Inferring the ecological and evolutionary determinants of community genetic diversity
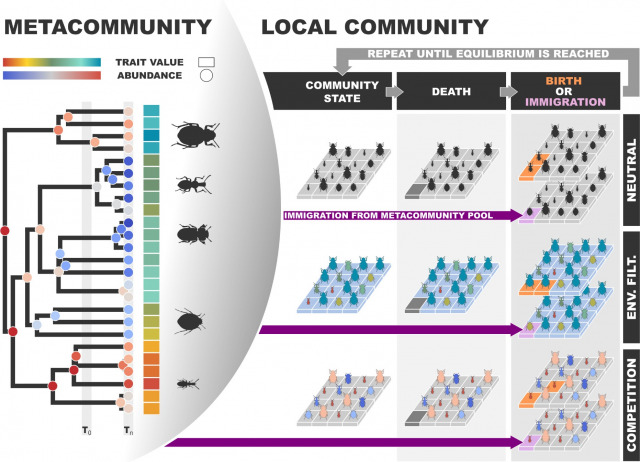
Understanding the relative contributions of ecological and evolutionary processes to the structuring of ecological communities is needed to improve our ability to predict how communities may respond to future changes in an increasingly human-modified world. Metabarcoding methods make it possible to gather population genetic data for all species within a community, unlocking a new axis of data to potentially unveil the origins and maintenance of biodiversity at local scales. Here, we present a new eco-evolutionary simulation model for investigating community assembly dynamics using metabarcoding data. The model makes joint predictions of species abundance, genetic variation, trait distributions and phylogenetic relationships under a wide range of parameter settings (e.g. high speciation/low dispersal or vice versa) and across a range of community states, from pristine and unmodified to heavily disturbed. We first demonstrate that parameters governing metacommunity and local community processes leave detectable signatures in simulated biodiversity data axes. Next, using a simulation-based machine learning approach we show that neutral and non-neutral models are distinguishable and that reasonable estimates of several model parameters within the local community can be obtained using only community-scale genetic data, while phylogenetic information is required to estimate those describing metacommunity dynamics. Finally, we apply the model to soil microarthropod metabarcoding data from the Troodos mountains of Cyprus, where we find that communities in widespread forest habitats are structured by neutral processes, while high-elevation and isolated habitats act as an abiotic filter generating non-neutral community structure. We implement our model within the ibiogen R package, a package dedicated to the investigation of island, and more generally community-scale, biodiversity using community-scale genetic data.
Overcast, Isaac; Noguerales, Víctor; Meramveliotakis, Emmanouil; Andújar, Carmelo; Arribas, Paula; Creedy, Thomas J.; Emerson, Brent C.; Vogler, Alfried P.; Papadopoulou, Anna; Morlon, Hélène.
Advanced Methods for Natural Products Discovery: Bioactivity Screening, Dereplication, Metabolomics Profiling, Genomic Sequencing, Databases and Informatic Tools, and Structure Elucidation
Natural Products (NP) are essential for the discovery of novel drugs and products for numerous biotechnological applications. The NP discovery process is expensive and time-consuming, having as major hurdles dereplication (early identification of known compounds) and structure elucidation, particularly the determination of the absolute configuration of metabolites with stereogenic centers. This review comprehensively focuses on recent technological and instrumental advances, highlighting the development of methods that alleviate these obstacles, paving the way for accelerating NP discovery towards biotechnological applications. Herein, we emphasize the most innovative high-throughput tools and methods for advancing bioactivity screening, NP chemical analysis, dereplication, metabolite profiling, metabolomics, genome sequencing and/or genomics approaches, databases, bioinformatics, chemoinformatics, and three-dimensional NP structure elucidation.
Gaudêncio, Susana P.; Bayram, Engin; Bilela, Lada Lukic; Cueto, Mercedes; DIAZ MARRERO, ANA RAQUEL; Haznedaroglu, Berat Z.; Jimenez, Carlos; Mandalakis, Manolis; Pereira, Florbela; Reyes, Fernando; Tasdemir, Deniz.
