Publications
This section includes a list of the latest IPNA scientific articles published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI).
In DIGITAL.CSIC, institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles since 1962, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc. of the centre. The aim of DIGITAL.CSIC is to organize, preserve and disseminate in open access the results of our research.
In the institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc.
Analysis of the IPNA 2014-2019 Scientific Production: bibliometric analysis from data collected in Scopus and Web of Science.

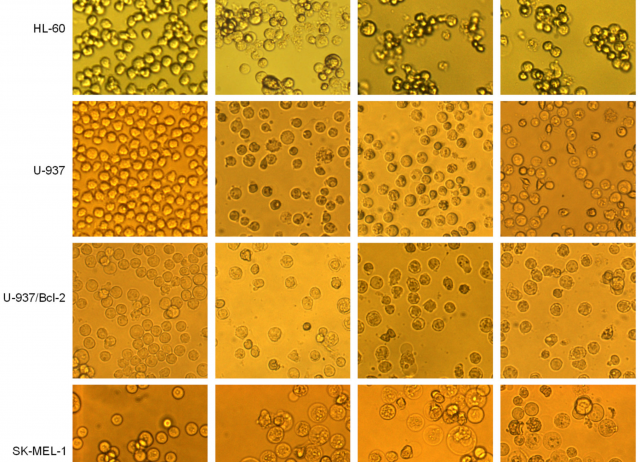
Chlorinated Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpene Lactones as Cytotoxic Agents against Human Tumor Cells
Guaiane-type sesquiterpene lactones are naturally occurring compounds which have attracted attention due to their array of biological activities. In this study, chlorinated guaianolides <b>1</b>–<b>8</b>, isolated from plants of the genus <i>Centaurea</i>, were evaluated against the human leukemia cell lines HL-60, U-937, a specific U-937 cell line that overexpresses the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and the human melanoma cell line SK-MEL-1. This established the relevant structure-growth inhibition relationships. Chlorohyssopifolins A (<b>1</b>), C (<b>3</b>) and D (<b>4</b>) and linichlorin A (<b>6</b>) were the most potent compounds in terms of inducing growth inhibition in the four cell lines. IC<sub>50</sub> values were below 10 μM in all cases. Chlorohyssopifolins A (<b>1</b>) and D (<b>4</b>) and linichlorin A (<b>6</b>) were potent apoptotic inducers in human U-937 leukemia cells, as determined by fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry, and their mechanism of action was associated with cytochrome <i>c</i> release, caspase activation and poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase cleavage. Overall this study shows that guaianolides induce cytotoxicity against human tumor cells and provides important insights into the cell death pathways that are involved.
Estévez-Sarmiento, Francisco; Saavedra, Ester; Ruiz-Estévez, Mercedes; León, Francisco; Quintana, José; Brouard, Ignacio; Estévez Francisco
Marine Anticancer Agents: An Overview with a Particular Focus on Their Chemical Classes
The marine environment is a rich source of biologically active molecules for the treatment of human diseases, especially cancer. The adaptation to unique environmental conditions led marine organisms to evolve di erent pathways than their terrestrial counterparts, thus producing unique chemicals with a broad diversity and complexity. So far, more than 36,000 compounds have been isolated from marine micro- and macro-organisms including but not limited to fungi, bacteria, microalgae, macroalgae, sponges, corals, mollusks and tunicates, with hundreds of new marine natural products (MNPs) being discovered every year.Marine-based pharmaceuticals have started to impactmodern pharmacology and different anti-cancer drugs derived frommarine compounds have been approved for clinical use, such as: cytarabine, vidarabine, nelarabine (prodrug of ara-G), fludarabine phosphate (pro-drug of ara-A), trabectedin, eribulin mesylate, brentuximab vedotin, polatuzumab vedotin, enfortumab vedotin, belantamab mafodotin, plitidepsin, and lurbinectedin. This review focuses on the bioactive molecules derived from the marine environment with anticancer activity, discussing their families, origin, structural features and therapeutic use.
