Publications
This section includes a list of the latest IPNA scientific articles published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI).
In DIGITAL.CSIC, institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles since 1962, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc. of the centre. The aim of DIGITAL.CSIC is to organize, preserve and disseminate in open access the results of our research.
In the institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc.
Analysis of the IPNA 2014-2019 Scientific Production: bibliometric analysis from data collected in Scopus and Web of Science.

Ovary Signals for Pollen Tube Guidance in Chalazogamous Mangifera indica L.
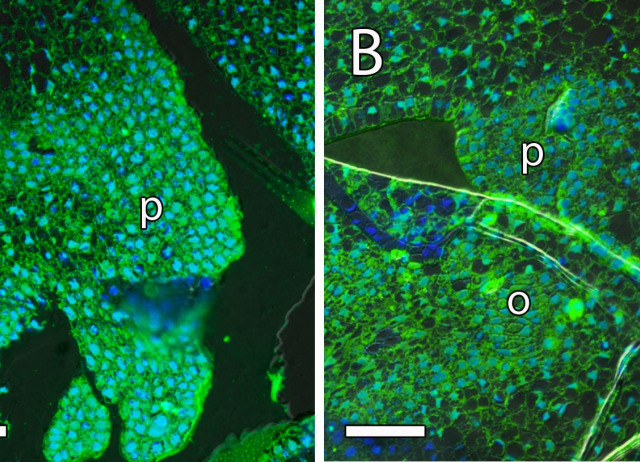
Most flowering plants show porogamy in which the pollen tubes reach the egg apparatus through the micropyle. However, several species show chalazogamy, an unusual pollen tube growth, in which the pollen tubes reach the embryo sac through the chalaza. While ovary signals for pollen tube growth and guidance have been extensively studied in porogamous species, few studies have addressed the process in chalazogamous species such as mango (Mangifera indica L.), one of the five most important fruit crops worldwide in terms of production. In this study, we characterize pollen–pistil interaction in mango, paying special attention to three key players known to be involved in the directional pollen tube growth of porogamous species such as starch, arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs), and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Starch grains were observed in the style and in the ponticulus at anthesis, but their number decreased 1 day after anthesis. AGPs, revealed by JIM8 and JIM13 antibodies, were homogenously observed in the style and ovary, but were more conspicuous in the nucellus around the egg apparatus. GABA, revealed by anti-GABA antibodies, was specifically observed in the transmitting tissue, including the ponticulus. Moreover, GABA was shown to stimulate in vitro mango pollen tube elongation. The results support the heterotrophic growth of mango pollen tubes in the style at the expense of starch, similarly to the observations in porogamous species. However, unlike porogamous species, the micropyle of mango does not show high levels of GABA and starch, although they were observed in the ponticulus and could play a role in supporting the unusual pollen tube growth in chalazogamous species.
Lora Cabrera, Jorge; Pérez Méndez, Verónica; Herrero Romero, María; Hormaza Urroz, José Ignacio
Genomic variation, population history and within-archipelago adaptation between island bird populations
Oceanic island archipelagos provide excellent models to understand evolutionary processes. Colonization events and gene flow can interact with selection to shape genetic variation at different spatial scales. Landscape-scale variation in biotic and abiotic factors may drive fine-scale selection within islands, while long-term evolutionary processes may drive divergence between distantly related populations. Here, we examine patterns of population history and selection between recently diverged populations of the Berthelot's pipit (Anthus berthelotii), a passerine endemic to three North Atlantic archipelagos. First, we use demographic trees and f3 statistics to show that genome-wide divergence across the species range is largely shaped by colonization and bottlenecks, with evidence of very weak gene flow between populations. Then, using a genome scan approach, we identify signatures of divergent selection within archipelagos at single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes potentially associated with craniofacial development and DNA repair. We did not detect within-archipelago selection at the same SNPs as were detected previously at broader spatial scales between archipelagos, but did identify signatures of selection at loci associated with similar biological functions. These findings suggest that similar ecological factors may repeatedly drive selection between recently separated populations, as well as at broad spatial scales across varied landscapes.
Martín, Clauida A.; Armstrong, Claire; Illera, Juan Carlos ; Emerson, Brent C. ; Richardson, David S.; Spurgin, Lewis G.
