Publications
This section includes a list of the latest IPNA scientific articles published in journals included in the Science Citation Index (SCI).
In DIGITAL.CSIC, institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles since 1962, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc. of the centre. The aim of DIGITAL.CSIC is to organize, preserve and disseminate in open access the results of our research.
In the institutional repository of the CSIC, you can find the complete list of scientific articles, as well as other collections of interest such as congresses, theses, books, informative material, etc.
Analysis of the IPNA 2014-2019 Scientific Production: bibliometric analysis from data collected in Scopus and Web of Science.

Habitat filtering and dispersal ability determine across-scale community turnover and rarity in Macaronesian island spider communities
Aim: Much research has focused on the separate and combined effects of habitat and geography on species communities, both in mainland and island ecosystems. However, few studies have looked into the differences among communities inhabiting different island habitats. Here we aim to determine the contributions of habitat filtering and dispersal to the differences in taxonomic structure of island communities across geographic scales. Location: Sixty plots in two habitats (forest and dry habitat) across eight islands of the Macaronesian archipelagos of the Azores, Madeira, Canary Islands and Cabo Verde. Taxon: Spiders (Araneae). Methods: We generated community data by using the optimised and standardised COBRA sampling protocols. We tested the differences in three beta diversity metrics ( βTotal, βReplacement and βRichness) for each habitat and dispersal category separately, across geographic scales through nested non-parametric PerMANOVA. We tested if dispersal and habitat influenced differences between the communities of the same area by applying a PERMDISP to βreplacement, and using the distances in linear mixed models. We tested the effects of habitat and dispersal on species relative abundances (SADs) and rarity by building Gambin models for each community and dispersal group separately. Results: Communities grouped according to archipelago and habitat, in terms of taxonomic similarity. In general, β diversity increased with geographic scale, and was greater in dry habitats. βReplacement among communities of the same region was greater in dry habitats than in forests, and this difference was stronger for rare ballooners. Dry habitat communities showed more species with low abundances (rare species) at different spatial scales. Main conclusions: Our findings reveal that habitat type does not only condition the processes behind community assembly but also the scale at which they occur. Indeed, our findings are highly relevant for theories on across and within island community assembly as well as for biodiversity conservation.
Malumbres-Olarte, Jagoba; Rigal, François; Girardello, Marco; Cardoso, Pedro; Crespo, Luís Carlos; Amorim, Isabel R.; Arnedo, Miquel; Boieiro, Mário; Carvalho, José Carlos; Carvalho, Rui; Gabriel, Rosalina; Lamelas-Lopez, Lucas; López, Heriberto; Paulo, Octávio S.; Pereira, Fernando; Pérez Delgado, Antonio J.; Rego, Carla; Romeiras, Maria; Ros Prieto, Alejandra; Oromí, Pedro; Vieira, Ana; Emerson, Brent C.; Borges, Paulo A.V.
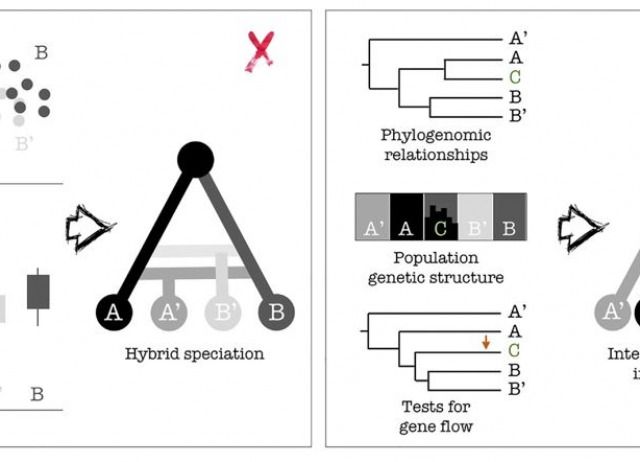
Digest: Revisiting morphology-derived hypotheses of hybridization in the light of genomics
Genetic exchange between independently evolving lineages may give rise to the formation of new taxa, and hypotheses for this have been derived from species with intermediate phenotypes, when compared to potential parental species. Goulet-Scott and collaborators (2021) evaluate such a hypothesis in a wildflower species complex by integrating genomic and trait information. They find no support for hybrid speciation, despite detecting signatures of genetic admixture in some individuals resulting from interspecific gene flow in a hybrid zone.