Barrera, Marilia; Spanò, Virginia; Montalbano, Alessandra; Cueto, Mercedes; Díaz Marrero, Ana R.; Deniz, Irem; Erdogan, Aysegül; Lukic Bilela, Lada; Moulin, Corentin; Taffin-de-Givenchy, Elisabeth; Spriano, Filippo; Perale, Giuseppe; Mehiri, Mohamed; Rotter, Ana; Thomas, Olivier P.; Barraja, Paola; Gaudêncio, Susana P.; Bertoni, Francesco
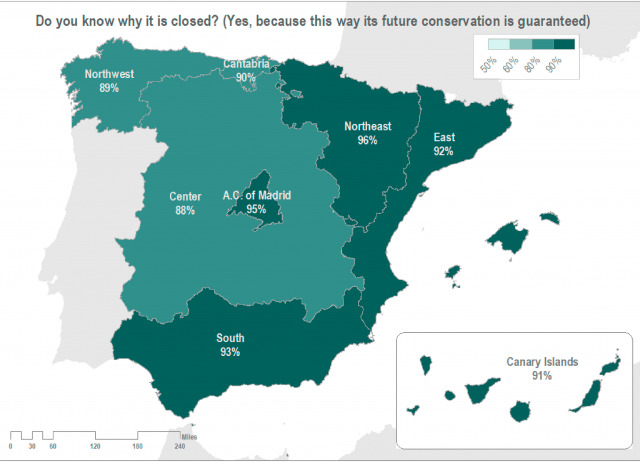
The social value of heritage: Balancing the promotion-preservation relationship in the Altamira World Heritage Site, Spain
The designation of World Heritage Sites (WHSs) by UNESCO strengthens the international and national image of heritage destinations in the growing market of cultural tourism. Understanding how different stakeholders interpret the value of cultural heritage is one of the most important assets for balancing the promotion and protection of WHSs. This study draws on the case of the Altamira Prehistoric Cave WHS (Spain), whose preservation is under threat and constant debate. It explores factors determining the social value of heritage, namely: existence, aesthetic, economic, and legacy value. In doing so, this paper contributes to emerging debates on heritage management and tourist destinations. Data were collected using two surveys, one focused on visitors, with a total of 1047 valid surveys, and another on the Spanish population as a WHS host community, with a total of 1000 valid surveys. The analysis of these surveys shows how the existence, aesthetic, economic and legacy value dimensions of cultural heritage can build up brands around WHSs. The social-value dimension of cultural heritage therefore affects the market potential of WHSs, whose market potential is closely related to the education levels of a given society. These findings provide valuable information and insights for academics, destination managers and policy-makers in the debate about the preservation and tourism branding of Altamira. This will allow different stakeholders to identify opportunities to develop synergies between tourism promotion and heritage preservation, to both strengthen the brand image of a WHS and preserve its heritage.
Parga-Dans, Eva; Alonso-González, Pablo; Otero Enríquez, Raimundo
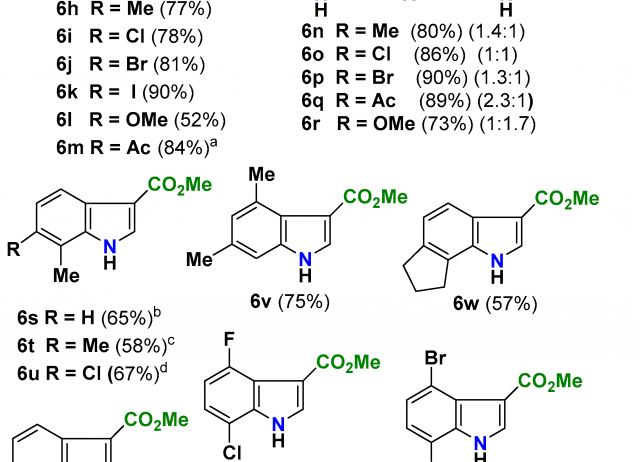
A General and Scalable Synthesis of Polysubstituted Indoles
A consecutive 2-step synthesis of N-unprotected polysubstituted indoles bearing an electron-withdrawing group at the C-3 position from readily available nitroarenes is reported. The protocol is based on the [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of N-oxyenamines generated by the DABCO-catalyzed reaction of N-arylhydroxylamines and conjugated terminal alkynes, and delivers indoles endowed with a wide array of substitution patterns and topologies.
Tejedor, David; Diana-Rivero, Raquel; García-Tellado, Fernando
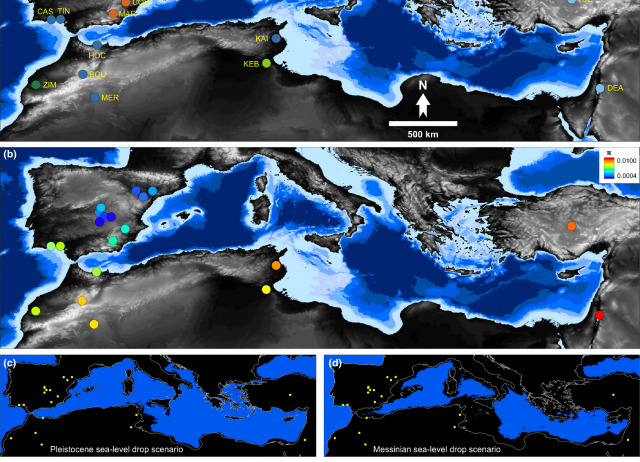
Genomic insights into the origin of trans‐Mediterranean disjunct distributions
Aim
Two main biogeographical hypotheses have been proposed to explain the Mediterranean‐Turanian disjunct distributions exhibited by numerous steppe‐dwelling organisms, namely (a) dispersal during the Messinian salinity crisis (∼5.96–5.33 Ma) followed by range fragmentation and vicariance, and (b) Pleistocene colonization and recent processes of population subdivision (<2 Ma). Despite the two hypotheses postulate the role of climatic alterations and changes in landmass configuration on determining such disjunct distributions, estimates of the timing of lineage diversification have not been complemented so far with spatially‐explicit tests providing independent evidence on the proximate processes underlying geographical patterns of population genetic connectivity/fragmentation.
