Publications
This section includes a list of the latest IPNA scientific articles published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI).
In DIGITAL.CSIC, institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles since 1962, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc. of the centre. The aim of DIGITAL.CSIC is to organize, preserve and disseminate in open access the results of our research.
In the institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc.
Analysis of the IPNA 2014-2019 Scientific Production: bibliometric analysis from data collected in Scopus and Web of Science.

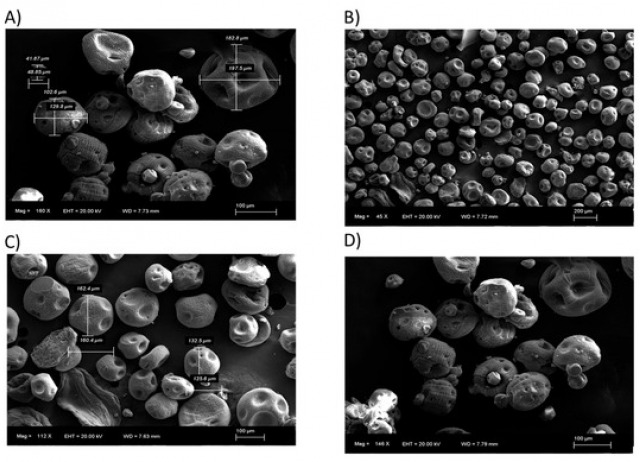
Alginate Microencapsulation as a Tool to Improve Biostimulant Activity Against Water Deficits
Climate change is reducing agricultural productivity through altered weather patterns and extreme events, potentially decreasing yields by 10–25%. Biostimulants like pyroglutamic acid can enhance plant tolerance to water stress, but their rapid degradation in the soil limits effectiveness. Encapsulation in alginate matrices promises to be a good solution, protecting the compound and enabling controlled release. This study reports, for the first time, that encapsulated pyroglutamic acid markedly enhances drought tolerance in tomato and maize plants. The encapsulation strategy reduces effective concentration by an order of magnitude while significantly improving water use efficiency, photo-synthetic performance, and overall stress resilience. These findings demonstrate that alginate-based encapsulation substantially increases biostimulant uptake and efficacy, providing a novel and efficient strategy to mitigate water stress in crops, with important implications for climate-resilient agriculture. Two encapsulation methods for generating the alginate microcapsules are compared: ionic gelation with Nisco® system and the electrospray technique.
Jiménez-Arias, David; Morales-Sierra, Sarai; García-García, Ana L.; Herrera, Antonio J.; Pérez Schmeller, Rayco; Suárez, Emma; Santana-Mayor, Álvaro; Silva, Patrícia; Borges, João Paulo; Pinheiro de Carvalho, Miguel Â. A.
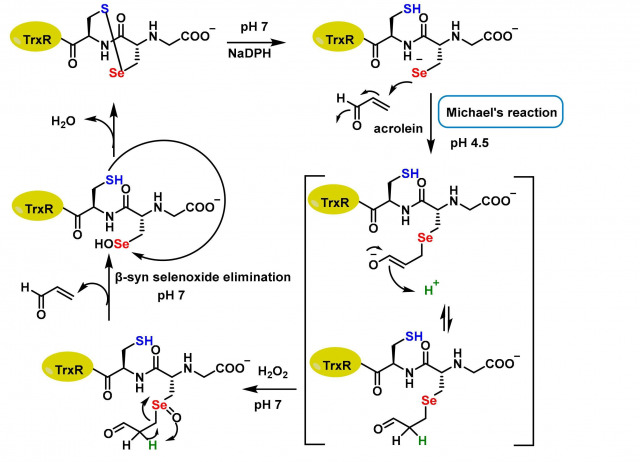
Cysteine Alkylation in Enzymes and Transcription Factors: A Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer
Metabolic enzymes and cancer-driving transcriptions factors are often overexpressed in neoplastic cells, and their exposed cysteine residues are amenable to chemical modification. This review explores cysteine alkylation as a cancer treatment strategy, focusing on Michael acceptors like curcumin and helenalin, which interact with transcription factors NF-κB, STAT3 and HIF-1α. Molecular docking studies using AutoDockFR revealed distinct binding affinities: curcumin showed strong interactions with STAT3 and NF-κB, while helenalin exhibited high affinity for STAT3 and HIF-1α. Synthetic compounds like STAT3-IN-1 and CDDO-Me demonstrated superior binding in most targets, except for CDDO-Me with HIF-1α, suggesting unique structural incompatibilities. Natural products such as zerumbone and umbelliferone displayed moderate activity, while palbociclib highlighted synthetic-drug advantages. These results underscore the importance of ligand−receptor structural complementarity, particularly for HIF-1α’s confined binding site, where helenalin’s terminal Michael acceptor system proved optimal. The findings advocate for integrating computational and experimental approaches to develop cysteine-targeted therapies, balancing synthetic precision with natural product versatility for context-dependent cancer treatment strategies.
Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Lobo, Fernando; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Bustamante Munguira, Elena; Andrés Juan, Celia; Pérez-Lebeña, Eduardo.
Pesticide Residues and Mycotoxins in Natural and Conventional Wines: Insights from Italy and Spain
Natural wine is a captivating and rapidly evolving phenomenon in the world of viticulture and winemaking. This movement, characterized by minimal intervention, low or no chemical additives, and a focus on terroir-driven expressions of grapes, has ignited a passionate following among wine enthusiasts, sommeliers, and eco-conscious consumers. It's more than just a beverage; it embodies a philosophy that aligns with contemporary sustainability and wellness trends. Though natural wine enthusiasts have produced ample coverage of the natural wine movement in books, essays and films, academics have lagged behind in their examination of this global phenomenon. In Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement, scholarly discussion reaches across disciplines to offer valuable insights for researchers, producers, wine enthusiasts and anyone with an interest in this movement. Exploring the relevance of natural wine offers a unique lens through which to examine the intersection of tradition, innovation, environmental stewardship, and the evolving tastes of modern consumers. Through the stories of the winemakers, the science behind natural fermentation, and the cultural and historical context, this book aims to provide a comprehensive look at how this movement is shaping the future of wine and our relationship with the natural world. Each essay from a thought leader in their respective field delves deep into the historical, ecological, and sociocultural dimensions of natural winemaking, shedding light on its ancient roots, ecological practices, and the philosophical underpinnings that drive the movement. Discussions of regulatory and consumer aspects will also elucidate the practical considerations of making and selling natural wine. Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement is a groundbreaking edited book that offers a comprehensive and scholarly exploration ofthe world of natural wine. This interdisciplinary volume brings together leading experts in fields ranging from enology and sensory studies to anthropology and philosophy, creating a rich tapestry of insights into the production, consumption, and cultural significance of natural wine. Academics, winemakers and wine enthusiasts alike will be illuminated by this volume.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Acosta-Dacal, Andrea; Zaccaroni, Annalisa; Luzardo, Octavio P.
Interview with Aaron Ayscough
Natural wine is a captivating and rapidly evolving phenomenon in the world of viticulture and winemaking. This movement, characterized by minimal intervention, low or no chemical additives, and a focus on terroir-driven expressions of grapes, has ignited a passionate following among wine enthusiasts, sommeliers, and eco-conscious consumers. It's more than just a beverage; it embodies a philosophy that aligns with contemporary sustainability and wellness trends. Though natural wine enthusiasts have produced ample coverage of the natural wine movement in books, essays and films, academics have lagged behind in their examination of this global phenomenon. In Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement, scholarly discussion reaches across disciplines to offer valuable insights for researchers, producers, wine enthusiasts and anyone with an interest in this movement. Exploring the relevance of natural wine offers a unique lens through which to examine the intersection of tradition, innovation, environmental stewardship, and the evolving tastes of modern consumers. Through the stories of the winemakers, the science behind natural fermentation, and the cultural and historical context, this book aims to provide a comprehensive look at how this movement is shaping the future of wine and our relationship with the natural world. Each essay from a thought leader in their respective field delves deep into the historical, ecological, and sociocultural dimensions of natural winemaking, shedding light on its ancient roots, ecological practices, and the philosophical underpinnings that drive the movement. Discussions of regulatory and consumer aspects will also elucidate the practical considerations of making and selling natural wine. Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement is a groundbreaking edited book that offers a comprehensive and scholarly exploration ofthe world of natural wine. This interdisciplinary volume brings together leading experts in fields ranging from enology and sensory studies to anthropology and philosophy, creating a rich tapestry of insights into the production, consumption, and cultural significance of natural wine. Academics, winemakers and wine enthusiasts alike will be illuminated by this volume.
Ayscough, Aaron; Alonso-González, Pablo.