Bifurcaria bifurcata extract exerts antioxidant effects on human Caco-2 cells
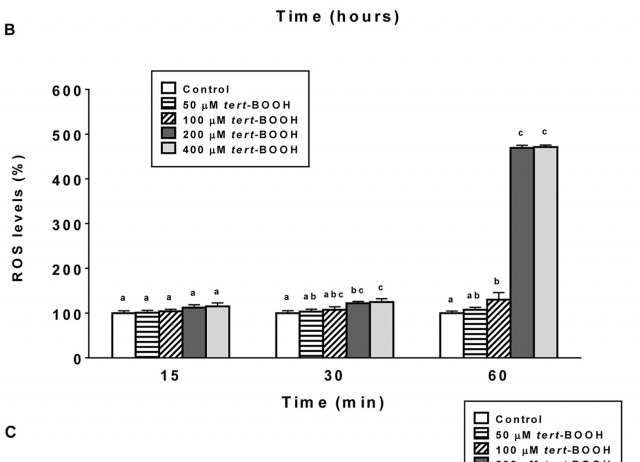
The present research study investigated the potential protective effect of Bifurcaria bifurcata extract on cell viability and antioxidant defences of cultured human Caco-2 cells submitted to oxidative stress induced by tert-butylhydroperoxide (tert-BOOH). Aqueous extracts were firstly characterized in terms of total phenolic contents. Concentrations of reduced glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA), generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO) production, antioxidant enzymes activities [NADPH quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) and glutathione S-transferase (GST)], caspase 3/7 activity and gene expression linked to apoptosis, proinflammation and oxidative stress signaling pathways were used as markers of cellular oxidative status. B. bifurcata extract prevented the cytotoxicity, the decrease of GSH, the increase of MDA levels and the ROS generation induced by tert-BOOH. B. bifurcata extract prevented the significant decrease of NQO1 and GST activities, and the significant increase of caspase 3/7 activity induced by tert-BOOH. B. bifurcata extract also caused an over-expression of GSTM2, Nrf2 and AKT1 transcriptors, as well as reduced ERK1, JNK1, Bax, BNIP3, NFκB1, IL-6 and HO-1 gene expressions induced by tert-BOOH suggesting an increase in cellular resistance against oxidative stress. The results of the biomarkers analyzed show that treatment of Caco-2 cells with B. bifurcata extract enhance antioxidant defences, which imply an improved cell response to an oxidative challenge. B. bifurcata extract possesses strong antioxidant properties and may be a potential effective alternative to oxidant agents in the functional food industry.
Martínez, María Aránzazu; Aedo, Hugo; López-Torres, Bernardo; Maximiliano, Jorge Enrique; Martínez-Larrañaga, María Rosa; Anadón, Arturo; Martínez, Marta; Peteiro, César; Cueto, Mercedes; Rubiño, Susana; Hortos, María; Ares, Irma
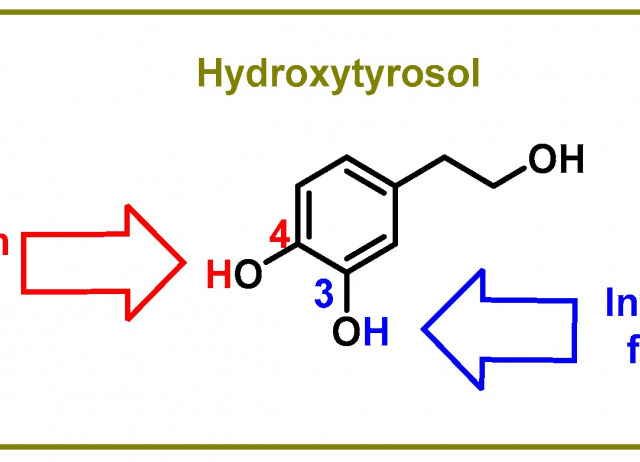
Hydroxytyrosol and Arginine as Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Immunostimulant Dietary Supplements for COVID-19 and Long COVID
Phytochemicals from plant extracts are becoming increasingly popular in the world of food science and technology because they have positive effects on human health. In particular, several bioactive foods and dietary supplements are being investigated as potential treatments for chronic COVID. Hydroxytyrosol (HXT) is a natural antioxidant, found in olive oil, with antioxidant anti-inflammatory properties that has been consumed by humans for centuries without reported adverse effects. Its use was approved by the European Food Safety Authority as a protective agent for the cardiovascular system. Similarly, arginine is a natural amino acid with anti-inflammatory properties that can modulate the activity of immune cells, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α. The properties of both substances may be particularly beneficial in the context of COVID-19 and long COVID, which are characterised by inflammation and oxidative stress. While l-arginine promotes the formation of •NO, HXT prevents oxidative stress and inflammation in infected cells. This combination could prevent the formation of harmful peroxynitrite, a potent pro-inflammatory substance implicated in pneumonia and COVID-19-associated organ dysfunction, as well as reduce inflammation, improve immune function, protect against free radical damage and prevent blood vessel injury. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of HXT and arginine in the context of COVID-19.
Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel; Curieses Andrés, Celia María; Andrés Juan, Celia; Plou Gasca, Francisco José; Pérez-Lebeña, Eduardo.