Noguerales, Víctor
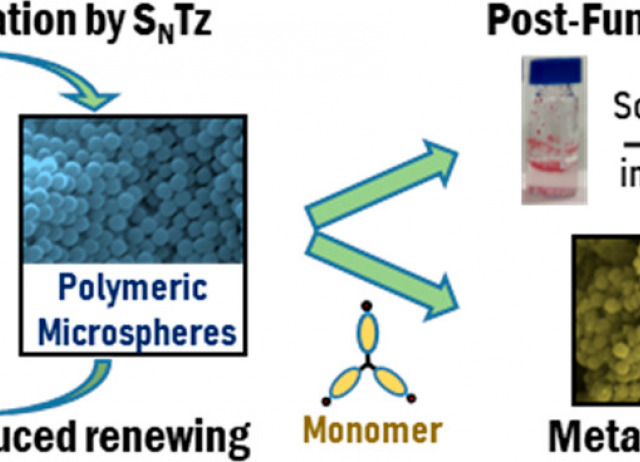
Tetrazine Dynamic Covalent Polymer Networks
Dynamic nucleophilic aromatic substitution of tetrazines (SNTz) has been used for the synthesis of dynamic covalent polymer networks that take advantage of both the reversible nature of the reaction and the versatility of the tetrazine ring. Polymer microspheres were easily synthesized and they were proved to be degraded either by UV irradiation or by a chemical stimulus, recovering the original monomer, which allows an efficient recycling. It was also possible to convert one polymer into another one (metamorphosis) by irreversible exchange of monomers. Additionally, the backbone of the polymers could be reduced/oxidized or postfunctionalized with polar groups by the inverse electron demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) reaction, which not only locked the exchange but also allows for the modulation of the polymer properties, such as solubility in water. Tetrazine dynamic polymers are a recyclable and highly versatile kind of material that enables postsynthetic modulation of their properties as well as provides novel chemical methods and photodegradation.
Rivero, David S.; Paiva-Feener, Rafael E.; Santos, Tanausú; Martín-Encinas, Endika; Carrillo Fumero, Romen
Root treatment with a vitamin K3 derivative: a promising alternative to synthetic fungicides against Botrytis cinerea in tomato plants
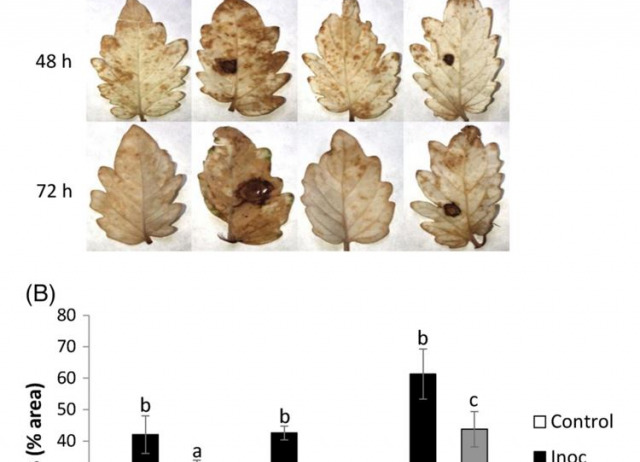
BACKGROUND Botrytis cinerea, the causal agent of gray mold has a great economic impact on several important crops. This necrotrophic fungus causes disease symptoms during vegetative growth and also into postharvest stages. The current method to combat this disease is fungicide application, with high economic costs and environmentally unsustainable impacts. Moreover, there is an increasing general public health concern about these strategies of crop protection. We studied the protection of tomato plants against B. cinerea by previous root treatment with menadione sodium bisulfite (MSB), a known plant defense activator.
RESULTS Root treatment 48 h before inoculation with MSB 0.6 mmol L−1 reduced leaf lesion diameter by 30% and notably cell deaths, compared to control plants 72 h after inoculation. We studied the expression level of several pathogenesis-related (PR) genes from different defense transduction pathways, and found that MSB primes higher PR1 expression against B. cinerea. However, this stronger induced resistance was impaired in transgenic salicylic acid-deficient NahG line. Additionally, in the absence of pathogen challenge, MSB increased tomato plant growth by 28% after 10 days. Our data provide evidence that MSB protects tomato plants against B. cinerea by priming defense responses through the salicylic acid (SA)-dependent signaling pathway and reducing oxidative stress.
CONCLUSION This work confirms the efficacy of MSB as plant defense activator against B. cinerea and presents a novel alternative to combat gray mold in important crops.
