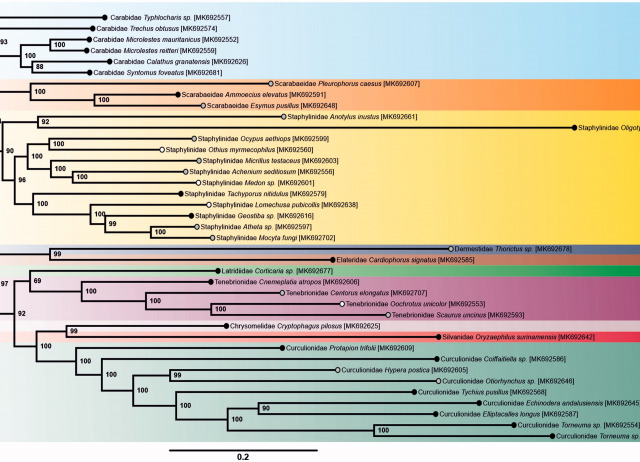
New mitochondrial genomes of 39 soil dwelling Coleoptera from metagenome sequencing
High-throughput DNA methods hold great promise for the study of the hyperdiverse arthropod fauna of the soil. We used the mitochondrial metagenomic approach to generate 39 mitochondrial genomes from adult and larval specimens of Coleoptera collected from soil samples. The mitogenomes correspond to species from the families Carabidae (6), Chrysomelidae (1), Curculionidae (9), Dermestidae (1), Elateridae (1), Latridiidae (1), Scarabaeidae (3), Silvanidae (1), Staphylinidae (12), and Tenebrionidae (4). All the mitogenomes followed the putative ancestral gene order for Coleoptera. We provide the first available mitogenome for 30 genera of Coleoptera, including endogean representatives of the genera Torneuma, Coiffaitiella, Otiorhynchus, Oligotyphlopsis, and Typhlocharis.
Andújar, Carmelo; Arribas, Paula; Motyka, Michal; Bocek, Mathew; Bocak, Ladislav; Linard, Benjamin; Vogler, Alfried P.
Expanding the limits of amide–triazole isosteric substitution in bisamide-based physical gels
Gelation of organic solvents using N,N′-((1S,2S)-cyclohexane-1,2-diyl)didodecanamide (C12–Cyc) is driven by its self-assembly via antiparallel hydrogen bonds and van der Waals intermolecular interactions. In this work we carried out a dual isosteric substitution of the two amide groups with 1,2,3-triazole rings affording the corresponding isosteric gelator (click-C12–Cyc). A detailed comparative study in terms of the gelation ability and gel properties demonstrated that the 1,2,3-triazoles can take over all of the functions derived from the amide groups offering a versatile strategy for tuning the properties of the corresponding gels. This is not an obvious outcome because the directional amide groups in C12–Cyc constitute the source of the hydrogen bonds to build the 3D self-assembled network. Furthermore, theoretical calculations revealed that click-C12–Cyc can adopt a wide variety of interacting patterns, whose relative stability depends on the polarity of the environment, this is in good agreement with the experimental data obtained regarding its gelation ability. Other important features of click-C12–Cyc for potential practical applications are its non-cytotoxic character and its phase-selective gelation of water–oil mixtures.
Tautz, Markus; Torras, Juan; Grijalvo, Santiago; Eritja Casadellà, Ramón; Saldías, César; Alemán, Carlos; Díaz Díaz, David
Recent Strategies in Resveratrol Delivery Systems
Resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic stilbenoid widely found in grapes and wines, displays beneficial properties such as cardio-protective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Trans-resveratrol (RSV) is the most bioactive and more abundant stereoisomer found in nature. Despite the positive properties of RSV, there are various factors that limit its effectiveness, including low aqueous solubility, low oral bioavailability and chemical instability. During the last years, an increasing number of strategies such as nano and micro encapsulation have been developed in order to overcome these limitations and enhance the use of RSV in nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. This Review summarizes the advances and main properties of several RSV carriers and delivery systems reported during the last 5 years.