Dispersal ability and niche breadth influence interspecific variation in spider abundance and occupancy
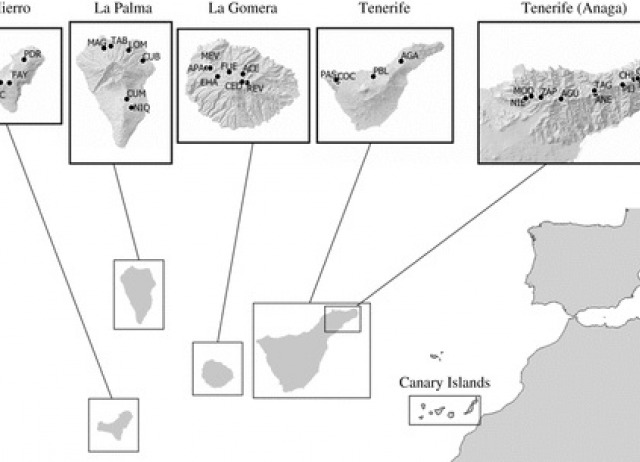
The relationship between species local abundance and their regional distribution (occupancy) is one of the most extensively recognized and investigated patterns in ecology. While exceptions exist, the generally held model is that locally abundant species also tend to be more widespread geographically. However, there is only a limited understanding of both the mechanisms driving this relationship, and their scale dependency. Here we use occupancy and abundance data for 123 species of spider from across the Canary Islands to understand how both dispersal ability and niche breadth might mediate variation among species for local abundance and occupancy. We test the predictions that (i) dispersal ability explains variation among species for both abundance and occupancy, and (ii) species with a higher degree of habitat specialization, reflecting more limited niche breadth, will have both higher occupancy and abundance. We find no evidence within habitat patches for an effect of dispersal ability on either local abundance or site occupancy, while across all patches species with higher dispersal ability tend to occupy more sites. Species largely restricted to laurel forests have higher abundance than species with broader niche breadth, but similar occupancy. The study revealed that dispersal ability and niche breadth were significant predictors of the abundance–occupancy relationship, highlighting the importance of both factors for understanding patterns of abundance and occupancy among spider species.
Suárez, Daniel; Arribas, Paula; Macías-Hernández, Nuria; Emerson, Brent C.
A Certification for Natural Wine? A Comparative Analysis of Consumer Drivers in Italy and Spain
The 2020 certification of natural wine (NW) in France has unleashed a heated debate in Europe. However, knowledge about NW consumer profiles and preferences in a comparative perspective remains scarce in the academic literature. This study aims to define the perceptions, preferences and profiles of wine consumers who support a NW label. For this purpose, we employed analysis of variance, aprioristic factor analysis and multiple regression analysis to examine data from a direct survey performed in Italy and Spain in 2020. Findings reveal that NW consumers in both countries deem it necessary to establish a certification for NW. However, we found significant differences regarding consumers’ profiles, as well as purchasing preferences. In Spain, demand for NW certification is linked to eco-healthy and proximity-craft attributes of wine, and is considered more important by non-professional consumers and those with lower educational level. In Italy, information on the label and the purchase experience are the most important factors to aid in recognizing NW, while women show a significant interest in the NW certification. These findings may help policy-makers to establish homogeneous parameters to differentiate and certify NW.
Parga-Dans, Eva; Vecchio, Riccardo; Annunziata, Azzurra; Alonso-González, Pablo; Otero Enríquez, Raimundo.
Teleost Piscidins—In Silico Perspective of Natural Peptide Antibiotics from Marine Sources
Fish, like all other animals, are exposed to constant contact with microbes, both on their skin and on the surfaces of their respiratory and digestive systems. Fish have a system of non-specific immune responses that provides them with initial protection against infection and allows them to survive under normal conditions despite the presence of these potential invaders. However, fish are less protected against invading diseases than other marine vertebrates because their epidermal surface, composed primarily of living cells, lacks the keratinized skin that serves as an efficient natural barrier in other marine vertebrates. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are one type of innate immune protection present in all life forms. AMPs have been shown to have a broader range of biological effects than conventional antibiotics, including antibacterial, antiviral, antiprotozoal, and antifungal effects. Although other AMPs, such as defensins and hepcidins, are found in all vertebrates and are relatively well conserved, piscidins are found exclusively in Teleost fish and are not found in any other animal. Therefore, there is less information on the expression and bioactivity of piscidins than on other AMPs. Piscidins are highly effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that cause disease in fish and humans and have the potential to be used as pharmacological anti-infectives in biomedicine and aquaculture. To better understand the potential benefits and limitations of using these peptides as therapeutic agents, we are conducting a comprehensive study of the Teleost piscidins included in the “reviewed” category of the UniProt database using bioinformatics tools. They all have amphipathic alpha-helical structures. The amphipathic architecture of piscidin peptides and positively charged residues influence their antibacterial activity. These alpha-helices are intriguing antimicrobial drugs due to their stability in high-salt and metal environments. New treatments for multidrug-resistant bacteria, cancer, and inflammation may be inspired by piscidin peptides.