Location
Mediterranean‐Turanian region.
Taxon
Saltmarsh band‐winged grasshopper (Mioscirtus wagneri).
Methods
We integrate different sources of genetic (mtDNA and ddRADseq) and spatial information (configuration of emerged lands and niche modelling) to evaluate competing hypotheses of lineage diversification in the saltmarsh band‐winged grasshopper, a halophile species showing a classical Mediterranean‐Turanian disjunct distribution.
Results
Phylogenomic analyses reveal the presence of two North African cryptic lineages and support that trans‐Mediterranean populations of the species diverged in the Pleistocene, with evidence of post‐Messinian permeability of the Strait of Gibraltar to gene flow likely associated with sea level drops during glacial periods. Accordingly, spatial patterns of genetic differentiation are best explained by a scenario of population connectivity defined by the configuration of emerged landmasses and environmentally suitable habitats during glacial periods, a time when effective population sizes of the species peaked as inferred by genomic‐based demographic reconstructions.
Main conclusions
Our results support post‐Messinian colonization and Pleistocene diversification as the biogeographical scenario best explaining the trans‐Mediterranean disjunct distributions of halophilous organisms.
Noguerales, Víctor; Cordero, Pedro J.; Knowles, L. Lacey; Ortego, Joaquín
Species functional traits and abundance as drivers of multiplex ecological networks: first empirical quantification of inter-layer edge weights
Many vertebrate species act as both plant pollinators and seed-dispersers, thus interconnecting these processes, particularly on islands. Ecological multilayer networks are a powerful tool to explore interdependencies between processes; however, quantifying the links between species engaging in different types of interactions (i.e. inter-layer edges) remains a great challenge. Here, we empirically measured inter-layer edge weights by quantifying the role of individually marked birds as both pollinators and seed-dispersers of Galápagos plant species over an entire year. Although most species (80%) engaged in both functions, we show that only a small proportion of individuals actually linked the two processes, highlighting the need to further consider intra-specific variability in individuals' functional roles. Furthermore, we found a high variation among species in linking both processes, i.e. some species contribute more than others to the modular organization of the multilayer network. Small and abundant species are particularly important for the cohesion of pollinator seed-dispersal networks, demonstrating the interplay between species traits and neutral processes structuring natural communities.
Hervías-Parejo, Sandra; Tur, Cristina; Heleno, Rubén; Nogales, Manuel; Timóteo, Sérgio; Traveset, Anna
Food habits of the Macaronesian Sparrowhawk (Accipiter Nisus Granti) on Madeira
The Eurasian Sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus) is a small bird of prey distributed throughout Europe and Asia and closely linked to forest environments. It is a predator of a wide diversity of prey, primarily birds (Newton et al. 1986). On the mainland, the male Eurasian Sparrowhawk typically captures small birds (40–120 g in mass), whereas females (nearly twice the mass of males) prey on larger birds (up to 500 g; Opdam 1975, Newton 1978).
González, Yolanda; Hervías-Parejo, Sandra; Pereira, Estefanía; Vulcano, Antonio; Álvarez, Soledad; Gouveia, Cátia; Nunes, Marta; Castelló, Laura; Fagundes, Isabel; Coelho, Nádia; Delgado, Guillermo, Nogales, Manuel
Prorocentroic Acid, a Neuroactive Super-Carbon-Chain Compound from the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum hoffmannianum
Prorocentroic acid (PA) was isolated from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum hoffmannianum. Relative configurations for its 35 asymmetric centers, were determined by analysis of NMR data including heteronuclear couplings and quantum mechanical calculations. PA was tested by using murine cortical neurons grown on microelectrode-arrays. Long term exposure to subtoxic concentrations induced a significant reorganization of neuronal signaling, mainly by changes in the bursting activity. The observed effects could be due to the activation of a plasticity process.