Bioactive Metabolites from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus sp. SPH2
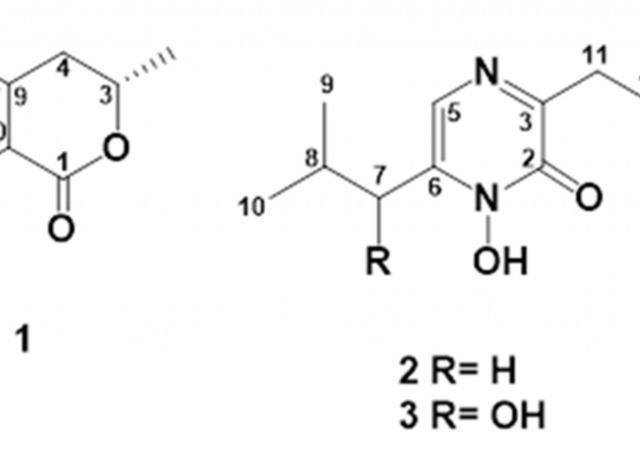
In the current study, an ethyl acetate extract from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. SPH2 isolated from the stem parts of the endemic plant Bethencourtia palmensis was screened for its biocontrol properties against plant pathogens (Fusarium moniliforme, Alternaria alternata, and Botrytis cinerea), insect pests (Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae, Rhopalosiphum padi), plant parasites (Meloidogyne javanica), and ticks (Hyalomma lusitanicum). SPH2 gave extracts with strong fungicidal and ixodicidal effects at different fermentation times. The bioguided isolation of these extracts gave compounds 1–3. Mellein (1) showed strong ixodicidal effects and was also fungicidal. This is the first report on the ixodicidal effects of 1. Neoaspergillic acid (2) showed potent antifungal effects. Compound 2 appeared during the exponential phase of the fungal growth while neohydroxyaspergillic acid (3) appeared during the stationary phase, suggesting that 2 is the biosynthetic precursor of 3. The mycotoxin ochratoxin A was not detected under the fermentation conditions used in this work. Therefore, SPH2 could be a potential biotechnological tool for the production of ixodicidal extracts rich in mellein.
Morales-Sánchez, Viridiana; Díaz, Carmen E.; Trujillo, Elena; Olmeda, Sonia A.; Valcarcel, Félix; Muñoz, Rubén; Andrés, María Fe; González-Coloma, Azucena
Long‐term cloud forest response to climate warming revealed by insect speciation history
Montane cloud forests are areas of high endemism, and are one of the more vulnerable terrestrial ecosystems to climate change. Thus, understanding how they both contribute to the generation of biodiversity, and will respond to ongoing climate change, are important and related challenges. The widely accepted model for montane cloud forest dynamics involves upslope forcing of their range limits with global climate warming. However, limited climate data provides some support for an alternative model, where range limits are forced downslope with climate warming. Testing between these two models is challenging, due to the inherent limitations of climate and pollen records. We overcome this with an alternative source of historical information, testing between competing model predictions using genomic data and demographic analyses for a species of beetle tightly associated to an oceanic island cloud forest. Results unequivocally support the alternative model: populations that were isolated at higher elevation peaks during the Last Glacial Maximum are now in contact and hybridizing at lower elevations. Our results suggest that genomic data are a rich source of information to further understand how montane cloud forest biodiversity originates, and how it is likely to be impacted by ongoing climate change.
Salces-Castellano, Antonia; Stankowski, Sean; Arribas, Paula; Patiño, Jairo; Karger, Dirk N.; Butlin, Roger; Emerson, Brent C.
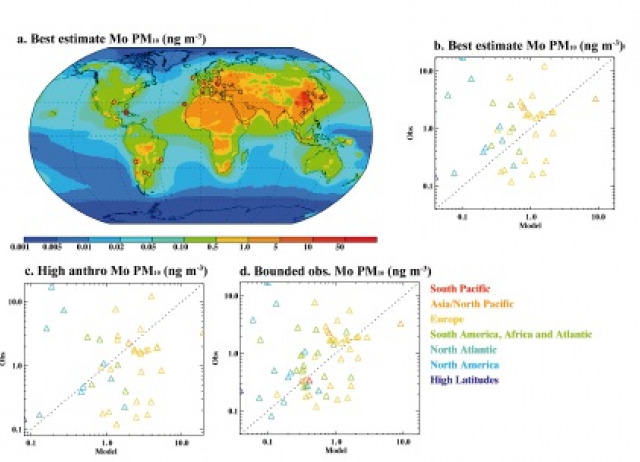
Anthropogenic Perturbations to the Atmospheric Molybdenum Cycle
Molybdenum (Mo) is a key cofactor in enzymes used for nitrogen (N) fixation and nitrate reduction, and the low availability of Mo can constrain N inputs, affecting ecosystem productivity. Natural atmospheric Mo aerosolization and deposition from sources such as desert dust, sea‐salt spray, and volcanoes can affect ecosystem function across long timescales, but anthropogenic activities such as combustion, motor vehicles, and agricultural dust have accelerated the natural Mo cycle. Here we combined a synthesis of global atmospheric concentration observations and modeling to identify and estimate anthropogenic sources of atmospheric Mo. To project the impact of atmospheric Mo on terrestrial ecosystems, we synthesized soil Mo data and estimated the global distribution of soil Mo using two approaches to calculate turnover times. We estimated global emissions of atmospheric Mo in aerosols (<10 μm in diameter) to be 23 Gg Mo yr‐1, with 40 to 75% from anthropogenic sources. We approximated that for the top meter of soil, Mo turnover times range between 1,000 to 1,000,000 years. In some industrialized regions, anthropogenic inputs have enhanced Mo deposition 100‐fold, lowering the soil Mo turnover time considerably. Our synthesis of global observational data, modeling, and a mass balance comparison with riverine Mo exports suggest that anthropogenic activity has greatly accelerated the Mo cycle, with potential to influence N‐limited ecosystems.