Machado, Noelia D.; Fernández, Mariana A.; Díaz Díaz, David
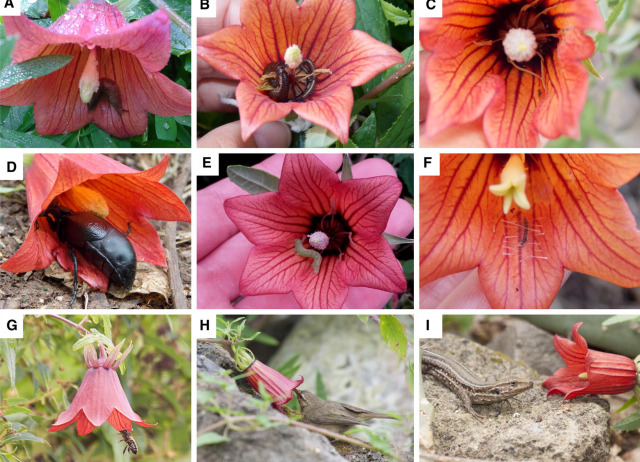
Impact of alien rats and honeybees on the reproductive success of an ornithophilous endemic plant in Canarian thermosclerophyllous woodland relicts
Islands harbor a considerable portion of global biodiversity and endemic biota, and also are the recipients of the largest proportional numbers of alien invaders. Such invaders may jeopardize the performance of native species, through either their direct or indirect effects. In this study, we investigated the reproductive ecology of the endemic scrambling perennial herb Canarina canariensis in remnants of the former thermosclerophyllous woodland of Tenerife (Canary Islands), assessing how two widespread alien invasive species, the honeybee (Apis mellifera) and the black rat (Rattus rattus), affect its reproductive success. Apis mellifera visits its flowers whereas the black rat consumes both its flowers and fruits. Here, we compared the pollination effectiveness of different animal guilds (vertebrates vs insects) by means of selective exclosures and determined the level of floral herbivory. Three bird species (Phylloscopus canariensis, Cyanistes teneriffae and Sylvia melanocephala), a lizard (Gallotia galloti) and two insects (A. mellifera and the butterfly Gonepteryx cleobule) were the main flower visitors. Phylloscopus canariensis was the most frequent visitor in the early flowering season whereas A. mellifera predominated in the flowers during mid and late flowering periods. Birds increased fruit set, whilst lizards and insects had a negligible effect. Rats consumed about 10% of the flowers and reduced fruit set to one third. Besides contributing little to plant reproduction, A. mellifera might interfere with bird pollination by depleting flowers of nectar. We conclude that both alien species can threaten C. canariensis reproduction and hence population sustainability in the thermosclerophyllous vegetation. Apis mellifera, in particular, may become especially detrimental if apiculture keeps expanding, or if this bee becomes active earlier in the season due to global warming.
Jaca, Julia; Rodríguez, Noemí; Nogales, Manuel; Traveset, Anna
Insect Antifeedant Components of Senecio fistulosus var. fistulosus—Hualtata
From a bioactive methanolic extract of Senecio fistulosus, the antifeedant effects of the alkaloidal and non-alkaloidal fractions were tested against the insects Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae and Rhopalosiphum padi, with the non-alkaloidal fraction being antifeedant. The phytochemical study of the non-alkaloidal fraction of S. fistulosus, resulted in the isolation of four compounds, two 9-oxo-furanoeremophilanes (1, 2), an eremophilanolide, 1β,10β-epoxy-6-acetoxy-8α-hydroxy-eremofil-7(11)-en-8β,12-olide (3) and a maaliol derivative (4). The alkaloidal fraction yielded two known pyrrolizidine alkaloids (5, 6). Compounds 1, 3 and 4 are new natural products. Furanoeremophilane 2 was a strong antifeedant against S. littoralis and maaliane 4 inhibited the settling of M. persicae.
Ruiz-Vasquez, Liliana; Reina, Matías; Fajardo, Víctor; López, Matías; González-Coloma, Azucena
Insect Antifeedant Components of Senecio fistulosus var. fistulosus—Hualtata
From a bioactive methanolic extract of Senecio fistulosus, the antifeedant effects of the alkaloidal and non-alkaloidal fractions were tested against the insects Spodoptera littoralis, Myzus persicae and Rhopalosiphum padi, with the non-alkaloidal fraction being antifeedant. The phytochemical study of the non-alkaloidal fraction of S. fistulosus, resulted in the isolation of four compounds, two 9-oxo-furanoeremophilanes (1, 2), an eremophilanolide, 1β,10β-epoxy-6-acetoxy-8α-hydroxy-eremofil-7(11)-en-8β,12-olide (3) and a maaliol derivative (4). The alkaloidal fraction yielded two known pyrrolizidine alkaloids (5, 6). Compounds 1, 3 and 4 are new natural products. Furanoeremophilane 2 was a strong antifeedant against S. littoralis and maaliane 4 inhibited the settling of M. persicae.
