First report of the invasive alien species Caenoplana coerulea Moseley, 1877 (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida, Geoplanidae) in the subterranean environment of the Canary Islands
The blue land planarian Caenoplana coerulea Moseley, 1877 is reported for the first time in the hypogean environment. Seven individuals of C. coerulea were collected in the most humid branch of an abandoned water mine in Gran Canaria (Canary Islands). Due to its character of generalist predator, it should be considered a threat for the endemic subterranean fauna.
Suárez, Daniel; Martín, Sonia; Naranjo, Manuel
An analogue of dominance of tectonic over climatic forcing in intermontane coal-bearing basins: Padul (SE Spain)
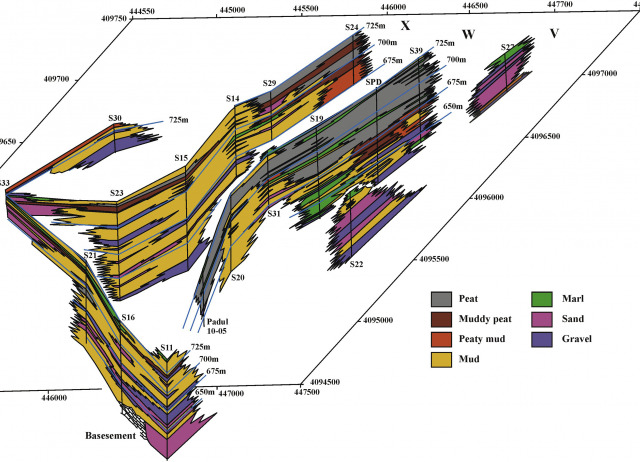
A multiproxy study based on sedimentology, mineralogy, magnetic susceptibility, organic geochemistry and fossil content allowed to establish the sedimentary evolution of palustrine basins and to study the interplay between tectonic and climatic forcings in the sedimentation and facies arrangement that can be extrapolated to other coal-bearing basins. The reinterpretation of the data from 18 cores allowed to determine the facies distribution and to model the sedimentary evolution of the Padul Basin, with the longest continuous continental Quaternary record in the Southwestern Mediterranean region. The Padul Basin sediment record and facies successions provide an outstanding example of tectonically and environmentally controlled sedimentation. The sedimentary characteristics of the cores and thickness distribution revealed that recent tectonics was a more important forcing than other processes (e.g. climate). The influence of recent tectonics was determinant in facies arrangement, that is to say that the activity of a rotated fault produced a differential subsidence, causing more than 100 m of palustrine deposits to stack. On the basis of the sedimentological record combined with data on the mineralogy, fossil content, magnetic susceptibility and total organic carbon, three main sedimentary units were identified, linked to diverse subsidence rates and paleoenvironmental oscillations. The magnetic susceptibility was likely to have been controlled by the organic matter content (TOC values), linked to oxic/anoxic conditions. In the lower part of the record, Unit A (107.0–68.7 m), shallow lacustrine conditions were dominant, with an important influx associated with considerable runoff from active alluvial fans, linked to a higher subsidence rate. Unit B (68.7–37.6 m) had a transitional character, with a considerable decrease in the influence of the alluvial fan system. The lake recharge through overland flow markedly diminished and pre-existing groundwater recharge was dominant. A sudden change to peaty materials indicated that surface runoff was directly diverted to the recently excavated Dúrcal River gorge, thereby precluding the basin from becoming a swampy environment with stagnant waters. Unit C (upper 37.6 m) was almost exclusively fed by bicarbonate groundwater and subsurface runoff through the highly permeable coarse alluvial fan deposits. Within these main sedimentary units, minor mud-peat shallowing-upward sequences were identified