Introduction: The Past and Future of Natural Wine
Natural wine is a captivating and rapidly evolving phenomenon in the world of viticulture and winemaking. This movement, characterized by minimal intervention, low or no chemical additives, and a focus on terroir-driven expressions of grapes, has ignited a passionate following among wine enthusiasts, sommeliers, and eco-conscious consumers. It's more than just a beverage; it embodies a philosophy that aligns with contemporary sustainability and wellness trends. Though natural wine enthusiasts have produced ample coverage of the natural wine movement in books, essays and films, academics have lagged behind in their examination of this global phenomenon. In Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement, scholarly discussion reaches across disciplines to offer valuable insights for researchers, producers, wine enthusiasts and anyone with an interest in this movement. Exploring the relevance of natural wine offers a unique lens through which to examine the intersection of tradition, innovation, environmental stewardship, and the evolving tastes of modern consumers. Through the stories of the winemakers, the science behind natural fermentation, and the cultural and historical context, this book aims to provide a comprehensive look at how this movement is shaping the future of wine and our relationship with the natural world. Each essay from a thought leader in their respective field delves deep into the historical, ecological, and sociocultural dimensions of natural winemaking, shedding light on its ancient roots, ecological practices, and the philosophical underpinnings that drive the movement. Discussions of regulatory and consumer aspects will also elucidate the practical considerations of making and selling natural wine. Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement is a groundbreaking edited book that offers a comprehensive and scholarly exploration ofthe world of natural wine. This interdisciplinary volume brings together leading experts in fields ranging from enology and sensory studies to anthropology and philosophy, creating a rich tapestry of insights into the production, consumption, and cultural significance of natural wine. Academics, winemakers and wine enthusiasts alike will be illuminated by this volume.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva.
Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement
Natural wine is a captivating and rapidly evolving phenomenon in the world of viticulture and winemaking. This movement, characterized by minimal intervention, low or no chemical additives, and a focus on terroir-driven expressions of grapes, has ignited a passionate following among wine enthusiasts, sommeliers, and eco-conscious consumers. It's more than just a beverage; it embodies a philosophy that aligns with contemporary sustainability and wellness trends. Though natural wine enthusiasts have produced ample coverage of the natural wine movement in books, essays and films, academics have lagged behind in their examination of this global phenomenon.
In Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement, scholarly discussion reaches across disciplines to offer valuable insights for researchers, producers, wine enthusiasts and anyone with an interest in this movement. Exploring the relevance of natural wine offers a unique lens through which to examine the intersection of tradition, innovation, environmental stewardship, and the evolving tastes of modern consumers. Through the stories of the winemakers, the science behind natural fermentation, and the cultural and historical context, this book aims to provide a comprehensive look at how this movement is shaping the future of wine and our relationship with the natural world. Each essay from a thought leader in their respective field delves deep into the historical, ecological, and sociocultural dimensions of natural winemaking, shedding light on its ancient roots, ecological practices, and the philosophical underpinnings that drive the movement. Discussions of regulatory and consumer aspects will also elucidate the practical considerations of making and selling natural wine.
Uncorked: Negotiating Science and Belief in the Natural Wine Movement is a groundbreaking edited book that offers a comprehensive and scholarly exploration ofthe world of natural wine. This interdisciplinary volume brings together leading experts in fields ranging from enology and sensory studies to anthropology and philosophy, creating a rich tapestry of insights into the production, consumption, and cultural significance of natural wine. Academics, winemakers and wine enthusiasts alike will be illuminated by this volume.
Alonso-González, Pablo (Ed.); Parga-Dans, Eva (Ed.)
Physiological Traits Combination Shapes Common Strategies of Water and Carbon Use Regulation Across Fruit Tree Species
Crop plants, including fruit trees, are particularly vulnerable to water scarcity because past selection prioritized productivity over drought resistance, making it challenging to maintain productivity with minimal water use in the context of climate change. This study aims to determine which trait combination of 10 fruit tree species influences their water and carbon use, with the goal of understanding their adaptability to water scarcity. The results showed that water stress traits (turgor loss point, TLP; vulnerability index, VI), a carbon-related trait (specific leaf area; SLA), and a biomass allocation trait (Huber value; Hv) define the major axis of variability and present the strongest correlations with other traits. Two distinct strategies emerged: the first, mainly around Prunus species, was characterized by high Hv, low SLA, more negative TLP, and low VI, indicating greater water-stress tolerance due to sapwood redundancy and reduced organ vulnerability. They also exhibited higher maximum photosynthetic rates, indicating greater assimilation rates. The second strategy, mainly including Citrus species, exhibited opposite traits and trends. These trait combinations were likely shaped by shared ancestry and environmental factors. Understanding these correlations can guide irrigation practices and the selection of resilient species, contributing to more robust agricultural systems in a changing climate scenario.