Ruiz-Vasquez, Liliana; Reina, Matías; Fajardo, Víctor; López, Matías; González-Coloma, Azucena
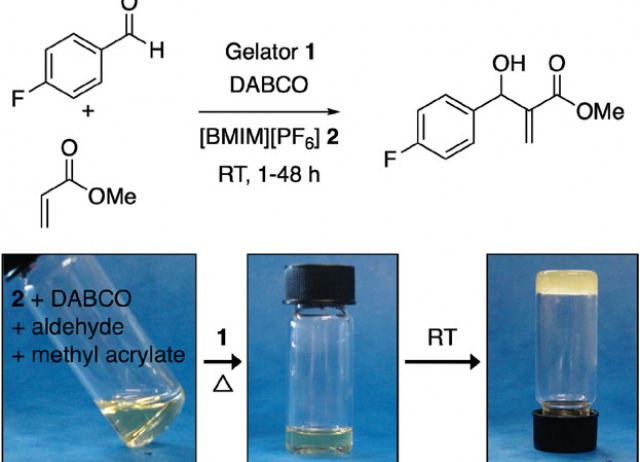
A Preliminary Comparative Study of the Baylis–Hillman Reaction in Ionic Liquid Solution and Gelled Ionic Liquid
Baylis–Hillman reaction in ionic liquid ([BMIM][PF]) solution under stirring conditions and in the presence of a base (DABCO) can also be performed efficiently in non-stirred gel phase upon gelation of the ionic liquid using a LMW gelator (i.e., (S)-N-(1-oxo-3-phenyl-1-(tridecylamino)propan-2-yl)benzamide). In this preliminary study, the authors have compared both reaction media and the results showed similar behaviors. Interestingly, the ionogel is found to be slightly more effective affording the desired products with moderately higher yields within a reaction period of 24 h.
Schön, Eva-María; Saldías, César; Haldar, Debasish; Díaz Díaz, David
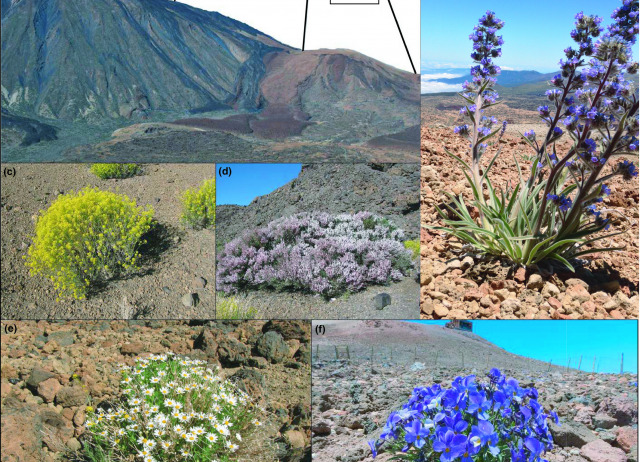
Beta diversity and specialization in plant–pollinator networks along an elevational gradient
[Aim] To assess whether the reduced nutritional resources available for pollinators due to plant community simplification along an elevational plant-diversity gradient changes pollinator niche breadth and richness. Additionally, we evaluated how body size and proboscis length of pollinators shifted along the gradient, and whether these changes were related to pollinator niche breadth, [Location] An elevational gradient (2,350–3,520 m a.s.l.) on the oceanic high-mountain strato-volcano of El Teide (Tenerife, Canary Islands), [Taxon] Flowering plant and pollinator species, [Methods] We compared quantitative plant–pollinator networks along the plant-diversity gradient. We calculated a set of niche-based topological metrics that capture the degree of specialization, niche breadth and niche overlap. Furthermore, we obtained β-diversity measures and the proportion of replacement and richness components, [Results] There was an overall decline in species richness of pollinators with increasing elevation. This decline was mainly driven by the loss of species along the elevational gradient, which conformed a nested subset pattern. The whole network showed less specialization, greater connectance and lower modularity towards the summit. At high elevations, pollinators were more generalized and less selective in their flower choice, showing a greater trophic niche breadth compared to pollinators at lower elevations. Mean body size of pollinators increased with elevation, and species body size and proboscis length were positively associated with the number of plant species visited, [Main conclusions] Overall, results indicated that the elevational gradient filters pollinator species, probably according to their thermal tolerance and ability to exploit a wide range of trophic resources. The finding that pollinators become more generalized and opportunistic at higher elevations is a novel result, which may have implications for new research into how ecological networks vary over environmental gradients. From an applied perspective, our results highlight the importance of considering the spatial variation of species assemblages when aiming to construct functionally reliable interaction networks along environmental gradients.