Wong, Michelle Y.; Rathod, Sagar D.; Marino, Roxanne; Li, Longlei; Howarth, Robert W.; Alastuey, Andres; Alaimo, Maria Grazia; Barraza, Francisco; Carneiro, Manuel Castro; Chellam, Shankararaman; Chen Yu-Cheng; Cohen, David D.; Connelly, David; Dongarra, Gaetano; Gomez, Dario; Hand, Jenny; Harrison, R.M.; Hopke, Philip K.; Hueglin, Christoph; Kuang, Yuan-wen; Lambert, Fabrice; Liang, James; Losno, Remi; Maenhaut, Willy; Milando, Chad; Couto Monteiro, Maria Inês; Morera-Gómez, Yasser; Querol, Xavier; Rodríguez, Sergio; Smichowski, Patricia; Varrica, Daniela; Xiao, Yi-hua; Xu, Yangjunjie; Mahowald, Natalie M.
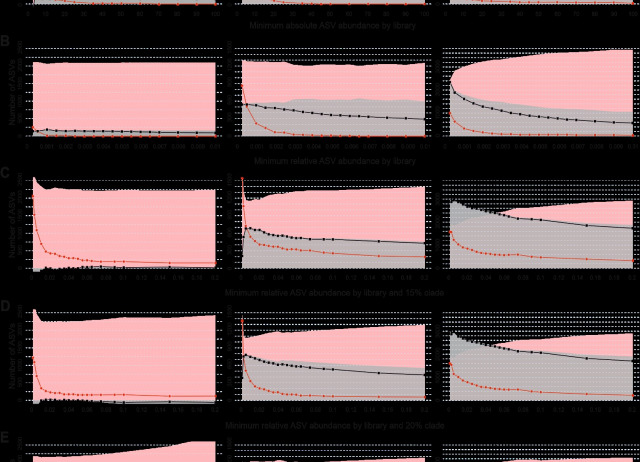
Validated removal of nuclear pseudogenes and sequencing artefacts from mitochondrial metabarcode data
Metabarcoding of Metazoa using mitochondrial genes may be confounded by both the accumulation of PCR and sequencing artefacts and the co-amplification of nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes (NUMTs). The application of read abundance thresholds and denoising methods is efficient in reducing noise accompanying authentic mitochondrial amplicon sequence variants (ASVs). However, these procedures do not fully account for the complex nature of concomitant sequences and the highly variable DNA contribution of specimens in a metabarcoding sample. We propose, as a complement to denoising, the metabarcoding Multidimensional Abundance Threshold Evaluation (metaMATE) framework, a novel approach that allows comprehensive examination of multiple dimensions of abundance filtering and the evaluation of the prevalence of unwanted concomitant sequences in denoised metabarcoding datasets. metaMATE requires a denoised set of ASVs as input, and designates a subset of ASVs as being either authentic (mitochondrial DNA haplotypes) or nonauthentic ASVs (NUMTs and erroneous sequences) by comparison to external reference data and by analysing nucleotide substitution patterns. metaMATE (i) facilitates the application of read abundance filtering strategies, which are structured with regard to sequence library and phylogeny and applied for a range of increasing abundance threshold values, and (ii) evaluates their performance by quantifying the prevalence of nonauthentic ASVs and the collateral effects on the removal of authentic ASVs. The output from metaMATE facilitates decision-making about required filtering stringency and can be used to improve the reliability of intraspecific genetic information derived from metabarcode data. The framework is implemented in the metaMATE software (available at https://github.com/tjcreedy/metamate).