Torres, Trinidad; Ortiz, José E.; Soler, Vicente; Delgado, Antonio; Araujo, Rafael; Valle, Maruja.; Rivas, María. R.; Julià Brugués, Ramón; Sánchez-Palencia, Yolanda; Vega-Panizo, Rogelio
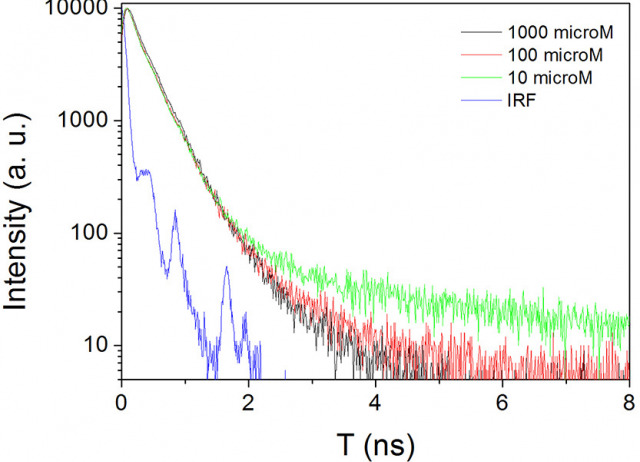
Opto-chemical and laser properties of FLTX1, a novel fluorescent tamoxifen derivative, and its potential applications in breast cancer photodynamic chemotherapy
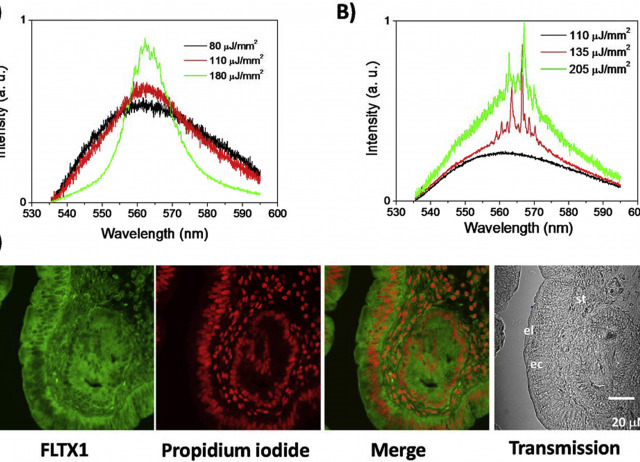
Tamoxifen is the most common antiestrogen used in the chronic treatment of breast cancer. In these cells, it mainly binds to intracellular receptors (estrogen receptor alpha, ERα) and antagonizes the binding of its cognate ligand, 17β-estradiol, thereby preventing uncontrolled hormone-dependent cellular proliferation and growth. In the last decade, in our laboratories we have developed and characterized different tamoxifen derivatives, including a novel fluorescent tamoxifen conjugate: FLTX1. FLTX1 is formed by the covalent binding of tamoxifen to a common fluorescent biomarker NBD. This new prodrug was originally designed as a fluorescent biomarker to localize intracellular targets, which not only keeps the pharmacological activity of tamoxifen but also adds a luminescent functionality. Strikingly, the quantum efficiency of FLTX1 is so high that laser emission has been obtained as an emerging property. In this review, we will show its laser properties under three different configurations. First, as amplified spontaneous emission or mirrorless laser; second, through the evanescent field of WGMs of a ring resonator around an optical fiber; and finally as random laser in uterine tissues impregnated with the prodrug. Further, we observed another emergent property for FLTX1: this molecule, but not tamoxifen alone or NBD, was able to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon irradiation. This property is extremely interesting as FLTX1 might be used for photodynamic therapy. Under this paradigm, FLTX1 would act as a sensitizer in ERα-overexpressing cells (which feature the most prevalent form of hormone-dependent breast cancer), causing cell death in ERα+ cells but reducing damage to other non-cancer (healthy) cells or surrounding tissues. We show here time resolved fluorescence results that suggest molecular aggregations, which could explain the subsequent generation of ROS. This is an original cancer therapy strategy that combines the pharmacological properties of a new tamoxifen derivative and its laser dye features with a highly selective photodynamic therapy.
