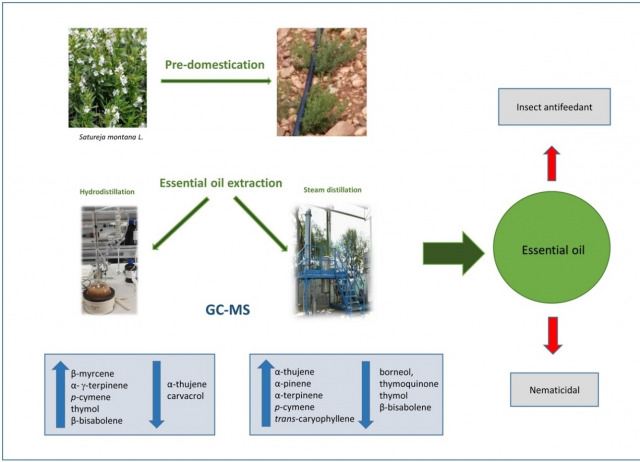
Composition and biocidal properties of essential oil from pre-domesticated Spanish Satureja Montana
The aim of this study was to develop a chemically stable plant following a pre-domestication process and the valorization of its essential oil for the production of biopesticides. This study was conducted during four growing seasons to give a pre-domesticated population (SAMO-0). The resulting pre-domesticated population increased the hydrodistilled oil yield (average 0.45%) and maintained a stable yield of dry material (44.5%). The plant material was submitted to pilot plant scale steam distillation under three pressures (0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 bar) with lower yield (average 0.15%). The essential oil showed a carvacrol / p-cymene chemotype. The pre-domestication process increased β-myrcene, α- and γ-terpinene, p-cymene, thymol and β-bisabolene; and decreased α-thujene and carvacrol. The steam distillation increased the oil content in α-thujene, α-pinene, α-terpinene, p-cymene and trans-caryophyllene, and decreased borneol, thymoquinone thymol and β-bisabolene. Pressure increased α-terpinene, thymol and carvacrol Additionally, the study of the biocidal effects (against the insect pests Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae and Leptinotarsa decemlineata and the phytopathogenic nematode Meloydogine javanica) of the EOs showed that overall, the most active oils were the hydrodistilled (to all insect species), followed by the steam distilled oils with higher carvacrol and thymol content (pressures of 1.5 and 1.0 bar). Carvacrol and thymol were responsible for the activity of these oils on M. persicae, and L. decemlineata but only partially on S. littoralis. The steam distilled oils showed strong nematicidal activity against M. javanica that could be partially explained by their content in active carvacrol and thymol.
Navarro-Rocha, Juliana; Andrés, María Fe; Díaz, Carmen E.; Burillo, Jesús; González-Coloma, Azucena
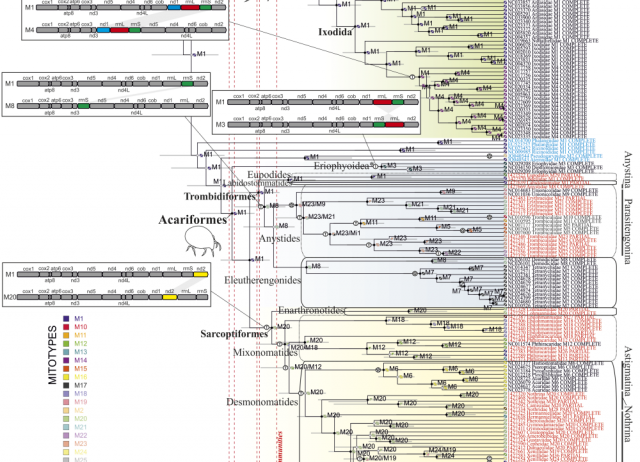
Mitochondrial Metagenomics Reveals the Ancient Origin and Phylodiversity of Soil Mites and Provides a Phylogeny of the Acari
High-throughput DNA methods hold great promise for phylogenetic analysis of lineages that are difficult to study with conventional molecular and morphological approaches. The mites (Acari), and in particular the highly diverse soil-dwelling lineages, are among the least known branches of the metazoan Tree-of-Life. We extracted numerous minute mites from soils in an area of mixed forest and grassland in southern Iberia. Selected specimens representing the full morphological diversity were shotgun sequenced in bulk, followed by genome assembly of short reads from the mixture, which produced >100 mitochondrial genomes representing diverse acarine lineages. Phylogenetic analyses in combination with taxonomically limited mitogenomes available publicly resulted in plausible trees defining basal relationships of the Acari. Several critical nodes were supported by ancestral-state reconstructions of mitochondrial gene rearrangements. Molecular calibration placed the minimum age for the common ancestor of the superorder Acariformes, which includes most soil-dwelling mites, to the Cambrian–Ordovician (likely within 455–552 Ma), whereas the origin of the superorder Parasitiformes was placed later in the Carboniferous-Permian. Most family-level taxa within the Acariformes were dated to the Jurassic and Triassic. The ancient origin of Acariformes and the early diversification of major extant lineages linked to the soil are consistent with a pioneering role for mites in building the earliest terrestrial ecosystems.
Arribas, Paula; Andújar, Carmelo ; Lourdes Moraza, María; Linard, Benjamin; Emerson, Brent C.; Vogler, Alfried P.