Andújar, Carmelo; Creedy, Thomas J.; Arribas, Paula; López, Heriberto; Salces-Castellano, Antonia; Pérez‐Delgado, Antonio José; Vogler, Alfried P.; Emerson, Brent C.
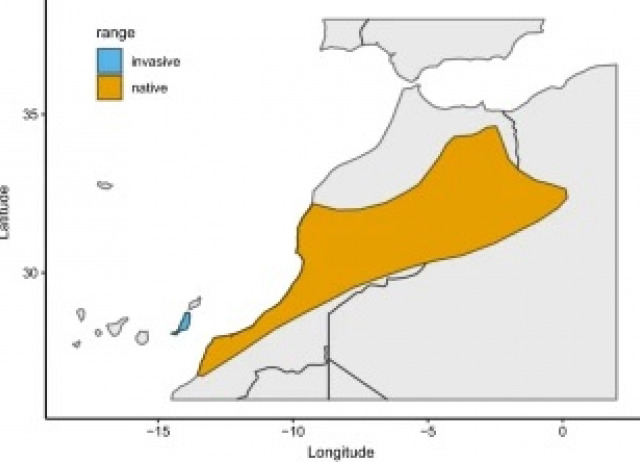
Exploring the role of life history traits and introduction effort in understanding invasion success in mammals: a case study of Barbary ground squirrels
Invasive species–species that have successfully overcome the barriers of transport, introduction, establishment, and spread—are a risk to biodiversity and ecosystem function. Introduction effort is one of the main factors underlying invasion success, but life history traits are also important as they influence population growth. In this contribution, we first investigated life history traits of the Barbary ground squirrel, Atlantoxerus getulus, a species with a very low introduction effort. We then studied if their invasion success was due to a very fast life history profile by comparing their life history traits to those of other successful invasive mammals. Next, we examined whether the number of founders and/or a fast life history influences the invasion success of squirrels. Barbary ground squirrels were on the fast end of the “fast-slow continuum”, but their life history was not the only contributing factor to their invasion success, as the life history profile is comparable to other invasive species that do not have such a low introduction effort. We also found that neither life history traits nor the number of founders explained the invasion success of introduced squirrels in general. These results contradict the concept that introduction effort is the main factor explaining invasion success, especially in squirrels. Instead, we argue that invasion success can be influenced by multiple aspects of the new habitat or the biology of the introduced species.
van der Marel, Annemarie; Waterman, Jane M.; López-Darias, Marta
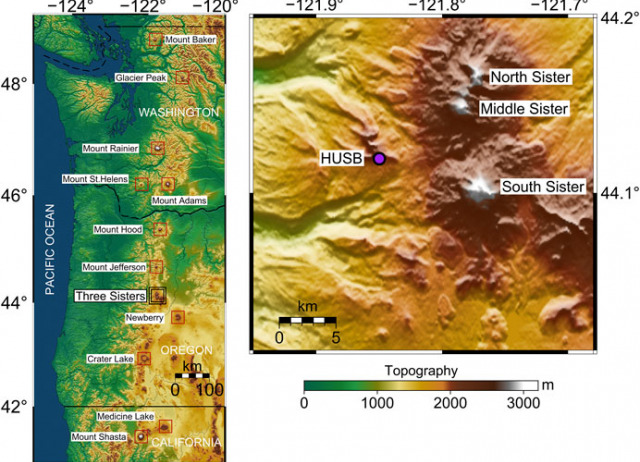
Time-Scales of Inter-eruptive Volcano Uplift Signals: Three Sisters Volcanic center, Oregon (USA)
A classical inflation-eruption-deflation cycle of a volcano is useful to conceptualize the time-evolving deformation of volcanic systems. Such a model predicts accelerated uplift during pre-eruptive periods, followed by subsidence during the co-eruptive stage. Some volcanoes show puzzling persistent uplift signals with minor or no other geophysical or geochemical variations, which are difficult to interpret. Such temporal behaviors are usually observed in large calderas (e.g., Yellowstone, Long Valley, Campi Flegrei, Rabaul), but less commonly for stratovolcanoes. Volcano deformation needs to be better understood during inter-eruptive stages, to assess its value as a tool for forecasting eruptions and to understand the processes governing the unrest behavior. Here, we analyze inter-eruptive uplift signals at Three Sisters, a complex stratovolcano in Oregon (United States), which in recent decades shows persistent inter-eruptive uplift signals without associated eruptive activity. Using a Bayesian inversion method, we re-assessed the source characteristics (magmatic system geometry and location) and its uncertainties. Furthermore, we evaluate the most recent evolution of the surface deformation signals combining both GPS and InSAR data through a new non-subjective linear regularization inversion procedure to estimate the 26 years-long time-series. Our results constrain the onset of the Three Sisters volcano inflation to be between October 1998 and August 1999. In the absence of new magmatic inputs, we estimate a continuous uplift signal, at diminishing but detectable rates, to last for few decades. The observed uplift decay observed at Three Sisters is consistent with a viscoelastic response of the crust, with viscosity of ∼1018 Pa s around a magmatic source with a pressure change which increases in finite time to a constant value. Finally, we compare Three Sisters volcano time series with historical uplift at different volcanic systems. Proper modeling of scaled inflation time series indicates a unique and well-defined exponential decay in temporal behavior. Such evidence supports that this common temporal evolution of uplift rates could be a potential indicator of a rather reduced set of physical processes behind inter-eruptive uplift signals.