García-Machado, Francisco J.; García-García, Ana L.; Borges, Andrés A.; Jiménez-Arias, David
Democratising Heritage Values: A Methodological Review
This paper explores the transformation of heritage values from a critical perspective. The de-authorising conceptual shift in cultural heritage has not always been accompanied by a revitalisation of the dynamics of valorisation. To achieve the integration of multivocal discourses in sustainable preservation strategies, experts and academics need to work with methods that enable this to happen. This article presents a methodological analysis articulated through three different case studies that bring new experiences regarding the decolonisation of knowledge in the field of heritage values, addressing different aspects of the social dimension of cultural heritage. The first deals with contestation processes associated with productive winemaking traditions in the Rias Baixas, Galicia, Spain. The second case addresses the rebellious Paris of the Commune and the narratives associated with the valorisation of the traces that it has left in the city’s landscape. Finally, the third case analyses the values that come into play when citizens’ participation governs the transformation of an archaeological site in Barcelona. To conclude, we reflect on the idea of sustainability as a way of listening to, sharing and co-creating knowledge connected to communities.
Pastor Pérez, Ana; Barreiro Martínez, David; Parga-Dans, Eva; Alonso-González, Pablo
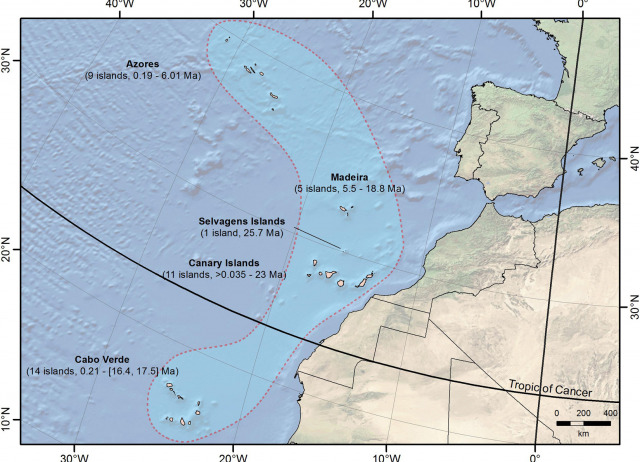
Macaronesia as a Fruitful Arena for Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation Biology
Research in Macaronesia has led to substantial advances in ecology, evolution and conservation biology. We review the scientific developments achieved in this region, and outline promising research avenues enhancing conservation. Some of these discoveries indicate that the Macaronesian flora and fauna are composed of rather young lineages, not Tertiary relicts, predominantly of European origin. Macaronesia also seems to be an important source region for back-colonisation of continental fringe regions on both sides of the Atlantic. This group of archipelagos (Azores, Madeira, Selvagens, Canary Islands, and Cabo Verde) has been crucial to learn about the particularities of macroecological patterns and interaction networks on islands, providing evidence for the development of the General Dynamic Model of oceanic island biogeography and subsequent updates. However, in addition to exceptionally high richness of endemic species, Macaronesia is also home to a growing number of threatened species, along with invasive alien plants and animals. Several innovative conservation and management actions are in place to protect its biodiversity from these and other drivers of global change. The Macaronesian Islands are a well-suited field of study for island ecology and evolution research, mostly due to its special geological layout with 40 islands grouped within five archipelagos differing in geological age, climate and isolation. A large amount of data is now available for several groups of organisms on and around many of these islands. However, continued efforts should be made toward compiling new information on their biodiversity, to pursue various fruitful research avenues and develop appropriate conservation management tools.
Florencio, Margarita; Patiño, Jairo; Nogué, Sandra; Traveset, Anna; Borges, Paulo A. V.; Schaefer, Hanno; Amorim, Isabel R.; Arnedo, Miquel; Ávila, Sérgio P.; Cardoso, Pedro; de Nascimento, Lea; Fernández-Palacios, José María; Gabriel, Sofia I.; Gil, Artur; Gonçalves, Vítor; Haroun, Ricardo; Illera, Juan Carlos; López-Darias, Marta; Martínez, Alejandro; Martins, Gustavo M.; Neto, Ana I.; Nogales, Manuel; Oromí, Pedro; Rando, Juan Carlos; Raposeiro, Pedro M.; Rigal, François; Romeiras, Maria M.; Silva, Luís; Valido, Alfredo; Vanderpoorten, Alain; Vasconcelos, Raquel; Santos, Ana M. C.
1,5-Hydrogen Atom Transfer/Surzur–Tanner Rearrangement: A Radical Cascade Approach for the Synthesis of 1,6-Dioxaspiro[4.5]decane and 6,8-Dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane Scaffolds in Carbohydrate Systems
The 1,5-HAT–1,2-(ester)alkyl radical migration (Surzur–Tanner rearrangement) radical/polar sequence triggered by alkoxyl radicals has been studied on a series of C-glycosyl substrates with 3-C-(α,β-d,l-glycopyranosyl)1-propanol and C-(α-d,l-glycopyranosyl)methanol structures prepared from chiral pool d- and l-sugar. The use of acetoxy and diphenoxyphosphatoxy as leaving groups provides an efficient construction of 10-deoxy-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane and 4-deoxy-6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane frameworks. The alkoxyl radicals were generated by the reaction of the corresponding N-alkoxyphthalimides with group 14 hydrides [n-Bu3SnH(D) and (TMS)3SiH], and in comparative terms, the reaction was also initiated by visible light photocatalysis using the Hantzsch ester/fac-Ir(ppy)3 procedure. Special attention was devoted to the influence of the relative stereochemistry of the centers involved in the radical sequence on the reaction outcome. The addition of BF3•Et2O as a catalyst to the radical sequence resulted in a significant increase in the yields of the desired bicyclic ketals.
