Latest News
Here you will find the latest news on research, events, activities and new findings at the Institute of Natural Products and Agrobiology.
Upcoming Events
Publicaciones recientes
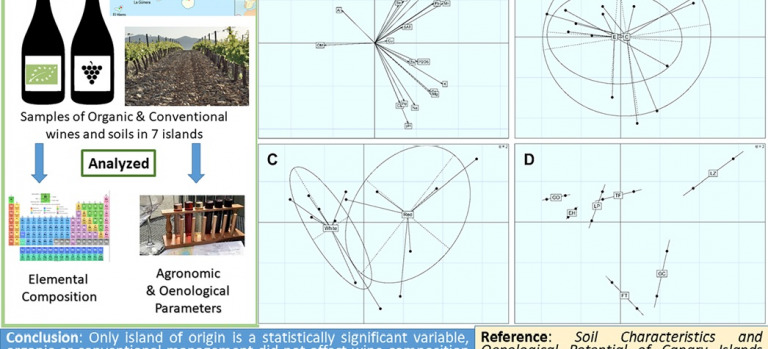
Unveiling terroir: evaluating the magnitude of the heterogeneity and its main drivers in the Canary Islands wines
The Canary Islands are a Spanish archipelago of volcanic origin in the Atlantic Ocean near the Saharan coast. The extensive intricacy and multitude of variables inherent in the Canary Islands winemaking tradition have posed a substantial challenge, preventing comprehensive research on the main factors contributing to the character of local wine, thus, far. This challenge arises from a convergence of factors including the presence of 14 different grape varieties, and radically different climatic, soil and geographic conditions. This investigation sought to start unraveling this complexity by discerning the impacts of various geographical (specifically, island-related) and management factors (namely, organic vs. conventional practices) on soils and wines within the Canary Islands. Additional variables, such as wine type (red and white) and island of origin, were explored and correlated with the chosen management system. Pairs of organic and conventional wine and soil samples, possessing similar characteristics, were systematically collected from each of the seven wine-producing islands in the Canary archipelago. An examination of elemental composition, oenological attributes and fertility parameters was conducted, followed by comprehensive statistical analysis. Among the variables examined, only the island of origin emerged as statistically significant within the sample. Concerning soil fertility, organic samples exhibited elevated levels of organic matter compared to their conventional counterparts. No notable disparities were observed between the two production methods in terms of soil metal composition and other fertility parameters. However, it is noteworthy that four soil samples surpassed the legally permissible limits for Nickel (Ni) and Mercury (Hg), with three of these instances originating from Lanzarote.
Alonso-González, Pablo; Parga-Dans, Eva; Hernández González, María Mercedes; Arribas, Paula; Acosta Dacal, Andrea Carolina; Pérez Luzardo, Octavio.
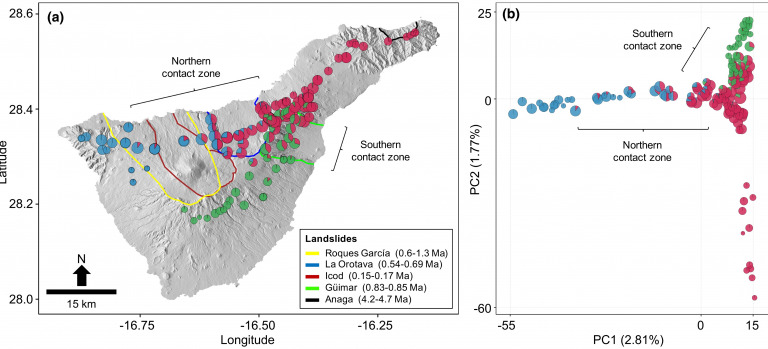
Genetic legacies of mega-landslides: Cycles of isolation and contact across flank collapses in an oceanic island
Catastrophic flank collapses are recognized as important drivers of insular biodiversity dynamics, through the disruption of species ranges and subsequent allopatric divergence. However, little empirical data supports this conjecture, with their evolutionary consequences remaining poorly understood. Using genome-wide data within a population genomics and phylogenomics framework, we evaluate how mega-landslides have impacted evolutionary and demographic history within a species complex of weevils (Curculionidae) within the Canary Island of Tenerife. We reveal a complex genomic landscape, within which individuals of single ancestry were sampled in areas characterized by long-term geological stability, relative to the timing of flank collapses. In contrast, individuals of admixed ancestry were almost exclusively sampled within the boundaries of flank collapses. Estimated divergence times among ancestral populations aligned with the timings of mega-landslide events. Our results provide first evidence for a cyclical dynamic of range fragmentation and secondary contact across flank collapse landscapes, with support for a model where this dynamic is mediated by Quaternary climate oscillations. The context within which we reveal climate and topography to interact cyclically through time to shape the geographic structure of genetic variation, together with related recent work, highlights the importance of topoclimatic phenomena as an agent of diversification within insular invertebrates.