Hernández Santana, V.; Sebastián Azcona, Jaime; Rodríguez Domínguez, Celia M.; Pérez Martín, Alfonso; Montero de Espinosa, Antonio; Benzal Moreno, Daniel; Rossi, Federica; Pérez-Romero, Luis F.; Díaz-Espejo, Antonio.
In Silico Exploration of Natural Antioxidants for Sepsis Drug Discovery
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by immune dysregulation and organ damage, remains a significant clinical challenge. Natural antioxidant compounds (NAOs) such as quercetin, EGCG, resveratrol, curcumin, and chlorogenic acid have shown promising anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in preclinical models of sepsis and related conditions, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying their actions remain incompletely defined. In this study, we performed comprehensive molecular docking analyses to investigate the binding affinities and interaction profiles of these NAOs with three key proteins central to inflammatory and apoptotic signaling: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4), interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), and caspase-3. Our results demonstrate that all five compounds exhibit favorable binding affinities with these targets, forming multiple hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions with critical active site residues. Notably, curcumin and EGCG consistently displayed the strongest binding affinities across the three proteins, with docking scores comparable to or surpassing those of reference inhibitors. Resveratrol demonstrated highly stable binding poses, particularly with caspase-3, while quercetin and chlorogenic acid showed moderate but reproducible affinities. Overall, this study provides new mechanistic insights into how NAOs may target central mediators of inflammation and cell death. Experimental validation is essential to confirm these interactions, assess binding affinities, and fully elucidate the therapeutic potential of NAOs in sepsis.
Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Bustamante Munguira, Elena; Andrés Juan, Celia; Lobo, Fernando; Pérez-Lebeña, Eduardo; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
The Multifaceted Health Benefits of Broccoli—A Review of Glucosinolates, Phenolics and Antimicrobial Peptides
Broccoli, a highly valued Brassica vegetable, is renowned for its rich content of bioactive substances, including glucosinolates, phenolic compounds, vitamins, and essential minerals. Glucosinolates (GSLs), secondary plant metabolites, are particularly abundant in broccoli. The global consumption of broccoli has increased due to its high nutritional value. This review examines the essential bioactive compounds in broccoli and their biological properties. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that broccoli exhibits various biological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects. This review analyzes several aspects of the chemical and biological activity of GSLs and their hydrolysis products, isothiocyanates such as sulforaphane, as well as phenolic compounds. Particular emphasis is placed on sulforaphane’s chemical structure, the reactivity of its isothiocyanate fraction (-NCS), and given the different behavior of SFN enantiomers, a wide and detailed review of the chemical synthesis methods described, by microbial oxidation, or using a chiral ruthenium catalyst and more widely using chiral auxiliaries for synthesizing sulforaphane enantiomers. In addition, the methods of chiral resolution of racemates by HPLC are reviewed, explaining the different chiral fillers used for this resolution and a third section on resolution using the formation of diastereomeric complexes and subsequent separation on achiral columns. Additionally, this review highlights the presence of antimicrobial peptides in broccoli, which have shown potential applications in food preservation and as natural alternatives to synthetic antibiotics. The antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from broccoli target bacterial membranes, enzymes, oxidative stress pathways and inflammatory mediators, contributing to their effectiveness against a wide range of pathogens and with potential therapeutic applications.
Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Bustamante Munguira, Elena; Andrés Juan, Celia; Pérez-Lebeña, Eduardo.
Wine is alive: the vitalist and theological roots of natural wine in 19th and 20th century Spain
This paper explores the intersection of vitalism, theology, and science in 19th and 20th century Spanish winemaking, focusing on the influential figures of Lucio Bascuñana and Eduardo Vitoria. Both men were engaged in the complex debate over the nature of wine, particularly regarding its production and the use of additives during a period marked by industrialization and scientific advancement, but also by a conflict between natural and artificial wines. Bascuñana’s radical rejection of additives and insistence on preserving the “living” essence of wine, influenced by vitalist and theological thought, is juxtaposed with Vitoria’s more pragmatic approach, which sought to balance scientific methods with traditional winemaking practices, especially in the context of sacramental wine. Drawing on Bruno Latour’s critique of the nature-culture dualism, the paper argues that both Bascuñana and Vitoria envisioned science not as a force of domination but as a partner in sustaining the natural vitality of wine. This study contributes to the historiography of enology by highlighting how debates on natural versus artificial wine in Spain anticipated contemporary concerns within the natural wine movement, emphasizing the ongoing dialog between tradition, scientific progress, and wine authenticity.
Alonso-González, Pablo.