León, Elisa I.; Martín, Ángeles; Montes, Adrián S.; Pérez-Martín, Inés; Rodríguez, María del Sol; Suárez, Ernesto
Elemental composition, rare earths and minority elements in organic and conventional wines from volcanic areas: The Canary Islands (Spain)
The organic wine market is rapidly growing worldwide, both in terms of production and consumption. However, the scientific literature is not conclusive regarding differences in the elemental composition of wines according to their production method, including both major and trace elements. Minerals can be present in wine as a result of both anthropogenic and environmental factors. To date, this has not been evaluated in volcanic contexts, neither has the emergent issue of rare earths and other minority elements as potential sources of food contamination. This study using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analyses organic and conventional wines produced in the Canary Islands (Spain), an archipelago of volcanic origin, to compare their content of 49 elements, including rare earths and minority elements. Our results showed that organic wines presented lower potential toxic element content on average than their conventional counterparts, but differences were not significant. Geographical origin of the wine samples (island) was the only significant variable differentiating wine samples by their composition profiles. By comparing our data with the literature, no agreement was found in terms of differences between organic and conventionally-produced wines. This confirms that other factors prevail over elemental composition when considering differences between wine production methods. Regarding the toxicological profile of the wines, five samples (three organic and two conventional) exceeded the maximum limits established by international legislation. This highlights the need for stricter analytical monitoring in the Canary Islands, with a particular focus on Cu and Ni concentration, and potentially in other volcanic areas.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva; Arribas, Paula; Pérez Luzardo, Octavio; Zumbado Peña, Manuel; Hernández González, María Mercedes; Rodríguez-Hernández, Ángel; Andújar, Carmelo
A unified model of species abundance, genetic diversity, and functional diversity reveals the mechanisms structuring ecological communities
Biodiversity accumulates hierarchically by means of ecological and evolutionary processes and feedbacks. Within ecological communities drift, dispersal, speciation, and selection operate simultaneously to shape patterns of biodiversity. Reconciling the relative importance of these is hindered by current models and inference methods, which tend to focus on a subset of processes and their resulting predictions. Here we introduce Massive Eco-evolutionary Synthesis Simulations (MESS), a unified mechanistic model of community assembly, rooted in classic island biogeography theory, which makes temporally explicit joint predictions across three biodiversity data axes: i) species richness and abundances; ii) population genetic diversities; and iii) trait variation in a phylogenetic context. Using simulations we demonstrate that each data axis captures information at different timescales, and that integrating these axes enables discriminating among previously unidentifiable community assembly models. MESS is unique in generating predictions of community-scale genetic diversity, and in characterizing joint patterns of genetic diversity, abundance, and trait values. MESS unlocks the full potential for investigation of biodiversity processes using multi-dimensional community data including a genetic component, such as might be produced by contemporary eDNA or metabarcoding studies. We combine with supervised machine learning to fit the parameters of the model to real data and infer processes underlying how biodiversity accumulates, using communities of tropical trees, arthropods, and gastropods as case studies that span a range of data availability scenarios, and spatial and taxonomic scales.
Overcast, Isaac; Ruffley, Megan; Rosindell, James; Harmon, Luke ; Borges, Paulo A. V.; Emerson, Brent C.; Etienne, Rampal S.; Gillespie, Rosemary; Krehenwinkel, Henrik; Mahler, D. Luke; Massol, Francois; Parent, Christine E.; Patiño, Jairo; Peter, Ben; Week, Bob; Wagner, Catherine; Hickerson, Michael J.; Rominger, Andrew
Calidad del aire ambiente, inhalación de contaminantes y consultas en los servicios de urgencia
Rodríguez, Sergio
![1,5-Hydrogen Atom Transfer/Surzur–Tanner Rearrangement: A Radical Cascade Approach for the Synthesis of 1,6-Dioxaspiro[4.5]decane and 6,8-Dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane Scaffolds in Carbohydrate Systems](/sites/default/files/styles/img_fondo_entradilla_640x462/public/2021-09/jo1c01376_0014.jpeg?h=2750187c&itok=IA5HufuU)