Noguerales, Víctor; Arjona, Yurena; García-Olivares, Víctor; Machado, Antonio; López, Heriberto; Patiño, Jairo; Emerson, Brent C.
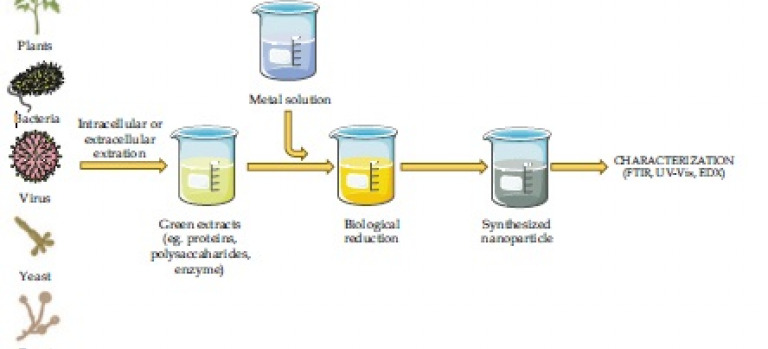
Harnessing the Power of Metallic Nanoparticles: Antimicrobial Peptide Functionalization with Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
This book accumulates the most recent advancements in the field of bioengineering regarding hybrid science named nanobiotechnology and enriches the readers with vast and comprehensive knowledge about different biomedical applications of nanomaterials. It includes drug and gene delivery, tissue engineering, antimicrobial properties, hyperthermia, cancer therapy, bioimaging, biosensing, photoablation therapy, etc., utilizing the potential of different nanomaterials that are helpful for the well-being of diseased individuals. Furthermore, the concerns about multidrug-resistant microorganisms are increasing daily in the healthcare system. Since conventional therapies fail to combat various infectious diseases, novel nanotechnology techniques provide an alternative approach to developing innovative biomaterials. The novel features of nanomaterials need to be exploited for use in the biomedical engineering domain. They should be fabricated so that the novel multifunctional nanomaterials notonly improve drug efficacy but also reduce their side effects. Moreover, a detailed understanding of the nanotoxicological effects of promising biomedical nanomaterials should necessarily be explored using the cell culture approach. Corona of nanomaterials should be investigated in detail to determine its fate in the biological system regarding safety concerns. This is the most important feature that is novel and explored in this book and would be very helpful for customers like clinicians, scientists, engineers, and technicians who will gain extensive knowledge from this book and work together to get the desired results in the healthcare sector.
González-Almécija, Beatriz; López, R. Manuel; Asensio-Calavia, Patricia; Otazo-Pérez, Andrea; González-Acosta, Sergio; Morales-delaNuez, Antonio; Pérez de Lastra, José Manuel.
Blog
The IPNA blog gathers informative articles on the different research projects developed in the centre, the latest advances in science and other topics of interest regarding scientific culture.