Díaz, Mario; Scholz, Laura E.; Marrero-Alonso, Jorge; Boto, Alicia; Marín, Raquel; Lobo, Fernando; Hernández, Dácil; Amesty, Ángel; Estévez-Braun, Ana; Quinto-Alemany, David; Puertas-Avedaño, Ricardo; Lahoz Zamarro, Fernando
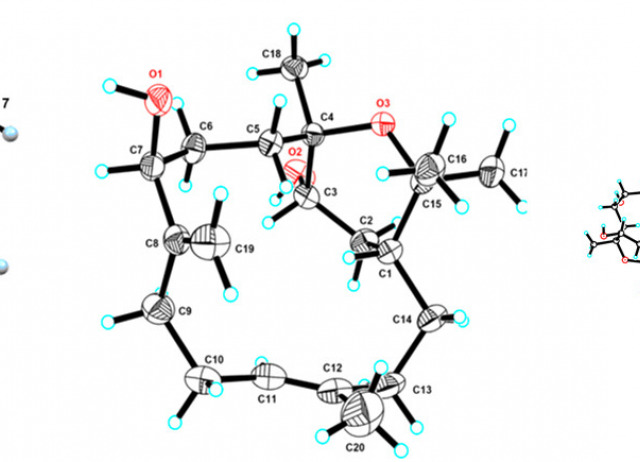
Synthesis of Diketopiperazine Scaffolds with Tailored N‐ and α‐Chains by Selective Modification of Customizable Units
The selective manipulation of Hyp customizable units in DKP substrates allows the generation of a rigid scaffold with four tailor‐made chains which are spatially‐orientated. The key step is a domino radical scission‐oxidation process which allows the generation of N‐substituted DKPs. The versatility of this methodology to produce scaffolds in high optical purity for material and drug discovery is described herein.
Saavedra, Carlos J.; Cuevas, Fernando; Romero-Estudillo, Iván; Boto, Alicia
Impact of Saharan dust exposure on airway inflammation in patients with ischemic heart disease
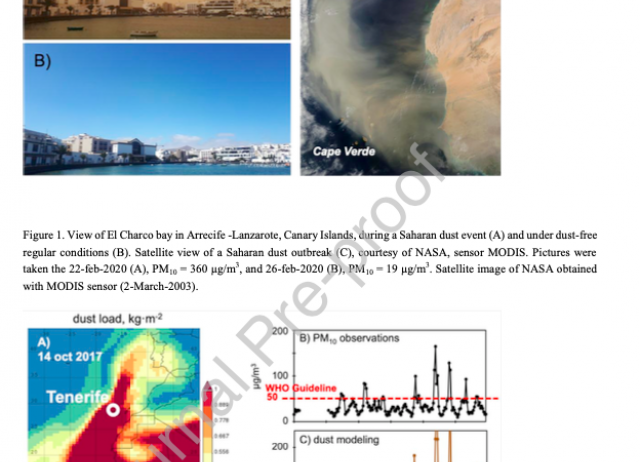
Epidemiological studies found that increases in the concentrations of airborne particulate matter (PM) smaller than 10 microns diameter (PM10) in the ambient air due to desert dust outbreaks contribute to global burden of diseases, primarily as a result of increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. No studies have investigated the possible association between desert dust inhalation and airway inflammation in patients with ischemic heart disease (IHD). Induced sputum was collected in 38 patients and analysed to determine markers of airway inflammation (Transforming Growth Factor-β1 [TGF-β1] and hydroxyproline) concentrations. For the purpose of the investigation, PM10 and reactive gases concentrations measured in the European Air Quality Network implemented in the Canary Islands were also used. We identified Saharan desert dust using meteorology and dust models. Patients affected by smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pulmonary abnormalities, acute bronchial or pulmonary disease were excluded. The median of age of patients was 64.71 years (56.35–71.54) and 14 (38.84%) of them were women. TGF-β1 and hydroxyproline in sputum were highly associated to PM10 inhalation from the Saharan desert. According to a regression model, an increase of 1 µg/m3 of PM10 concentrations due to desert dust, results in an increase of 3.84 pg/gwt of TGF-β1 (R2 adjusted= 89.69%) and of 0.80 μg/gwt of hydroxyproline (R2 adjusted= 85.28%) in the sputum of patients. The results of this study indicate that the exposure to high PM10 concentrations due to Saharan dust events are associated with intense inflammatory reaction in the airway mucosae of IHD-patients.