Lara-Romero, Carlos; Seguí, Jaume; Pérez-Delgado, Antonio; Nogales, Manuel; Traveset, Anna
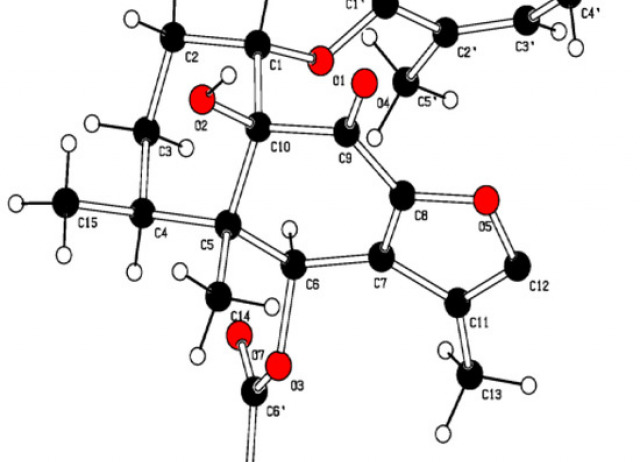
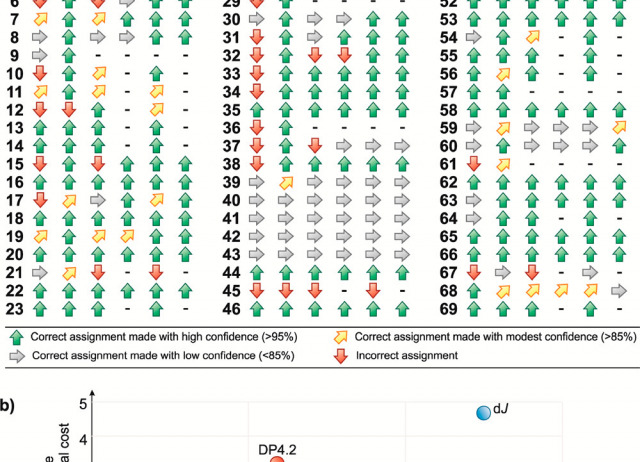
Combining the Power of J Coupling and DP4 Analysis on Stereochemical Assignments: The J-DP4 Methods
A systematic study to include J couplings into DP4 formalism (J-DP4) led to the development of three alternative strategies. The dJ-DP4 (direct) approach involves a new DP4-like equation including an additional probability term given by J. The iJ-DP4 (indirect) approach explores the original DP4 method with a restricted conformational search. Despite both strategies performing better than DP4, their combined use (iJ/dJ-DP4) provided the best results, with a 2.5-fold performance improvement at similar or lower computational cost.
Grimblat, Nicolás; Gavín, José A.; Hernández Daranas, Antonio; Sarotti, Ariel M.
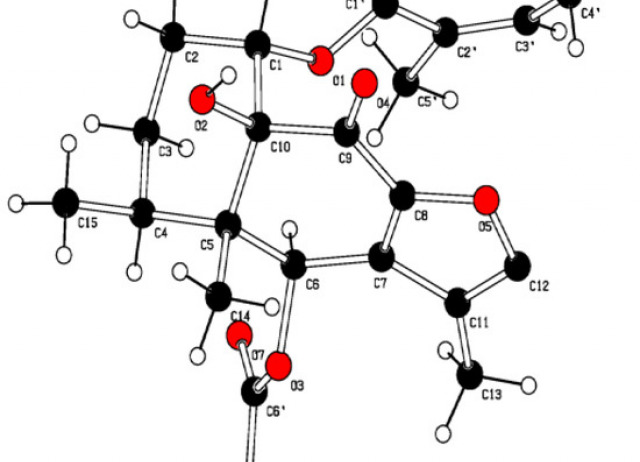
Combining the Power of J Coupling and DP4 Analysis on Stereochemical Assignments: The J-DP4 Methods
A systematic study to include J couplings into DP4 formalism (J-DP4) led to the development of three alternative strategies. The dJ-DP4 (direct) approach involves a new DP4-like equation including an additional probability term given by J. The iJ-DP4 (indirect) approach explores the original DP4 method with a restricted conformational search. Despite both strategies performing better than DP4, their combined use (iJ/dJ-DP4) provided the best results, with a 2.5-fold performance improvement at similar or lower computational cost.
Grimblat, Nicolás; Gavín, José A.; Hernández Daranas, Antonio; Sarotti, Ariel M.