Domínguez, Humberto J.; Cabrera-García, David; Cuadrado, Cristina; Novelli, Antonello; Fernández-Sánchez, M. Teresa; Fernández, José J.; Hernández Daranas, Antonio
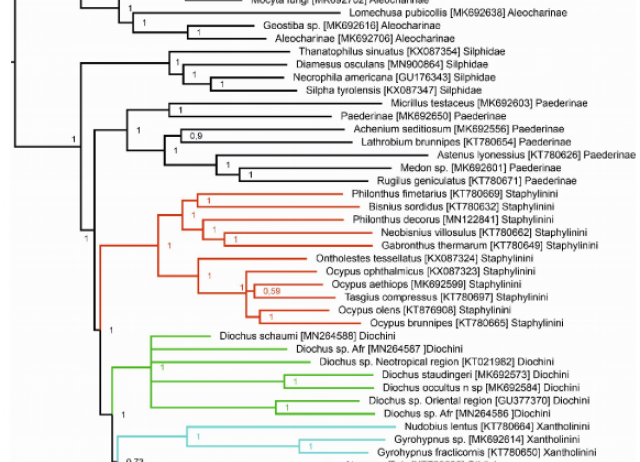
Mitogenomic phylogenetics of Diochus occultus n. sp., a palaeoendemic endogean species within the tribe Diochini (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Staphylininae)
The tribe Diochini has a worldwide distribution, with 2 and 74 epigean species within the genera Antarctothius and Diochus respectively. Recent phylogenetic studies suggest a sister relationship of Diochini and a lineage formed by Xantholinini, Maorothiini, and Othiini, within the subfamily Staphylininae. Here we describe the first known endogean representative of Diochini, Diochus occultus n. sp., and provide the first two complete mitogenomes for the tribe, corresponding to the two European Diochus species: Diochus occultus n. sp. and Diochus staudingeri. These sequences were combined with 40 additional mitogenomes from representatives within Staphylininae, Paederinae, Silphidae, and Aleocharinae, and COI sequences from 5 additional species of Diochus to conduct a series of mitogenomic phylogenetic and dating analyses. The estimated molecular phylogeny is fully consistent with previous studies based on morphology and molecular data, finding a sister relationship of Diochini with a clade formed by Xantholinini and Othiini (Maorothiini not sampled). Dating analyses inferred an early split of the tribe Diochini at 140-156 Mya. Morphology shows clear differences in the aedeagal and external morphology of D. occultus n. sp. and D. staudingeri, whereas a sister relationship of these taxa is found in the phylogenetic analyses, with the split dated at 48-61 Mya. Although the study of additional Palaearctic Diochus species will be required to conclusively establish that D. occultus n. sp. is a palaeoendemic taxon sister to D. staudingeri, associated to forests of Abies pinsapo in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, this conclusion is consistent with the ancient estimated age of speciation, endogean habitat specificity, low dispersal capacity (flightless species), and microendemicity of D. occultus. This is also consistent with the continued emersion of the Betic sub-plate along its tectonic evolution. The estimated ages of diversification of the Paederinae-Staphylininae lineage are also discussed.
Hernando, Carles; Andújar, Carmelo
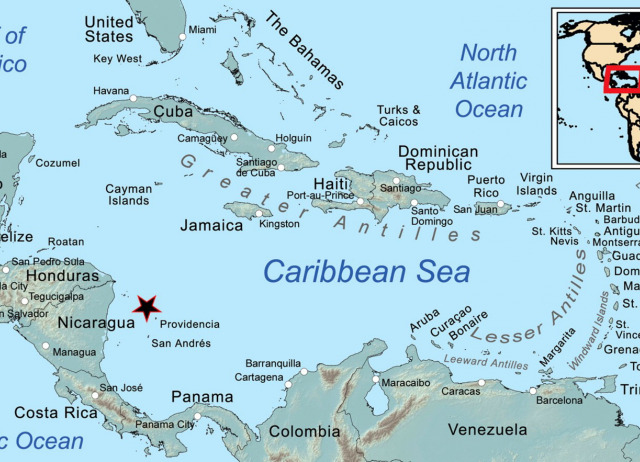
Equality and Hierarchy, Sovereignty and Multiculturalism: the Heritagisation of Raizals in Santa Catalina (Colombia)
Santa Catalina is a Caribbean island in the Colombian archipelago of Providencia y San Andrés, which has been at the center of a recent territorial dispute between Colombia and Nicaragua that has made the islands central to the geostrategic agenda of the Colombian state in its attempt to reaffirm political alliances with the United States. Within this context, our investigation explores recent processes of archaeological research, heritagisation and tourism promotion on Santa Catalina Island that triggered a conflict between the local raizal population (Afro-descendant, Caribbean, Puritan and English-speaking) and the State (white, Andean, Catholic and Spanish-speaking) around the meaning of two key sites of memory—Fuerte Libertad (Fort Warwick) and the Cabeza de Morgan (Morgan's Head). Drawing on long-term ethnography, this paper reveals how the neoliberal, multicultural state of Colombia has functioned as an investment facilitator and a key actor in transforming ethnic-racial differences into class inequalities.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Londoño, Wilhelm; Parga-Dans, Eva