Domínguez-Rodríguez, Alberto; Rodríguez, Sergio; Báez-Ferrer, Néstor; Abreu-González, Pedro; Abreu-González, Juan; Avanzas, Pablo; Carnero, Manuel; Morís, César; López-Darias, Jessica; Hernández-Vaquero, Daniel
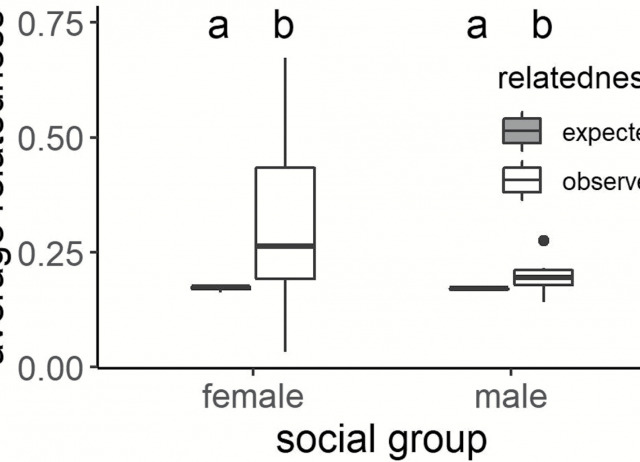
Social organization in a North African ground squirrel
Research on sociality in temperate ground-dwelling squirrels has focused on female philopatry and other life history trade-offs, which are influenced by constraints in the duration of the active growing season. Temperate ground-dwelling squirrels that experience high predation pressure, are large in body size, and have a short active season, show a more complex social organization. In contrast, African ground squirrels are active year-round, suggesting that instead of a short active season, distinct selective pressures influence their social organization. We examined the social organization of Barbary ground squirrels, Atlantoxerus getulus, and compared the social organization of temperate and African ground-dwelling sciurids. Anecdotal accounts on Barbary ground squirrels’ social organization suggested that they were either solitary or gregarious, or live in small family groups. We recorded the group size, composition, cohesion, and genetic relatedness, of the population on the arid island of Fuerteventura, Spain. Our data indicate that females live in small (1–8) all-female kin groups separate from adult males, and that unrelated adult males share sleeping burrows with immature individuals of either sex. We observed sex-biased dispersal with males primarily the dispersing sex and females primarily philopatric. Females sleep solitarily during gestation and lactation and nest either communally or singly after juvenile emergence. During the day, males and females can be active in the same area. Barbary ground squirrels are social because the squirrels share sleeping burrows and show spatiotemporal overlap. Barbary ground squirrels’ social organization resembles that of the closely related Cape ground squirrel rather than that of the temperate ground-dwelling sciurids, although the former are more temperate, seasonal breeders. In addition to describing the social organization of a previously unstudied species, this paper sheds light on the ecological drivers of sociality, and the evolution of distinct social organizations in ground-dwelling sciurids.
van der Marel, Annemarie; Waterman, Jane M.; López-Darias, Marta
FRET mechanism between a fluorescent breast-cancer drug and photodynamic therapy sensitizers
Tamoxifen is one of the most frequently used drugs for the treatment of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer, which is the most prevalent form of hormone dependent breast cancer. A few years ago, we developed a fluorescent derivative of tamoxifen formed by the covalent binding of tamoxifen to a common dye biomarker. The new compound, known as FLTX1, showed the pharmacological activity of the tamoxifen moiety and efficient fluorescence properties, which could be used synergistically to improve the effect of the drug. In this paper, we demonstrate that irradiation at the absorption band of FLTX1 can result in fluorescence resonance energy transfer to photosensitizers such as Rose Bengal and Merocyanine 540, activating the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Indeed, the generation of ROS was demonstrated using a colorimetric assay. Since FLTX1 mostly binds estrogen-receptor overexpressing cancer cells, the results obtained are very promising and suggest a new therapeutic strategy combining chemo- and photodynamic therapies.
Lahoz, Fernando; Scholz, Laura E.; Boto, Alicia; Díaz, Mario
Quantum Mechanical–NMR-Aided Configuration and Conformation of Two Unreported Macrocycles Isolated from the Soft Coral Lobophytum sp.: Energy Calculations versus Coupling Constants
Two new macrocyclic cembranoids were isolated from the South China Sea soft coral Lobophytum sp. Quantum mechanical–nuclear magnetic resonance (QM–NMR) methods were decisive in their structural elucidation. Better performance in arriving at definitive structures was obtained by QM–NMR methods upon incorporation of 3JHH values. The validity of this approach also supported an alternative conformational proposal versus that obtained by X-ray crystallography.