Potential role of lava lizards as pollinators across the Galápagos Islands
Lizards have been reported as important pollinators on several oceanic islands. Here we evaluate the potential role of Galápagos lava lizards (Microlophus spp.) as pollinators across their radiation. Over 3 years, we sampled pollen transport by 9 lava lizard species on the 10 islands where they are present, including 7 single‐island endemics. Overall, only 25 of 296 individuals sampled (8.4%) transported pollen of 10 plant species, the most common being Prosopis juliflora, Exodeconus miersii, Sesuvium sp. and Cordia leucophlyctis. At least 8 of these plant species were native, and none were confirmed as introduced to the archipelago. Despite the low overall proportion of individuals carrying pollen, this was observed in 7 of the nine lizard species, and on 8 of the ten main islands (Española, Fernandina, Floreana, Isabela, Marchena, Pinta, Santa Cruz and Santiago), suggesting that this is a widespread interaction. The results reported here support the potential role of lava lizards as pollinators across their radiation, although they may represent a relatively modest contribution when compared with birds and insects. However, we cannot discard that lizards may be ecologically significant for particular plant species and ecosystems given the specific climatic condition and functional diversity of each island.
Hervías-Parejo, Sandra; Nogales, Manuel; Guzmán, Beatriz; Trigo, María del Mar; Olesen, Jens M.; Vargas Pablo; Heleno, Rubén H.; Traveset, Anna
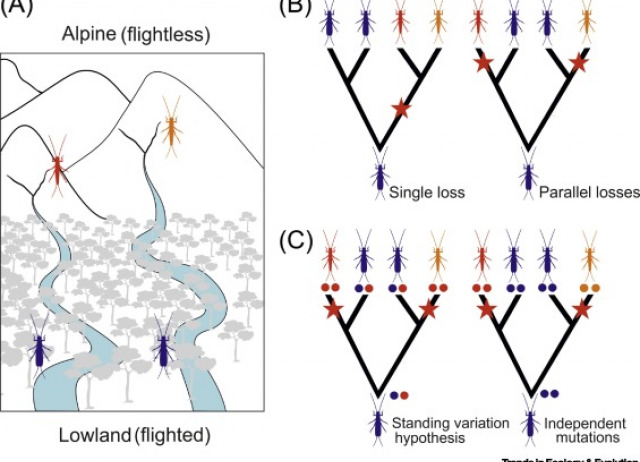
Dispersal Reduction: Causes, Genomic Mechanisms, and Evolutionary Consequences
Recent biological analyses suggest that reductions in dispersal ability have beenkey drivers of diversification across numerous lineages. We synthesise emergingdata to highlight similarities regarding the causes and consequences of dispersalreduction across taxa and ecosystems, as well as the diverse genomic mechanismsunderpinning these shifts. Natural selection has acted on standing genetic variationwithin taxa to drive often rapid–and in some cases parallel–losses of dispersal,and ultimately speciation. Such shifts can thus represent an important nexus be-tween adaptive and neutral diversification processes, with substantial evolutionaryconsequences. Recognition of the links between these concepts that are emergingfrom differentfields, taxa and ecosystems is transforming our understanding of thefascinating role of dispersal reduction in the formation of biodiversity.
Waters, J.M.; Emerson, Brent C.; Arribas, Paula; McCulloch, G. A.
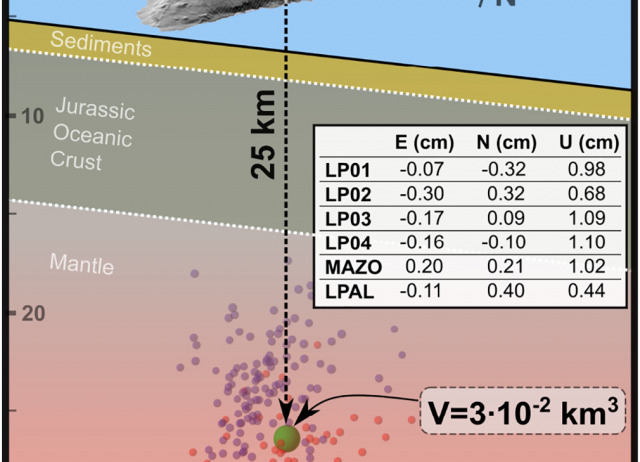
Unrest signals after 46 years of quiescence at Cumbre Vieja, La Palma, Canary Islands
Monogenetic eruptions are the most common volcanic activity in the world. However, unrest monitoring data are scarce due to the long intervening quiescence periods. This study analyzes unrest signals recorded in one of the largest monogenetic fields in the Canary Islands, Cumbre Vieja (La Palma). Two seismic swarms were registered in October 2017 and February 2018 with b-values of 1.6 ± 0.1 and 2.3 ± 0.2 respectively suggesting an intense magmatic fluids contribution, gas and/or magma. Both swarms were linked to changes in gas emissions. Increases in hydrogen concentration, and (R/R) up to 7.52 ± 0.05, were recorded before the first swarm, at the sampling point closest to where seismicity was located, indicating a deep gas input. After the second swarm, increases in (R/R) and thoron soil concentration were recorded at two locations. This dataset is compatible with a stalled magmatic intrusion at ca. 25 km depth, with an estimated volume between 5.5·10 km and 3·10 km.
Torres-González, Pedro A.; Luengo-Oroz, Natividad; Lamolda, Héctor; D'Alessandro, Walter; Albert, Helena; Iribarren, Ilazkiñe; Moure-García, David; Soler, Vicente