Asensio-Calavia, Patricia; González-Acosta, Sergio; Otazo-Pérez, Andrea; López, Manuel R.; Morales-delaNuez, Antonio; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
Recirculating packed-bed biofilm photobioreactor combined with membrane ultrafiltration as advanced wastewater treatment
Packed-bed biofilm photobioreactor combined with ultrafiltration membrane was investigated for intensifying the process for secondary wastewater effluent treatment. Cylindrical glass carriers were used as supporting material for the microalgal-bacterial biofilm, which developed from indigenous microbial consortium. Glass carriers allowed adequate growth of the biofilm with limited suspended biomass. Stable operation was achieved after a start-up period of 1000 h, where supernatant biopolymer clusters were minimized and complete nitrification was observed. After that time, biomass productivity was 54 ± 18 mg·L−1·day−1. Green microalgae Tetradesmus obliquus and several strains of heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification bacteria and fungi were identified. Combined process exhibited COD, nitrogen and phosphorus removal rates of 56 ± 5%, 12 ± 2% and 20 ± 6%, respectively. Membrane fouling was mainly caused by biofilm formation, which was not effectively mitigated by air-scouring aided backwashing.
Díaz, Oliver; González, Enrique; Vera, Luisa; Fernández, Luis Javier; DIAZ MARRERO, ANA RAQUEL ; Fernández, José J.
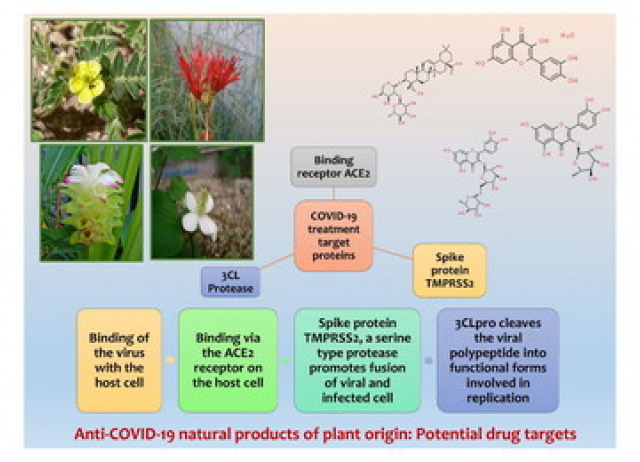
Harnessing and bioprospecting botanical-based herbal medicines against potential drug targets for COVID-19: a review coupled molecular docking studies
Since the end of February 2020, the world has come to a standstill due to the virus SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). Since then, the global scientific community has explored various remedies and treatments against this virus, including natural products that have always been a choice because of their many benefits. Various known phytochemicals are well documented for their antiviral properties. Research is being carried out to discover new natural plant products or existing ones as a treatment measure for this disease. The three important targets in this regard are—papain like protease (PLpro), spike protein, and 3 chymotrypsin like proteases (3CLpro). Various docking studies are also being elucidated to identify the phytochemicals that modulate crucial proteins of the virus. The paper is simultaneously a comprehensive review that covers recent advances in the domain of the effect of various botanically derived natural products as an alternative treatment approach against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, the docking analyses revealed that rutin (inhibitor of the major protease of SARS-CoV-2), gallocatechin (e.g., interacting with 03 hydrogen bonds with a spike-like protein), lycorine (showing the best binding affinity with amino acids GLN498, THR500 and GLY446 of the spike-like protein), and quercetrin (inhabiting at its residues ASP216, PHE219, and ILE259) are promising inhibitors of SARS‑CoV‑2.
Pal, Tarun; Anand, Uttpal; Mitrab, Shreya Sikdar; Biswasb, Protha; Tripathic, Vijay; Proćkówd, Jarosław; Deyb, Abhijit; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
Materia, vida y sociedad: Investigaciones del Instituto de Productos Naturales y Agrobiología
El artículo hace referencia a los objetivos y actividades, así como el papel científico que desempeña, el Instituto de Productos Naturales y Agrobiología (IPNA), institución que es una rareza entre los 121 centros que forman parte del Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC). Y lo es por varios motivos. El más evidente es su lejanía del continente y el hecho de que hasta 2022 fuera el único representante del CSIC en Canarias, algo que cambió con la incorporación del IEO y el IGME a la red. Esta circunstancia quizás sea la explicación de que en el IPNA se desarrollen estudios sobre las tres áreas claves del conocimiento: materia, vida y sociedad, las cuales se abordan y describen en el presente artículo, así como el impacto científico de este organismo, y los retos que afronta para el futuro.
Padrón, Juan I.; Pérez-Martín, Inés; Pérez Pérez, Beatriz.