Li, Song-Wei; Cuadrado, Cristina; Yao, Li-Gong; Hernández Daranas, Antonio; Guo, Yue-Wei
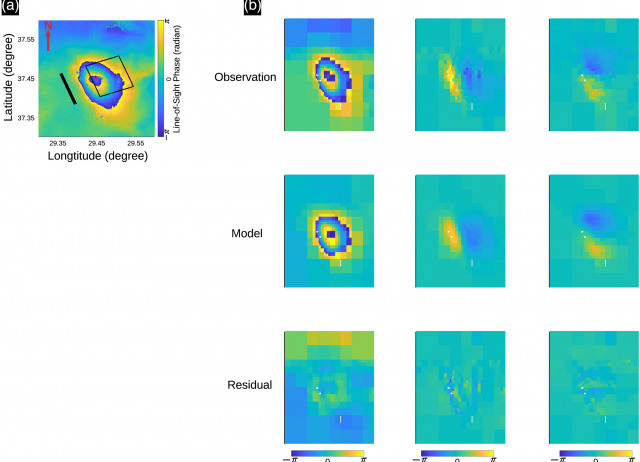
Bayesian Inversion of Wrapped Satellite Interferometric Phase to Estimate Fault and Volcano Surface Ground Deformation Models
| Bayesian inference and an improved downsampling method is used to determine earthquake and volcano source parameters using a popular geodetic observation method, satellite radar interferometry. The main novelty of the proposed approach is that the interferometric wrapped phase can be directly inverted, circumventing the ill‐posed phase unwrapping processing step. Phase unwrapping errors severely affect the estimation of earthquake and volcano source parameters using interferometric observations. Therefore, it is desirable to avoid phase unwrapping completely. To overcome the need for phase unwrapping, we propose a downsampling algorithm and a method to estimate the covariance function of the wrapped phase and establish an appropriate misfit function between the observed and simulated wrapped phase. Uncertainties in source parameters are assessed with a Bayesian approach, and finally, the robustness of the inversion methodology is tested in multiple simulations including variable decorrelation and atmospheric noise simulations. The method is shown to be robust in challenging noise scenarios. It features an improvement in performance with the Bayesian approach, compared to similar previous methods, avoiding any influence of seed starting models and escaping local minima. The impact of a small percentage of incorrectly unwrapped phase observations in current state‐of‐the‐art methods is shown to strongly affect the estimation process. We conclude that in the cases where phase unwrapping is difficult or even impossible, the proposed inversion methodology with wrapped phase will provide an alternative approach to assess earthquake and volcano source model parameters. |
Jiang, Yu; González, Pablo J.
A database of functional traits for spiders from native forests of the Iberian Peninsula and Macaronesia
Background
There is an increasing demand for databases including species trait information for
biodiversity and community ecology studies. The existence of trait databases is useful for
comparative studies within taxa or geographical regions, but there is low availability of
databases for certain organisms. Here we present an open access functional trait database
for spiders from Macaronesia and the Iberian Peninsula, recording several morphological
and ecological traits related to the species life histories, microhabitat and trophic
preferences.
New information
We present a database that includes 12 biological traits for 506 spider species present in
natural forests of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain) and three Macaronesian archipelagoes
(Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). The functional trait database consists of two
sections:
1. individual-level data for six morphological traits (total body size, prosoma length,
prosoma width, prosoma height, tibia I length and fang length), based on direct
measurements of 2844 specimens of all spider species; and
2. species-level aggregate data for 12 traits (same 6 morphological traits as in the
previous section plus dispersal ability, vertical stratification, circadian activity,
foraging strategy, trophic specialization and colonization status), based on either
the average of the direct measurements or bibliographic searches.
This functional trait database will serve as a data
Macías-Hernández, Nuria; Ramos, Cândida; Domènech, Marc; Febles, Sara; Santos, Irene; Arnedo, Miquel A,; Borges, Paulo A. V.; Emerson, Brent C.; Cardoso, Pedro