Rodríguez-Molina, Sara; González, Pablo J.; Charco, María; Negredo, Ana M.; Schmidt, David A.
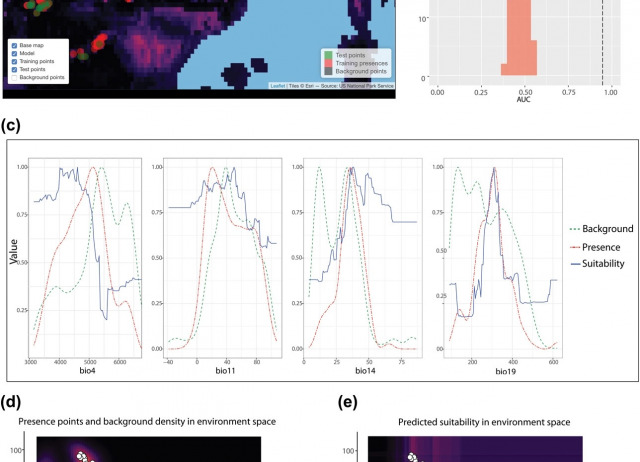
ENMTools 1.0: an R package for comparative ecological biogeography
The ENMTools software package was introduced in 2008 as a platform for making measurements on environmental niche models (ENMs, frequently referred to as species distribution models or SDMs), and for using those measurements in the context of newly developed Monte Carlo tests to evaluate hypotheses regarding niche evolution. Additional functionality was later added for model selection and simulation from ENMs, and the software package has been quite widely used. ENMTools was initially implemented as a Perl script, which was also compiled into an executable file for various platforms. However, the package had a number of significant limitations; it was only designed to fit models using Maxent, it relied on a specific Perl distribution to function, and its internal structure made it difficult to maintain and expand. Subsequently, the R programming language became the platform of choice for most ENM studies, making ENMTools less usable for many practitioners. Here we introduce a new R version of ENMTools that implements much of the functionality of its predecessor as well as numerous additions that simplify the construction, comparison and evaluation of niche models. These additions include new metrics for model fit, methods of measuring ENM overlap, and methods for testing evolutionary hypotheses. The new version of ENMTools is also designed to work within the expanding universe of R tools for ecological biogeography, and as such includes greatly simplified interfaces for analyses from several other R packages.
Warren, Dan L.; Matzke, Nicholas J.; Cardillo, Marcel; Baumgartner, John B.; Beaumont, Linda J.; Turelli, Michael; Glor, Richard E.; Huron, Nicholas A.; Simões, Marianna; Iglesias, Teresa L.; Piquet, Julien C.; Dinnage, Russell
El pino canario confiere matices únicos al vino palmero
El 25 de septiembre de 2015, los líderes mundiales adoptaron un conjunto de objetivos globales para erradicar la pobreza, proteger el planeta y asegurar la prosperidad para todos como parte de una nueva agenda de desarrollo sostenible. Cada objetivo tiene metas específicas que deben alcanzarse en los próximos 15 años. Para alcanzar estas metas, todo el mundo tiene que hacer su parte: los gobiernos, el sector privado, la sociedad civil y todos los estratos de la sociedad. Desde el IPNA-CSIC, hemos desarrollado una campaña de divulgación encaminada a explicar estos objetivos a la sociedad y, en particular, a los estudiantes de secundaria y universitarios. Las siguientes infografías exploran distintos de los retos planteados por la Organización de las Naciones Unidas en su Agenda 2030 y expone las distintas acciones que desde la investigación se plantean para superarlos. Además, al pinchar sobre cada cartel, se accederá a distintos materiales divulgativos sobre el tema, como un artículo de divulgación o un podcast con un investigador experto del IPNA. En esta infografía muestra el estudio las propiedades del vino de tea, fermentado en barricas obtenidas del núcleo del Pinus Canariensis.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva.